W1: Chapter 1 - Introduction to Marketing Research
Learning Objectives
Define marketing research and distinguish between problem-identification research and problem-solving research.
Describe a framework for conducting marketing research as well as the six steps of the marketing research process.
Understand the nature and scope of marketing research and its role in designing and implementing successful marketing programs.
Explain how the decision to conduct marketing research is made. Discuss the marketing research industry and the types of research suppliers, including internal, external, full-service, and limited-service suppliers.
Describe careers available in marketing research and the backgrounds and skills needed to succeed in them.
Acquire an appreciation of the international dimension and the complexity involved in international marketing research.
Describe the use of social media as a domain in which to conduct marketing research.
Discuss the developing field of mobile marketing research and its advantages and disadvantages.
Gain an understanding of the ethical aspects of marketing research and the responsibilities each of the marketing research stakeholders have to themselves, one another, and the research project.
Acronyms
The role and salient characteristics of marketing research may be described by the acronym
Research:
R ecognition of information needs
E ffective decision making
S ystematic and objective
E xude/disseminate information
A nalysis of information
R ecommendations for action
C ollection of information
H elpful to managers
Exercises Questions
How is accuracy attained in market research?
How do controllable and uncontrollable variables impact market research?
Define marketing research.
Suggest three different types of product research used to identify or find a solution to a problem.
Describe the steps in the marketing research process.
How should the decision to conduct research be made?
What are the differences between full-service and limited service market research suppliers?
What are customized services?
What is the main difference between a full-service and a limited-service supplier?
What are technical and analytical services?
List five guidelines for selecting an external marketing research supplier.
Why might a market research supervisor’s role be more “hands on” than a market research manager’s role?
What are the limitations of using social media for conducting marketing research?
Discuss the scope, advantages, and limitations of mobile marketing research.
Discuss three ethical issues in marketing research that relate to (1) the client, (2) the supplier, and (3) the respondent.
Problems
Browse the Internet and identify five distinct types of problemsolving research that fall into the categories of product research and promotional research.
Describe one kind of market research that would be useful to each of the following types of organization:
a) A local clothes store catering mainly to students and under 25s
b) An ATM business looking for new sites for its machines
c) A real estate company focusing on business premises sales and rentals
d) A pop-up restaurant seeking ideal locations for its services
e) A private art and culture museum
Introduction to Marketing Research
Marketing research is a crucial aspect of marketing.
In this chapter, we will:
Define marketing research.
Categorize it into problem identification and problem-solving research.
Provide real-life examples to illustrate key concepts.
Describe the marketing research process and its six steps.
Emphasize the role of marketing research in decision-making.
Overview marketing research suppliers and offer selection guidelines.
Explore career opportunities in marketing research.
Definition of Marketing Research
Marketing research involves systematic data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
It aims to provide insights for informed marketing decisions.
It can be classified into problem identification and problem-solving research.
Problem Identification vs. Problem-Solving Research
Problem identification research helps identify hidden or potential issues.
Problem-solving research finds solutions to specific marketing problems.
Both types of research are essential and often intertwined.
Real-Life Examples
Real-life examples are used to illustrate core marketing research concepts.
A department store patronage project serves as a recurring case study throughout the book.
The Marketing Research Process
The process includes six steps:
Problem definition.
Research design.
Data collection.
Data analysis.
Report preparation.
Decision-making.
Each step is meticulously planned and executed.
Nature of Marketing Research
Marketing research serves as a vital information source for decision-making.
It helps in understanding market dynamics, consumer behavior, and competition.
Marketing Research Suppliers
Various organizations form the marketing research industry.
Selection guidelines assist in choosing the right supplier for a project.
Career Opportunities
Marketing research offers exciting career prospects, including roles in data analysis, market research firms, and consultancy services.
Contemporary Issues in Marketing Research
The chapter addresses modern challenges and trends in marketing research, including:
International marketing research.
Social media's impact.
Mobile marketing research.
Ethical considerations.
Active Research and Experiential Research
These sections provide hands-on applications of marketing research concepts.
Exercises engage readers in practical research activities.
Live Research: Conducting a Marketing Research Project
A section for instructors interested in implementing real-life research projects.
Role of Marketing Research
Marketing research plays a vital role in shaping marketing strategies.
It guides decision-making by providing data-driven insights.
Conclusion
Marketing research is multifaceted and ever-evolving.
The chapter provides a comprehensive overview of its key components and applications.
Case Study - Fast Fruit?
Introduction to the Fast-Food Industry and Health Concerns
Consumers' growing concern for health and nutrition has impacted the fast-food industry.
Lawsuits related to obesity have been filed against fast-food giants known for offering unhealthy menu options.
