Module 1: Introduction to Environmental Management Systems (EMS)
> An Environmental Management System (EMS) helps strategic frameworks that organizations address its regulatory requirements in a systematic and cost-effective manner. This proactive approach can help reduce the risk of non-compliance and improve health and safety practices for employees and the public. It can also help address non-regulated issues, such as energy conservation, and can promote stronger operational control and employee stewardship. US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency).
> It can be developed in compliance with the ISO 14001 standard as part of an organization’s strategy to implement its environmental policy and address governmental regulations. It focuses resources on meeting the commitments identified in the organization’s policy, which could include reducing or eliminating the negative environmental impacts of its products, services, and activities and/or increasing their positive effects.
WHAT IS THE EPA? (Environmental Protection Agency).
> A United Stage federal government agency whose mission is to protect human and environmental health.
WHAT IS THE ISO 14001 standard
> International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 14001 is the international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system. It provides a framework that an organization can follow, rather than establishing environmental performance requirements.
> Part of the ISO 14000 family of standards on environmental management, ISO 14001 is a voluntary standard that organizations can certify to. Integrating it with other management systems standards, most commonly ISO 9001, can further assist in accomplishing organizational goals.
> It defines an environmental management system as “part of the management system used to manage environmental aspects, fulfill compliance obligations, and address risks and opportunities.” The framework in the ISO 14001 standard can be used within a plan-do-check-act (PDCA) approach to continuous improvement.
> Used by any organization that wishes to set up, improve, or maintain an environmental management system with its established environmental policy and requirements. The requirements of the standard can be incorporated into any environmental management system, the extent to which is determined by several factors including the organization’s industry, environmental policy, products and service offerings, and location. This is relevant to all organizations, regardless of size, location, sector, or industry.
WHAT IS THE STANDARD?
International standards ensure that the products and services you use daily are safe, reliable, and of high quality. They also guide businesses in adopting sustainable and ethical practices, helping to create a future where your purchases not only perform excellently but also safeguard our planet. In essence, standards seamlessly blend quality with conscience, enhancing your everyday experiences and choices.
WHAT IS THE plan-do-check-act (PDCA)
The Plan-do-check-act Procedure
Plan: Recognize an opportunity and plan a change.
Do: Test the change. Carry out a small-scale study.
Check: Review the test, analyze the results, and identify what you’ve learned.
Act: Take action based on what you learned in the study step. If the change did not work, go through the cycle again with a different plan. If you were successful, incorporate what you learned from the test into wider changes. Use what you learned to plan new improvements, beginning the cycle again.
WHEN TO USE THE PDCA CYCLE?
Use the PDCA cycle when:
Starting a new improvement project
Developing a new or improved design of a process, product, or service
Defining a repetitive work process
Planning data collection and analysis in order to verify and prioritize problems or root causes
Implementing any change
Working toward continuous improvement
WHAT TOPICS DOES ISO 14001:2015 COVER?
This is the following topics with regard to environmental management systems framework: Context of the organization
Leadership
Planning
Support
Operation
Performance evaluation
Improvement
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF ISO 14001:2015
Using ISO 14001:2015 has many benefits for organizations with environmental management systems. Organizations and companies find that using the standard helps them:
Improve resource efficiency
Reduce waste
Drive down costs
Provide assurance that environmental impact is being measured
Gain competitive advantage in supply chain design
Increase new business opportunities
Meet legal obligations
Increase stakeholder and customer trust
Improve overall environmental impact
Manage environmental obligations with consistency
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS COMPONENTS
The three primary processes of a management system:
Core processes, their outputs, and the identification of significant environmental aspects and impacts
Key supporting processes, such as those for maintaining awareness of legal requirements, ensuring competency of employees, providing infrastructure, communicating EMS information, and monitoring and evaluating environmental performance
Management system supporting processes, such as document control, record control, and internal auditing
Like many quality management systems, environmental management systems reinforce a need to align processes into integrated systems of processes, all focused on providing the highest value to the customer.
The primary customer of the EMS is the local, regional, and global environment.
The Secondary customers may include the organization’s owners or shareholders, customers, government agencies, and employees.
ISO 14001:2015 and Environmental Management Systems
> According to ISO, more than 300,000 organizations in 171 countries have certified to ISO 14001, including more than 3,800 companies in the Unites States.
> The ISO 14001 standard is developed around the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) model of improvement, an iterative process that must be applied regularly to ensure benefits are being realized and the standard is being upheld. The primary operational components of an ISO 14001 EMS can be grouped as follows:
Create/update environmental policy.
