Biology Unit 7 Ecology
Define: biosphere, biome, ecosystem, habitat, community, population.
List biotic and abiotic factors that affect the distribution of organisms.
Define and give examples of symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism.
Describe and explain the flow of energy through ecosystems.
Draw and interpret: food chains, food webs, and pyramids of numbers, biomass and energy.
Describe the energy losses between trophic levels and their implications for the length of food chains
Describe and explain factors that may cause changes in population, e.g. predator-prey interactions.
Describe the threats to biodiversity and the benefits of maintaining biodiversity.
Lo.. 1 define: Biosphere, Biome, ecosystem, habitat, community, population
Meaning of ecology:
The relationship between organisms and their environment
Biosphere:
All areas with living things on the planet
Ecosystem:
community interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Community:
Many individuals of different species live in the same place
Organism:
1 individual(1 member of a species)
Terrestrial Biomes:
Tundra:
Cold temperature, animals migrate during winters, dominated by slow frowin gvegetation, soil is frozen (permafrost)
Grass Lands:
Overall low to moderate rainfall(seasonal drought), Fertile soils, dominated by grasses
Examples: prairies, steppes, savannah
Coniferous forest:
Long cold winters, evergreen tress, short warm winters, some animals hibernate, poor soil.
Desert:
Driest Biome(lack of water), often hot with varitation in temperature during the day(sometimes cold), plants display adaptations to conserve water
Deciduous Forest:
High rainfall with no dry season, moderate temperature, Dominated by broad leaved trees
Tropical rain forest:
High temp, little seasonal variation, high rainfall no dry season, Dominated by large trees, highest biodiversity, plants grow very fast but usually soils arent fertile.
More looking at Land Biomes of the World
More desserts are found closer to the tropial o fcancer, further north has more tundra, southern areas below the equator had more tropical areas.
2 Key factors determining Biomes:
Climate determines the biome based on how much sunlight recieved
and the amount of rainfall also determines the biome.
Lo2. List Biotic and Abiotic factors that affect the distribution of organisms
Organisms are affected by both Biotic and Abiotic factors.
Abiotic meaning:
NOn living
Examples such as cement, rocks, dirt, mud, wind, cloud, sun.
Abiotic factors for a tree would be things such as Co2 levels, ight intensity, water in the soil, and temperature, fertilizers, and wind.
For Fish Abiotic factors would be
Water pollution(chemicals and plastic)
Currents
Salt level(salinity)