Shift Towards Healthier Alternatives
In response to health concerns, many fast-food chains are introducing healthier menu items like salads and fresh fruit.
Reducing serving sizes is another strategy to promote healthier eating.
Consumer Satisfaction in the Fast-Food Industry
According to the Quick-Track research study by Sandelman, Americans express satisfaction with fast food.
Quick-Track is a quarterly syndicated market research project that tracks consumer behavior and attitudes towards major fast-food and pizza chains.
Data Collection in the Quick-Track Study
The study surveys 400 respondents quarterly in each market.
Data collection methods include telephone (landline and mobile) and Internet interviews.
Respondents are selected randomly via computer-generated samples.
The study ensures reliability and representativeness by considering only chains with a minimum of 150 responses.
Key Attributes for Respondents
Respondents rate their opinions on various attributes on a scale from 1 (Poor) to 5 (Excellent).
The top three attributes rated as extremely important by respondents are cleanliness (77 percent), food taste and flavor (74 percent), and order accuracy (66 percent).
The availability of healthy and nutritious food is becoming increasingly important, with 40 percent rating it as extremely important.
Impact of Consumer Demand on Satisfaction
The overall increase in satisfaction with fast-food chains is attributed to their responsiveness to customer demands for food quality, taste, health, and nutrition.
Examples of Healthier Menu Options
Fast-food chains are responding to the desire for healthier and tastier food options by offering fresh fruit on their menus.
Examples include Wendy's fresh fruit bowls, McDonald's fruit and walnut salad, and IHOP's fruit plate entrées.
Wendy's sees this as an opportunity due to people seeking new tastes and healthier alternatives.
Role of Marketing Research
Marketing research plays a critical role in designing and implementing successful marketing programs.
It is utilized not only by fast-food restaurants but also by various organizations, including Boeing, NBC, and others.
Marketing research has evolved to become global, real-time, and integrated with marketing and product development.
Various methods, such as surveys (telephone, mobile, personal, and online), focus groups, in-depth interviews, and internet research, are employed in marketing research.
Importance of Understanding Marketing Research
This book introduces a range of marketing research techniques and their applications in formulating effective marketing strategies.
Understanding marketing research is key to comprehending its role in decision-making processes.
Definition of Marketing Research
Marketing research is formally defined by the American Marketing Association as a systematic and objective process.
It involves the identification, collection, analysis, dissemination, and use of information.
The purpose of marketing research is to assist management in decision-making related to marketing problems and opportunities.
Key Aspects of the Definition
Systematic: Marketing research requires careful planning and a structured approach at every stage of the research process.
Objective: It should be conducted impartially, without personal or political biases, to maintain professional standards.
Scientific Method: Marketing research employs scientific principles, including data collection and analysis to test hypotheses and provide accurate insights.
Information Phases: The marketing research process encompasses several phases, including problem/opportunity identification, information source identification, data collection method selection, data collection, analysis, interpretation, and reporting.
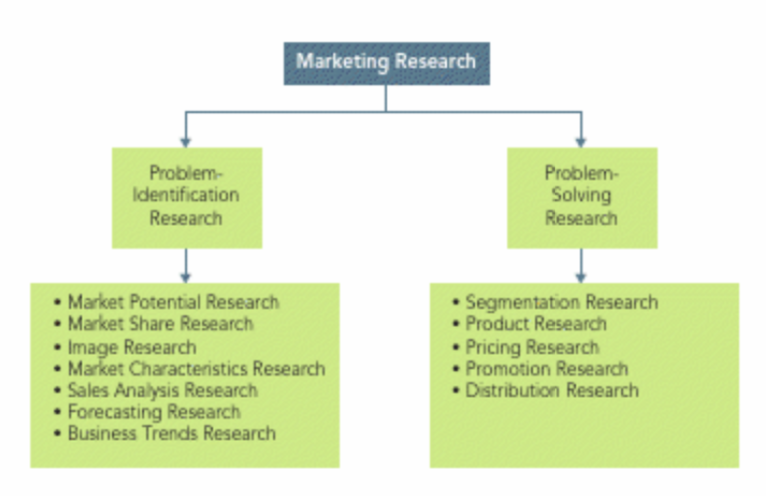
Problem-Identification Research
This type of research helps identify marketing problems or opportunities that may not be immediately apparent.
It aids in diagnosing issues in the marketing environment, such as market potential, market share, brand image, and consumer trends.
Problem identification research is essential for recognizing underlying problems or opportunities.
Problem-Solving Research
Problem-solving research is conducted to find solutions to specific marketing problems identified through problem-identification research.