Plan:
Environmental aspects
Legal and other requirements
Objectives, targets, and programs
Do:
Resources, responsibilities, and authority
Competence, training, and awareness
Communication
Documentation
Control of documents
Operational control
Emergency preparedness and response
Check:
Monitor and measure
Evaluate compliance
Nonconformity, corrective and preventive action
Control of records
Internal audits
Act:
Management review
ISO 14001 audit
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF AN ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
Ensuring a holistic approach to environmental impacts
Focusing on only critical aspects and processes
Making use of time-tested, mature approaches recognized worldwide
Establishing positive relationships with regulators
Economic benefits of implementing an environmental management system or good environmental stewardship that an organization can expect include:
Corporate reputation and image
Lower environmentally related costs and fees
Increased access to new customers
Direct savings through environmental source reduction
Susan L.K. Briggs discusses the ways to measure and show value of an EMS within an organization in the Quality Progress article, "Do Environmental Management Systems Improve Performance?" . There are three approaches to measuring improvements within an organization:
Management system improvement: Qualitative and quantitative improvements to management support processes, such as employee training and awareness, compliance assurance processes, or corrective/preventative action programs
Organizational reputation: Unquantifiable improvements in an organization’s reputation or improved relations with regulatory bodies, community organizations, or other interested parties
Financial benefits: Quantitative cost savings or cost avoidance associated with any of the improvements
Since the ISO 14001 standard is non-prescriptive,
Evolutionary model of Environmental Management System development
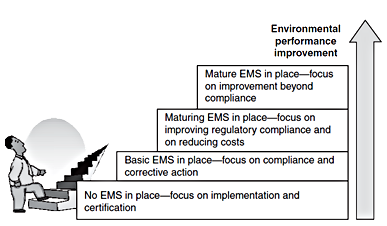
the highest point is: Environmental Peroformance Improvemment
The History of Environmental Management SystemsEnvironmental and sustainability goals for quality initiatives are relatively recent. Because the business world is accustomed to treating environmental practices as sources of added costs, the challenge for quality practitioners is to identify where environmental and sustainability quality issues,
The characteristics of each stage in the evolution of compliance management to sustainability:
1990 to 1994: Compliance management (CM) meant focusing on regulation and relying on environmental departments to react to issues.
1994 to 1998: Environmental management systems (EMS) brought a more systematic, organization-wide focus on environmental issues.
1998 to 2002: Environmental information management systems (EIMS) involve using web-based systems and integrating multiple systems.
2002 to 2006: Environmental process management systems (EPMS) make use of quality tools, using a project focus to drive improvements.
2006 to current: Sustainability requires integrating environmental, social, and economic goals and using best practices to address risk and uncertainty.
BASIC ELEMENTS OF AN EMS INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING:
Reviewing the organization's environmental goals;
Analyzing its environmental impacts and compliance obligations (or legal and other requirements);
Setting environmental objectives and targets to reduce environmental impacts and conform with compliance obligations;
Establishing programs to meet these objectives and targets;
Monitoring and measuring progress in achieving the objectives;
Ensuring employees' environmental awareness and competence; and,
Reviewing progress of the EMS and achieving improvements.
THE STEPS IN CREATING AN ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Organizations can follow 4 steps to create and implement an environmental management system.
Establish an environmental policy: The policy must align with the organization's values and objectives. The policy should clearly articulate the commitment to environmental protection and sustainability.
Identify environmental aspects: This involves determining how their activities, products, and services interact with the environment, and identifying potential environmental impacts.
Develop implementation plans: Organizations can develop detailed plans outlining the actions required to achieve them. This includes assigning responsibilities, allocating resources, and establishing timelines.
Implement and monitor: Regular monitoring allows organizations to track their environmental performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement corrective actions if necessary.
The importance of the environmental management systemCompliance: Organizations can avoid legal penalties and reputational damage, by proactively managing their environmental impacts.
Cost savings: Organizations can minimize waste generation and associated disposal costs, by optimizing their processes,
Risk mitigation: Organizations can prevent incidents, reduce liabilities, and protect the health and safety of employees, communities, and ecosystems, by addressing potential risks upstream.
Enhanced reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to environmental sustainability enhances an organization's reputation among stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulators.
Stakeholder engagement: Engaging stakeholders fosters collaboration, innovation, and a shared sense of responsibility.
The components of an environmental management system
An effective EMS typically consists of the following 6 components:
Environmental Policy
Planning
Implementation and operation
Checking and corrective action
Management review
Employee training and awareness
An example of an environmental management system
Let's take for example a manufacturing company that aims to implement an EMS:
The company establishes an environmental policy that emphasizes resource conservation, pollution prevention, and sustainable practices.
Through a comprehensive assessment, the company identifies its environmental aspects, such as energy consumption, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
The company sets objectives and targets, such as reducing energy consumption by 20% within two years and achieving zero-waste-to-landfill status.
Implementation plans outline specific actions like upgrading equipment for energy efficiency, implementing recycling programs, and conducting regular energy audits.
The company monitors its energy consumption, waste generation, and recycling rates to track progress toward the objectives set, and makes adjustments when necessary.
Regular management reviews are conducted to evaluate the EMS's effectiveness, identify improvement areas, and allocate necessary resources.
 Knowt
Knowt