Reproduction and inheritance
Reproduction
Sexual and asexual reproduction:
In asexual reproduction usually cells in one part of the body divide by mitosis and then break off from the parent to form a new organism. All the offspring are genetically identical.
Sexual reproduction is the production of new organisms by the combination of genetic information of two individuals of different sexes.
Germination:
Definition: Germination is a process in which a seeding grows into a plant.
Conditions that germination requires:
water (allows the enzymes to work properly)
oxygen (allows respiration to release energy)
warmth (enzymes only work if there is kinetic energy)
After the conditions were met, the enzymes will break down the starch into maltose and glucose
Reproduction in plants:
Seeds must be carried away (dispersed / scattered) from the parent plant to:
Reduce overcrowding
Reduce competition for:
Water
Light
Nutrients
Component | Explanation |
Anther | Where the pollen grains are made and stored |
Filament | Hold up the anther |
Petals | Provides protection to the interior of the flower and to attract insects |
Stigma | Collects the pollen grains during pollination |
Style | Links the stigma to the ovary. |
Ovary | Produces the ovule |
Ovule | Contains the female gamete (the ovum) |
https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/labelling_interactives/15-label-the-flower-parts
Insect pollination: Insect-pollinated plants have large and sticky pollen. This allows the pollen to be easily picked up by insects by brushing the anther and the stigma.
The plant attracts the insect by having colorful petals and sweet and nice smelling nectar.
Wild pollination: Wind-pollinate plants have small and light pollen. This allows for the pollen to be easily carried by the wind.
Male reproductive system:
Scrotum
The sac that holds the testes and helps regulate their temperature
Sperm ducts
Transport sperm from the testes to the urethra
Sex gland
Produces semen that contains sperm cells
Sperm duct
Sperm passes through this
Testis
Contained in scrotum (bag of skin) and produces sperm and testosterone