Most organizations engage in problem-solving research to make informed decisions that address marketing challenges effectively.
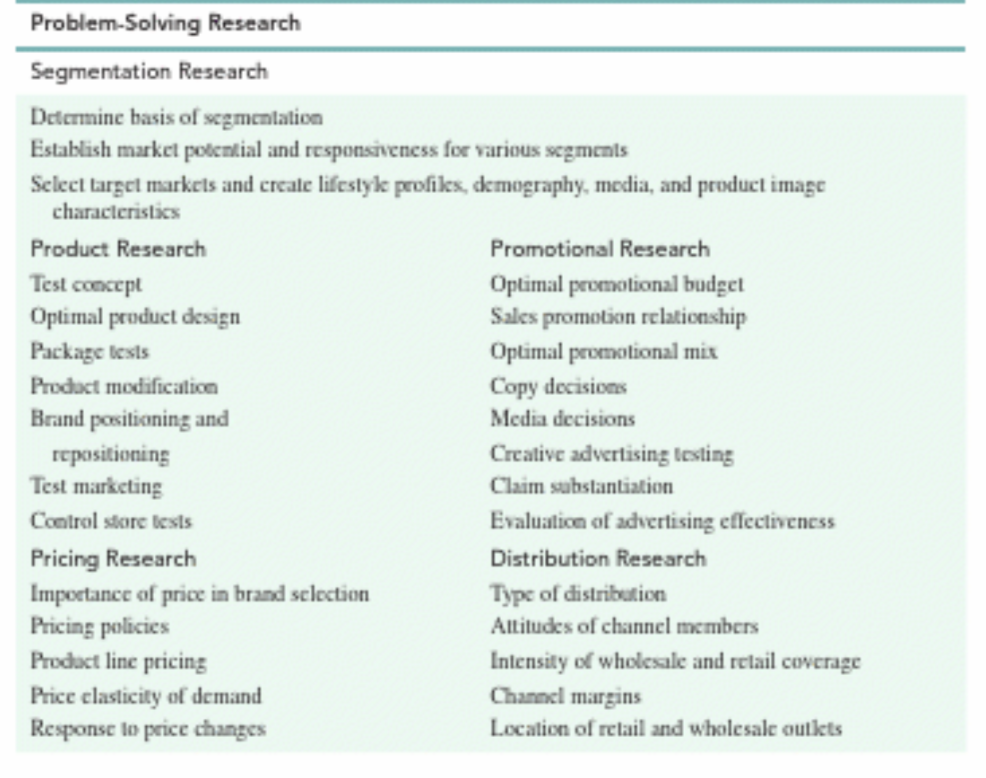
Types of Problem-Solving Research
Problem-solving research addresses various marketing issues, including:
Segmentation Research: Understanding and dividing the market into distinct segments.
Product Research: Developing and improving products based on consumer preferences and needs.
Pricing Research: Determining optimal pricing strategies.
Promotion Research: Assessing the effectiveness of marketing and advertising efforts.
Distribution Research: Optimizing distribution channels and strategies.
Combining Problem-Identification and Problem-Solving Research
While problem-identification and problem-solving research are distinct, they often go hand in hand.
A comprehensive marketing research project may involve both types to thoroughly address marketing challenges and opportunities.
Examples of Marketing Research
The Boeing example illustrates how problem-identification research (consumer surveys) identified demand for smaller planes.
Problem-solving research (product research) resulted in the introduction of new plane versions catering to specific market segments.
Importance of Marketing Research
Marketing research plays a crucial role in decision-making across various industries.
It assists in understanding consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes.
The insights gained from marketing research inform marketing strategies and improve overall decision-making.
Case Study: Kellogg Cereal
While not explicitly mentioned, Kellogg's likely employs marketing research to address challenges or opportunities within the cereal industry.
Marketing research aids in understanding consumer preferences, market dynamics, and product development.
Kellogg's Cereal Sales Challenge
Kellogg's, operating in over 180 countries, faced declining cereal sales.
To address this issue, the company employed marketing research to identify and solve the problem.
Problem-Identification Research
Kellogg's employed problem-identification research to uncover the root of declining cereal sales.
This involved speaking to decision-makers, interviewing industry experts, analyzing available data, studying social media data, performing qualitative research, and surveying consumers.
Identified Problems
The research revealed several issues:
Products were predominantly marketed towards children.
Bagels and muffins were preferred breakfast foods.
High prices led consumers to opt for generic brands.
Adults sought quick, low-preparation foods.
The key problem was a lack of creativity in introducing new products catering to the adult market.
Problem-Solving Research
To address the problems identified, Kellogg's engaged in problem-solving research.