Biotic meaning:
Living
Examples: Plants, animals, insects, parasites, protists, predators
Biotic factors for insects
Pollinators
pests
habitats
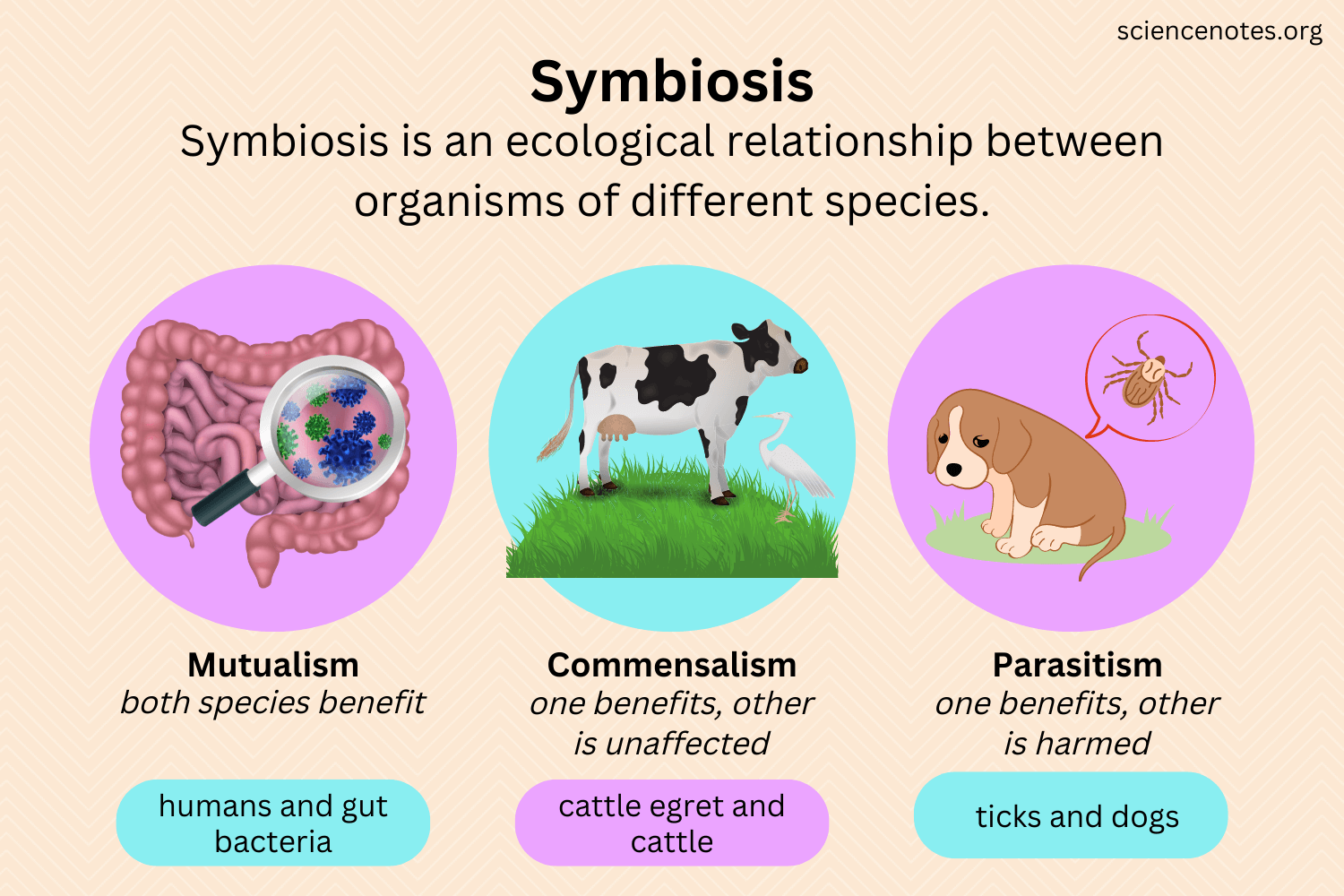
Lo. 3 Define and give exapmles of symbiotic relationships, mutualism, commensualism, nand parasitism.
Three types of symbiotic relationship:
Mutualism: where both organisms benefit
Commensalism: only one organism benefits while the other is unaffected/unharmed
Parasitism: One organism benefits while the other is harmed. It is usually a parasite feeding on the host
Predator-Prey Relationships
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism hunts(predator) and feeds on another(prey)
Herbivory is a form of predation in which the prey organism is a plant.
Competition:
Competition describes an interaction between 2 organisms that harms both. (cannot coexist in the same habitat as they are competing for the same resources)
Intraspecific competition occurs between members of the same species
Interspecific competition is competition between members of different species.
Walruses:
Mates
Territory
Mates
Intra-specific
Trees:
Sunlight
Minerals
interspecific
Lo. 4 Describe and explain the flow of energy through ecosystems
Autotrophs: Make their own food molecules from simple substances (CO2, etc) Examples: photosynthesis from sunlight
Because autotrophs synthesize their own organic molecules, they are called Producers.
Heterotrophs:
Obtain food molecules from other organisms. Heterotrophs cannot produce their own organic molecules and get their food from other organisms so they are called Consumers
Types of Heterotrophs
Herbivores - consumers mostly feeding on plant matter (eg. Sheep, rabbits, cows)
Carnivores are consumers that feed mainly on animal matter (lions, wolves, crocodiles)
Omnivores are consumers that have a diet of both plant and animal matter (pandas, humans)
Scavengers- Mainly feed on dead and decaying animals, bodies rather than live prey:
Examples Include Hyenas, vultures, and crows.
Detritivores are a type of heterotroph that obtains nutrients from nonliving organisms
Detritus is dead organic matter (fecal matter)
Humus specifically means the decay of leaf litter
Detritivores include dung beetles, earthworms, woodlice, snails, crabs
They help with the decomposition
Saprotrophs
Live on or in non-living organic matter, secrete digestive enzymes into it and absrobing the products of digestion
Examples of saprotrophs include bacteria and fungi (Decomposer)
Two processes essential to ecosystem function are energy flow and chemical cycling. Example of this would be the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells use the products of photosynthesis as fuel for cellular respiration.