Penis
Passes urine and semen out of the body
Urethra
Tube inside the penis to carry urine and semen (the two liquids don’t mix)
https://anatomy-quiz.com/male-sex-organs.html
Female reproductive system:
Uterus
Sometimes called the womb.
Muscular organ about the size of a pear.
Where developing baby, called a fetus, grows and is fed.
Has a blood rich lining that is lost each month
Vagina: passageway joining outside and uterus.
Oviducts: Narrow tubes between the uterus and the ovary
Ovaries: Glands that make egg cells and female sex hormones
Cervix
The lower part of the uterus.
Has opening where sperm enter uterus and where the baby comes out of the uterus
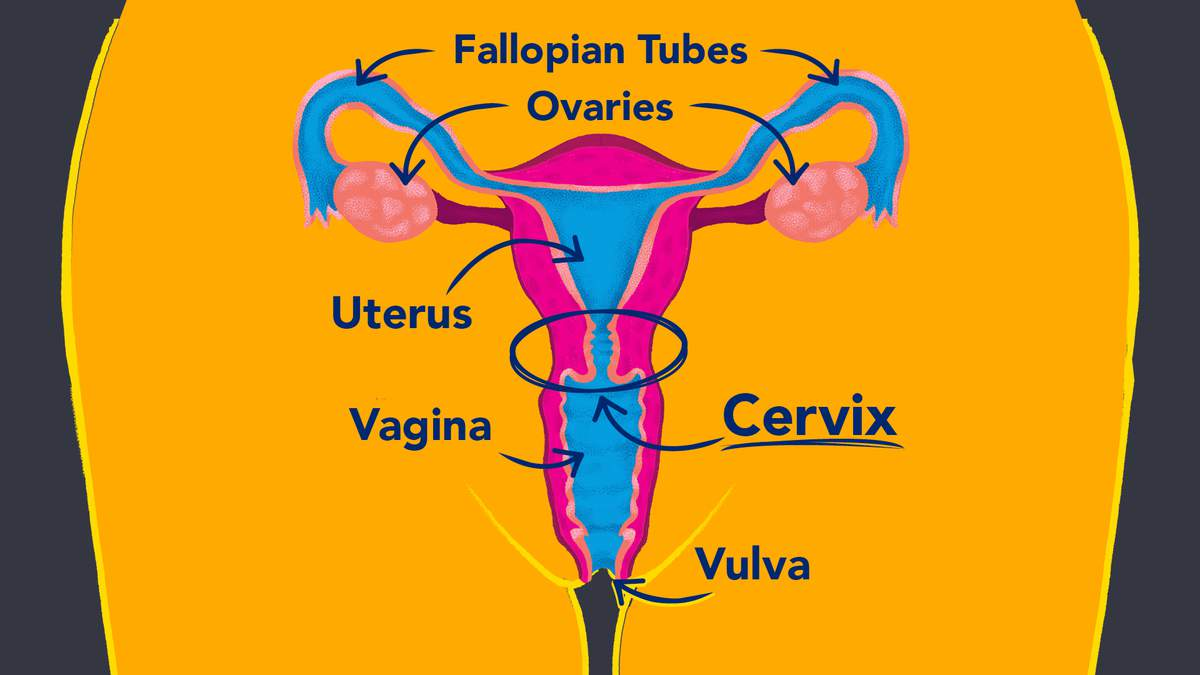
https://anatomy-quiz.com/female-sex-organs.html
Hormone | Gland | Role |
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) | Pituitary gland | Causes an egg to mature in an ovary. Stimulates the ovaries to release oestrogen. |
Oestrogen | Ovaries | Stops FSH being produced (so that only one egg matures in a cycle). Repairs, thickens and maintains the uterus lining. Stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH. |
LH (luteinising hormone) | Pituitary gland | Triggers ovulation (the release of a mature egg). |
Progesterone | Ovaries | Maintains the lining of the uterus during the latter part of the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy. |
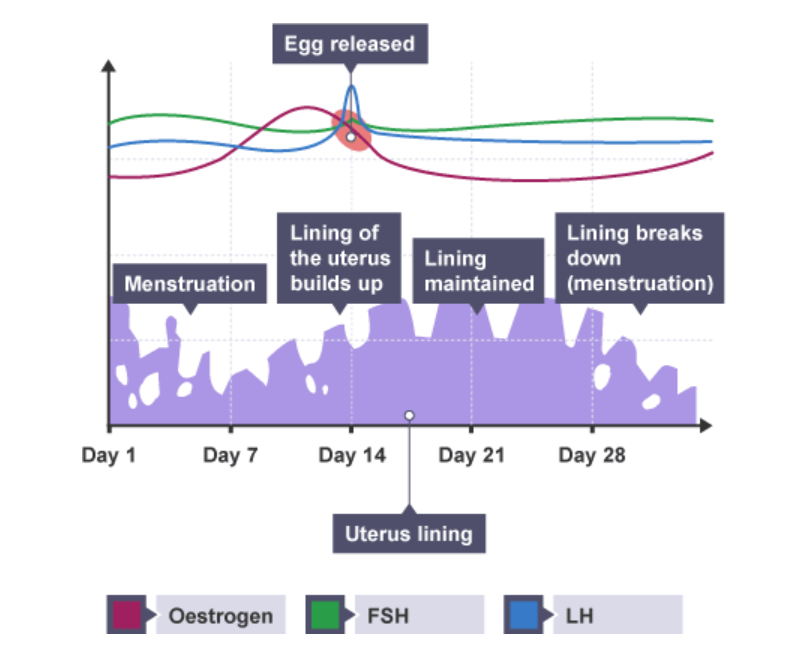
Pregnancy:
The foetus is attached to the placenta.
The placenta is a temporary organ that grows next to the foetus.
The placenta connects the foetus to the umbilical cord.
Timeline:
Week 5: The brain and spinal chord are starting to develop.
Week 6: A heart has started to beat. Arms and legs start to form.
Week 8: It is producing it’s own stomach digestive juices.
Week 9: Fingerprints are now formed and it will grip objects placed in its hand
Why does alcohol affect the foetus?
- Because the placenta does not filter alcohol or drugs, so they will be stuck in the babies system
Which hormones control secondary characteristical changes?