It developed and tested new cereal flavors through mall intercept interviews with adult consumers.
New flavors were introduced, such as Special K Nourish, consisting of multigrain flakes, granola, almonds, apples, and raspberries.
An ad campaign and in-store promotions supported the new products.
The Marketing Research Process
The marketing research process consists of six steps, as follows:
Step 1: Problem Definition
Defining the research problem by considering its purpose, background information, needed information, and how it aids in decision-making.
Involves discussions with decision-makers, interviews with industry experts, analysis of secondary data, and qualitative research.
Step 2: Development of an Approach to the Problem
Creating an approach to the problem by formulating objectives, analytical models, research questions, and hypotheses.
Involves discussions with management, analysis of secondary data, qualitative research, and pragmatic considerations.
Step 3: Research Design Formulation
Developing a framework for the research study, including the procedures for obtaining necessary information.
Addresses exploratory research, variable definition, scaling, questionnaire design, sampling, and data collection methods.
Also considers data analysis and reporting.
Step 4: Fieldwork or Data Collection
Data collection is carried out through field staff or other means such as phone, mail, or electronic surveys.
Proper training, supervision, and evaluation of data collectors are vital for accuracy.
Step 5: Data Preparation and Analysis
Data preparation includes editing, coding, transcription, and verification.
Data are analyzed to provide insights into the research problem and support decision-making.
Step 6: Report Preparation and Presentation
Documentation of the entire project, including research questions, approach, design, data collection, analysis, and results.
Findings are presented in a comprehensible format to assist in decision-making.
Oral presentations may be made to enhance clarity.
Interdependence of Steps
The steps in the marketing research process are interdependent and iterative.
Researchers should consider both preceding and succeeding steps at each stage.
Role of Marketing Research
Marketing research plays a crucial role in addressing business challenges and driving product innovation.
It assists in identifying and solving problems, supporting informed decision-making, and enhancing consumer satisfaction.
Marketing Research at Marriott Corporation
Marriott International, Inc. is a global hospitality company with a rich history.
Its marketing research is conducted at the corporate level through Corporate Marketing Services (CMS).
CMS aims to provide Marriott managers with essential information about the market and customers.
A variety of research methods are employed, including quantitative and qualitative approaches such as surveys, focus groups, and customer intercepts.
Research at Marriott follows a systematic process.
Steps in the Marriott Research Process
Problem Definition: The initial step is to clearly define the problem and objectives.
Approach Development: Developing an approach to address the problem.
Research Design Formulation: Creating a formal research design, including deciding whether to conduct in-house research or purchase it externally.
Data Collection and Analysis: Once a decision is made, data are collected and analyzed.
Report Presentation: Study findings are presented to the client unit in a formal report.
Constant Dialogue: Ongoing communication between the client and CMS to discuss research implications, decision-making, and future research suggestions.
The Role of Marketing Research in Decision Making
Marketing research plays a vital role in the marketing paradigm, which focuses on identifying and satisfying customer needs.
Marketing managers require information about customers, competitors, and market forces.
Factors like expanding markets, consumer sophistication, and increasing competition have raised the demand for more and better information.
Marketing research assesses information needs and provides management with relevant, accurate, reliable, valid, current, and actionable information.
In today's competitive environment, sound decisions are based on data, not intuition or gut feeling.
Importance of Marketing Research
Marketing research is essential to reduce the costs of poor decision-making.
It ensures that management decisions are well-informed and supported by data.
Incorrect decisions can be costly, as seen in the case of Johnson & Johnson baby aspirin.
Case Study: Johnson & Johnson's Baby Aspirin Mistake
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is a global healthcare product manufacturer with a wide presence.
In an attempt to use its name on baby aspirin, J&J faced a setback.
J&J's baby products are known for gentleness, but gentleness is not a desired quality in a baby aspirin.
People perceived that a gentle aspirin might not be effective enough.
This case illustrates the importance of proper marketing research before making product-related decisions.
Marketing Manager's Decision-Making Process
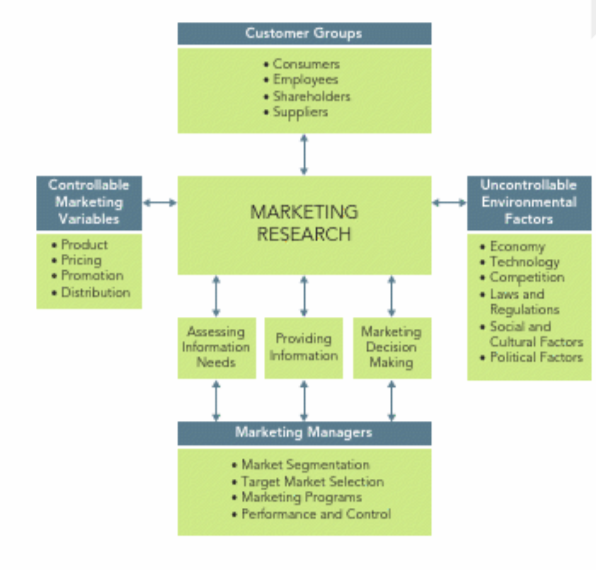
Marketing managers make a range of strategic and tactical decisions in identifying and satisfying customer needs.