Lo. 5 Draw and interpret: food chains, food webs, and pyramids of numbers, biomass and energy
What is a food chain> LInear feeding relationship between species
Arrows represent the transfer of energy and matter as one organism is eaten by another (energy flow direction)
The first organism is always the producer, followed by consumers
Examples of food chains in different habitats:
Producer (carrot plant) → 1st consumer (rabbit) -→ 2nd consumer(feral cat) → 3rd consumer (red fox)
Marine food chain:
Producer (bacteria) → 1st consumer (shrimp) → 2nd (atlantic) → 3rd (grey seal) consumer
Food web:
A diagram that shows how food chains are linked together into more complex feeding relationships.
Organisms can have more than 1 food source
Organisms can have more than 1 predator
Example of one food chain would be
Algae→ prawn→ trout
The effects of a decrease in prawn population will effect what?
The trout population will decrease(less food)
More algae
There are 3 ways to show information of each trophic level.
Examples of ecological pyramids for a specific food chain:
Pyramid of numbers: A pyramid of numbers shows the number of individuals at each level of the food chain.
Biomass can be lost between the stages because not all matter eaten can be digested and some is excreted in waste such: feces, sweat , hair, bones. feathers
Pyramid of energy: A pyramid of energy shows the total amount of energy of all individuals at each level of the food chain. A lot of the energy is lost between levels.
Each level is only 10% efficient (transferred) meaning 90% of energy is lost from respiration and heat.
Lo 6. Describe the energy losses between trophic levels and their implications for length of food chains and for feeding the growing human population.
Since energy and biomass is lost between each level of a food chain, the number of potential trophic levels are limited. Higher trophic levels receive less energy and biomass and need to eat larger quantities to obtain sufficient amounts.
Question
why is Meat-Free Mondays good for the planet
Less energy is being lost from the food chain n
reduces the amount of CO2 in the air as there is a reduction in airplane usage
Question 2
Which farm could feed the most people, a farm growing just vegetables, or a farm raising beef cattle on grass grown on the farm?
Just vegetables because it would use up less energy, as it is from vegetables → humans
whereas if it were cows, the food chain would be grass→ cows → Humans
meaning more energy loss
Lo. 7 Describe and explain factors that may cause changes in population
Limiting factors
Limiting factors are environmental conditions that determine the rate of population growth occurring
Biotic factor: Disease, predation, competition
Abiotic factors: food, water, temperature, Space, sunlight(light intensity)
Predator-prey interactions
A biological interaction where 1 organism hunts and feeds on the other
Because the predator relies on the prey as food, their populations are intertwined
It is a loop where populations rise and fall
Example:
Rabbits increase 1 year due to more grass availability -→ Gradually more foxes since there’s more food→ More rabbits eaten → Lower rabbits → lower foxes → then higher rabbits again
lo. 8 Describe the threats to biodiversity and the benefits of maintaining biodiversity
Threats to Biodiversity:
Habitat destruction and fragmentation
Invasive species
hunting(poaching), Collecting and harvesting
Pollution (air and water)
Biodiversity
The term biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms on the planet
Some parts have greater biodiversity. For example, the arctic Tundra has a lower biodiversity than a. tropical rain forest.
What is an endemic species
Native to a certain place
Whenever a species disappears it weakens the gene pools as it disrupts the entire system as all organisms are intertwined. Even taking 1 component away can hurt the entire system.
Example: coral reeds → organisms depend on coral for micro habitats and shelter→ fungi and bacteria → The coral is the loom and allows habitat and life for other organisms
Importance of biodiversity:
These 3 main features influence the difference between a strong and weak habitat:
Ecosystem
Species
Genetic
The more intertwined they are, the more resilient they are
Determining the nine categories of risks for animals:
EX (extinct)
EW (extinct in the wild)
CR (critically endangered)
EN (very highly endangered)
VU (vulnerable)
NT (near threat)
Least concern(LC)
Data Deficient (DD)
NE (not evaluating)
The value of biodiversity
Practical and economic value:
Provides resources (food, med, clothing, raw materials)
Water purification.
Soil fertility
Aesthetic value
Everything will look dull
natural beauty
Tourism
Moral value
Protecting all species equally
Responsibility to protect future generations
religious beliefs
Methods of preserving biodiversity
Habitat protection
National parks
limiting pollution
Zoos and botanical gardens