Females: Secondary sexual characteristics are controlled by the hormone oestrogen in girls
Males: Secondary sexual characteristics are controlled by the hormone testosterone in boys
Primary and secondary characteristics in males and females:
Primary:
Males: have a penis and testes
Females: females have a vagina and uterus
Secondary:
Males:
penis and testes grow
body hair starts to grow
muscles become more developed
the voice breaks
Females:
breast enlargement
body hair starts to grow
the menstraul cycle starts to begin
the hips become larger
Key words:
Gametes- sex cells, either female or male
Fertilization- the male gamete must move to the female gamete and fuse with it
Zygote- the new cell created after fertilization happened
Haploid- the presence of a single set of chromosomes in an organism's cells
Diploid- the presence of two complete sets of chromosomes in an organism's cells, with each parent contributing a chromosome to each pair
Placenta- The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients for the foetus and also removes waste products like CO2 and urea. Instead oxygen and nutrients diffuse across the placenta
The amniotic sack- It surrounds the baby. It protects the baby, as it is like a cushion.
Amniotic fluid- keeps the foetus at a optimal temperature
Inheritance
DNA:
It is a alpha double helix
Each nucleotide is made out of:
one sugar molecule
one phosphate group
one base pair (Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine)
A is complementary to T
C is complementary to G
Protein synthesis steps: (uses Uracil instead of Thymine)
DNA helix is untwisted and unzipped
mRNA (messenger RNA) match to their complementary base on the strand
The mRNA themselves are then joined together, creating a new strand called a template strand of the original DNA. This process is called transcription.
The template strand of mRNA then moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm and onto structures called ribosomes.
At the ribosomes, the bases on the mRNA are read in codons which then code for specific amino acids. This is called translation.
The corresponding amino acids are brought to the ribosomes by carrier molecules.
These amino acids connect together to form a protein. It is therefore the triplet code of bases that determines which protein is produced and therefore expressed.
When the chain is complete the protein folds to form a unique 3D structure.
Mitosis:
Definition: is a type of cell division where one cell divides to form two identical daughter cells.
Stages of Mitosis:
Prophase: Nucleus is still there with chromosomes condensing
Metaphase: Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Nucleus isn’t there anymore
Anaphase: Chromosomes move away from the middle and in the opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase: Two new nuclei are formed on opposite sides
Cytokinesis separates the cell into two identical daughter cells. This happens after PMAT
Meiosis:
Definition: is the cell division that forms four non-identical gametes
Stages of Meiosis:
Prophase: Nucleus is still there with chromosomes condensing
Metaphase: Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Nucleus isn’t there anymore
Anaphase: Chromosomes move away from the middle and in the opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase: Two new nuclei are formed on opposite sides
PMAT happens TWICE in meiosis
Genetic variation
Definition: it is the variation of DNA between individuals from the same species
There are two things that can determine the variation of the individuals:
Genetic variation: these things are determined by the DNA of the individual
Environmental variation: these are things that are determined by things like diet, climate, etc.
Mutations:
Definition: random changes in DNA
Charles Darwin:
“Survival of the fittest”
Evolution :a change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time through a process of natural selection which may result in the formation of a new species.
Speciation: when individuals of the same species change so much that they can no longer breed between each other, becoming two different species
Antibiotics resistance:
exposure to antibiotics creates a selection pressure, as those with antibiotic resistant genes survive and those without die
those with antibiotic resistance can reproduce and pass on the advantageous gene to their offspring
the population of antibiotic resistant bacteria increases.
Key words:
Allele- the different types of the genes
Recessive allele: is masked by the dominant allele (ignored if a dominant allele is present)
Dominant allele: masks the recessive allele
Homozygous- both inherited alleles are the same
Heterozygous- the inherited alleles are different
Phenotype- physical characteristics that can be seen (e.g. hair color, color skin)
Codominance- when none of the alleles are dominant so the offspring is mixt
Nucleotide- a molecule that is the basic building block of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
Codon- 3 base pairs
 Knowt
Knowt