These decisions encompass opportunities, target market selection, market segmentation, program planning, performance evaluation, and control.
Decisions are influenced by factors like product, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
External uncontrollable factors like economic conditions, technology, laws, competition, and social changes further complicate decisions.
The complexity of various customer groups adds to the challenge.
Marketing research helps bridge the gap between marketing variables, the environment, and customer groups.
It reduces uncertainty by providing essential information.
Evolution of Marketing Roles
Traditionally, marketing researchers assessed information needs and provided data, while managers made decisions.
However, roles are evolving; researchers are more involved in decision-making, and managers engage in research.
Factors driving this change include improved managerial training, technological advances, and ongoing marketing research trends.
Marketing research must add value to decision-making and the entire organization.
Cross-Functional Perspective
Marketing managers do not work in isolation; they have a cross-functional perspective to meet consumer needs and ensure long-term profitability.
Marketing research should interface with other organizational functions like manufacturing, R&D, finance, and accounting.
Marketing and marketing research are increasingly integrated.
Enhancing Decision-Making with Marketing Research
Marketing research enhances available information and improves decision-making.
Information obtained through marketing research becomes a vital part of the firm's Marketing Information System (MIS) and Decision Support System (DSS).
Marketing research also plays a crucial role in gathering competitive intelligence.
Marketing Research and Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence (CI): CI is the process of enhancing marketplace competitiveness through a deeper understanding of a firm's competitors and the competitive environment.
Ethical Process: CI is an ethical process that involves legal collection and analysis of information about competitors' capabilities, vulnerabilities, and intentions.
Collection Sources: CI utilizes various sources, including information databases, open sources, and ethical marketing research.
Evolved Discipline: While marketing research plays a crucial role in collecting, analyzing, and disseminating CI information, CI has evolved into a distinct discipline of its own.
Strategic and Competitive Intelligence Professionals (SCIP): SCIP is an organization comprising members engaged in CI for companies of all sizes, providing management with early warnings about changes in the competitive landscape.
The Decision to Conduct Marketing Research
Considerations: The decision to conduct marketing research is influenced by several considerations, including:
Costs vs. Benefits: The expected value of the information obtained should outweigh the costs of the research project.
Available Resources: The availability of resources, both for conducting the research and implementing its findings, is a crucial factor.
Management Attitude: The organization's attitude toward research and willingness to utilize research findings.
Importance of Decision: The significance of the decision at hand and the level of uncertainty or risk associated with it determine the value of the information obtained through research.
Quantifying Expected Value and Costs: Formal procedures exist for quantifying the expected value and costs of a marketing research project. In most cases, the value of information outweighs the costs, but exceptions can occur.
Resource Limitations: Limited resources, particularly time and money, can impact the decision to undertake a research project. If resources are insufficient to maintain research quality, it's better not to conduct the research to avoid compromising research integrity.
Implementation Resources: In some cases, an organization may lack the resources needed to implement the recommendations derived from research findings, making research unwarranted.
Management Attitude: The attitude of management towards research is a key factor. If management is not receptive to research, the project's findings may go unused.
Exceptions: There can be exceptions; for instance, even if store management opposes research findings, the parent organization might still implement recommendations.
Availability of Information: If the required information is already available within the organization or the decision has already been made, the value of conducting research diminishes.
Political Ends: Research should not be used for political or manipulative purposes, as it reduces the value of the generated information.
Role of Marketing Research Industry: When the decision is made to conduct marketing research, organizations can rely on the marketing research industry, including suppliers and services, to obtain specific information as needed.
The Marketing Research Industry
Marketing Research Industry: The marketing research industry encompasses various suppliers and services that provide information necessary for making marketing decisions.
Marketing Research Suppliers and Services: Suppliers in the marketing research industry offer a wide array of services. Many of the prominent suppliers have multiple subsidiaries and divisions that cater to different aspects of marketing research.
Classification of Suppliers: Marketing research suppliers can be broadly classified as either internal or external.
Internal Supplier:
An internal supplier refers to the marketing research department located within a firm.
Large organizations, such as automobile companies, consumer product firms, and banks, often maintain their own in-house marketing research departments.
The organizational structure of these departments can vary, from centralized (located at corporate headquarters) to decentralized (division-specific).
The appropriate organization depends on the firm's research needs and functional structure.
External Supplier:
External suppliers are independent firms outside the client organization that offer marketing research services.
These external suppliers collectively constitute the marketing research industry.
They range from small operations to large global corporations.
External suppliers can be classified as either full-service or limited-service suppliers.
Full-Service Suppliers:
Full-service suppliers provide a comprehensive range of marketing research services, including problem definition, approach development, questionnaire design, sampling, data collection, data analysis, interpretation, report preparation, and presentation.
They offer services tailored to the client's specific needs and may provide customized services, syndicated services, and services related to the Internet and social media.
Marketing Research Services Classification
Marketing research services come in various forms, tailored to meet specific client needs. These services can be broadly categorized into:
Customized Services:
Description: Customized services provide a wide range of marketing research services that are uniquely tailored to address a client's specific requirements. Each research project is treated as a distinct and individual undertaking.
Examples: Firms that offer customized services include Burke, Inc. and MaritzCX. The survey conducted by Harris Poll for Boeing, as mentioned earlier, is an example of customized research.
Syndicated Services:
Description: Syndicated services collect information of known commercial value and provide it to multiple clients through a subscription model. Data collection methods often include surveys, panels, scanners, and audits.
Examples: Firms like Nielsen provide data on television program viewership and scanner volume tracking data from supermarkets. The NPD Group maintains a large consumer panel in the United States. Sandelman & Associates' Quick-Track, mentioned in the earlier "Fast . . . Fruit" example, is an illustration of a syndicated service.
Internet/Social Media Services:
Description: Some marketing research firms specialize in offering services related to the Internet and social media research. These services may focus on online surveys, social media monitoring, and insights.
Examples: Companies like Toluna, a digital insights company, maintain a large social voting community and offer customized panels. Specialized social media research firms are also present in this category.
Limited-Service Suppliers:
Description: Limited-service suppliers specialize in specific phases or aspects of the marketing research project. These can include field services, qualitative services, technical and analytical services, and other specialized services.
Examples:
Field Services: These organizations collect data through various means, including mail, personal interviews, telephone, mobile, or electronic interviews. Firms like Field Work offer field services.
Qualitative Services: These providers offer facilities, respondent recruitment, and support for qualitative research, such as focus groups and one-on-one depth interviews. Companies like Jackson Associates and First In Focus Research are examples.
Technical and Analytical Services: Firms specializing in design and advanced statistical analysis of quantitative data, as obtained in large surveys. Examples include SDR and Sawtooth Technologies.
Other Services: These can encompass a wide range of specialized services, such as research in ethnic markets (e.g., Hispanic, African, multicultural). Multicultural Insights is an example in this category.
The choice of supplier, whether full-service or limited-service, should align with the specific needs of the research project and the available resources.
These service categories provide a spectrum of options for clients seeking marketing research support, enabling them to select the most suitable services for their unique requirements.
Selecting a Research Supplier
When an organization cannot conduct an entire marketing research project in-house, it must identify and choose an external research supplier for one or more phases of the project. The process of selecting a research supplier should be thorough and well-considered. Here's how organizations typically approach this:
Compile a List of Prospective Suppliers:
Sources for identifying potential research suppliers include trade publications, professional directories, and recommendations from colleagues and industry contacts.
Determine Why External Support is Needed:
Organizations should clarify their reasons for seeking external marketing research support. This may include factors such as limited resources, technical expertise, or the need to avoid conflicts of interest.
Set Selection Criteria:
Develop clear criteria for choosing an outside research supplier. Consider the following:
Reputation and track record
Adherence to ethical standards
Flexibility
Quality of research projects
Relevant experience
Technical and nontechnical expertise
Professional certifications
Communication skills
Competitive Bidding Process:
For larger projects, organizations often use a competitive bidding process. This may involve issuing a Request for Proposal (RFP) or similar invitations for suppliers to submit their bids.
Quality Over Price:
Awarding projects based solely on the lowest price is not advisable. The completeness and quality of the research proposal, as well as the selection criteria, should all be considered when making a decision.
Long-Term Contracts:
For ongoing research needs, long-term contracts with research suppliers can be more beneficial than a project-by-project basis.
Get Everything in Writing:
It's essential to have a written bid or contract before starting a project to ensure clarity and transparency in expectations.
Use the Internet for Research:
The internet is a valuable tool for identifying research suppliers. Search engines, industry-specific directories, and association websites can help locate suitable firms. Websites often provide information about the company's history, services, clients, and personnel.
Remember that Price Isn't Everything:
Consider quality, reputation, and alignment with your project's specific needs. The cheapest bid may not always provide the best value.
Base Decisions on Sound Information:
Decisions about research suppliers, like other management choices, should be well-informed and based on reliable information.
Selecting a research supplier is a critical decision, and taking the time to evaluate and consider the various factors will contribute to the success of your marketing research project.
Employability in Marketing Research
The field of marketing research offers promising career opportunities, with potential employment both in marketing research firms and within various business and non-business organizations, including marketing research departments, advertising agencies, and governmental agencies. Below are some career positions available in marketing research:
Vice President of Marketing Research: This is a high-level position responsible for overseeing the entire marketing research function within an organization.
Research Director: Research directors manage and lead marketing research teams, ensuring the successful execution of projects.
Assistant Director of Research: This role assists the research director in various aspects of research management.
Project Manager: Project managers are responsible for the day-to-day operations and coordination of marketing research projects.
Statistician/Data Processing Specialist: These specialists focus on data analysis and statistical techniques.
Senior Analyst: Senior analysts have extensive experience and are involved in data analysis, report preparation, and decision support.
Analyst: Analysts handle data analysis and contribute to the research process.
Junior Analyst: Entry-level positions typically involving training in various research-related tasks.
Fieldwork Director: Responsible for overseeing fieldwork operations, which may include data collection, interviewing, and more.
Operational Supervisor: Operational supervisors manage specific aspects of research operations, such as data editing and coding.
In terms of educational background, the entry-level position for individuals with bachelor's degrees (e.g., BBA) is often an operational supervisor role. However, there's a growing preference in the marketing research industry for individuals with master's degrees. MBAs or equivalent degrees are likely to be employed as project managers who work closely with account directors in managing research projects.
In business firms, the typical entry-level positions include junior research analyst (for BBAs) and research analyst (for MBAs). The junior analyst learns about the industry, undergoes training, and prepares for the responsibilities of a research analyst. Research analysts are responsible for data accuracy, market forecasting, and primary and secondary data analysis.
Marketing research requires a diverse range of skills and backgrounds. Statisticians need a strong foundation in statistics and data analysis. For other positions, more general skills are required, such as managing the work of others. Effective written and verbal communication skills are vital, along with the ability to think creatively. A liberal education background is valuable as it allows marketers to understand and address business problems from a broader perspective.
It's important to stay informed about the latest developments in marketing research and to continuously build relevant skills. The field offers attractive employment opportunities and requires a combination of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills.
Case Study: The Department Store Patronage Project
The Department Store Patronage Project serves as an ongoing example in this text, demonstrating concepts and data analysis procedures. The project aimed to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of a major department store, referred to as "Wal-Mart" while maintaining anonymity, compared to a group of direct and indirect competitors. The primary goal was to create marketing programs to improve Wal-Mart's declining sales and profits.
The study considered ten major stores, including prestigious department stores (e.g., Saks Fifth Avenue, Neiman-Marcus), national chains (e.g., JCPenney), discount stores (e.g., Kmart), and some regional chains (e.g., Kohl’s). To gather data, a questionnaire was designed and administered through in-home personal interviews to a convenience sample of 271 households from a significant metropolitan area. A six-point scale was used for ratings.
The following information was collected:
Familiarity with the 10 department stores: To assess consumer awareness of these stores.
Frequency of household members' shopping: To understand how often people shopped at each of the 10 stores.
Relative importance of choice criteria: To evaluate the factors considered when selecting a department store. The factors included quality of merchandise, variety and assortment, return and adjustment policy, service quality, prices, convenience, store layout, and credit and billing policies.
Evaluation of the 10 stores on each of the choice criteria: To determine how well each store performed on these factors.
Preference ratings for each store: To gauge consumers' preference for each store.
Rankings of the 10 stores: To understand which stores were most and least preferred.
Degree of agreement with lifestyle statements: To delve into the lifestyle of respondents.
Standard demographic characteristics: To collect information about age, education, and more.
Contact information: To facilitate future communications.
This project allowed the sponsor to gain insights into consumer perceptions and preferences regarding department stores. It helped identify weaknesses concerning specific factors influencing consumer choice criteria and product categories. This information was instrumental in developing marketing programs to address these issues. Moreover, it helped establish a positioning strategy to create a favorable store image.
International Marketing Research
International marketing research is an essential component of the globalized business landscape. The United States represents only around 40 percent of worldwide marketing research expenditures, highlighting the international nature of this field. In Europe, major research activities are concentrated in countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, and Spain. Japan, China, and Australia take the lead in the Asia-Pacific region, with Korea and Taiwan following suit. Brazil and Mexico lead Central and South American markets in terms of marketing research expenditures.
Given the globalization of markets, international marketing research has become indispensable and is likely to keep expanding. It encompasses several facets, including:
International marketing research: Research for products intended for a global audience.
Foreign research: Research conducted in a country other than the one where the research-commissioning organization is based.
Multinational research: Research conducted in all or the most significant countries where a company is represented.
Conducting research at this scale, which often involves cross-cultural aspects, is far more intricate than domestic marketing research. All types of international research share complexities related to environmental factors, including culture, that influence how each stage of the marketing research process should be executed.
The globalization of companies is a prevailing trend, with many businesses expanding online or setting up physical operations in foreign countries. It's crucial to conduct research that considers the variations between the home country and the target market. Failing to account for these differences can lead to unforeseen issues and global business failures.
For example, the interpretation of web content may differ from one country to another, causing misunderstandings. Moreover, companies must adapt their content to different languages in regions with multiple dialects, such as India. Understanding these environmental factors is pivotal for achieving success and expanding sales in foreign markets.
Case Study: McDonald's Adapting to Local Culture with Its Global Image
McDonald's, the renowned fast-food chain, has demonstrated a remarkable ability to respect and adapt to local cultures and preferences while maintaining its global brand image across diverse international markets. This adaptability stems from a profound reliance on marketing research, allowing the company to tailor its offerings to meet the specific needs and beliefs of each local customer base.
One outstanding example of this adaptation is McDonald’s approach in India, where food consumption is significantly influenced by religious beliefs. In response to this cultural nuance, McDonald’s has made several key changes to its menu in India:
Vegetarian Focus: To respect the religious beliefs of Hindus and Muslims, who constitute a significant portion of India's population, McDonald's has removed beef and pork from its menu entirely. Instead, the menu features numerous vegetarian options like the McVeggie burger and McSpicy Paneer, alongside chicken offerings.
McAloo Tikki Burger: The McAloo Tikki burger, made from a potato-based patty, became a top seller in India and accounts for as much as 25 percent of total sales in McDonald’s restaurants within the country.
Separate Kitchens: Understanding the strict food habits and practices of vegetarians in India, McDonald’s kitchens in the country are organized into separate sections for cooking vegetarian and nonvegetarian food.
Vegetarian-Only Restaurants: In response to local preferences in pilgrimage areas, McDonald’s announced that new restaurants in such locations would be vegetarian-only. This move was designed to cater to the beliefs and dietary choices of the local customer base.
Local Breakfast Menu: McDonald’s introduced a new breakfast menu in India in 2017, which featured local favorites like "Masala Dosa Brioche" and "Masala Scrambled Eggs" alongside more globally familiar items such as waffles, hotcakes, and hash browns.
By making these strategic adjustments and launching offerings that align with local preferences, McDonald’s has maintained its global image while resonating with various local cultures. This balance between global branding and local adaptation contributes significantly to McDonald's global success. As of 2017, McDonald’s stands as the world’s leading global foodservice retailer, with more than 36,000 locations in over 100 countries. Furthermore, over 80 percent of McDonald’s restaurants worldwide are owned and operated by independent local businesspeople.
Case Study: The Star of Social Media ~ Starbucks
My Starbucks Idea (MSI):
Starbucks maintains a blog called My Starbucks Idea (MSI) where it not only connects with customers but also co-creates the company's future with them.
Customers on MSI can share ideas, vote on ideas suggested by others, discuss ideas with fellow customers, and view the ideas that Starbucks has already announced.
Starbucks' Idea Partners from various departments within the company actively participate in the blog, answering queries and providing insights to discussions.
The brand takes customer suggestions seriously and publishes implemented suggestions for all to see.
To encourage customer feedback, Starbucks offers online incentives in the form of virtual vouchers or purchase points, allowing for interaction with loyal customers.
The blog also includes qualitative and quantitative survey questions to gather marketing research data.
Impact of MSI:
On average, one in three suggestions on MSI is implemented, showcasing the influence of customer feedback.
Starbucks acknowledges and comments on all suggestions within an hour of posting, with an average of four suggestions made every hour.
Starbucks leverages its Facebook page, which has more than 36 million fans, to promote new products and gather customer feedback.
Starbucks uses its Facebook page to organize events and invite customers to attend, featuring photos from its products and events uploaded by fans.
Frequent updates on the page receive substantial user responses, and Starbucks actively engages with followers by commenting on their posts and photo tags.
Starbucks uses Twitter to update customers about new products and services through short messages and encourages users to retweet these updates.
Starbucks' Twitter account often directs followers to MSI for polls, surveys, or opinions.
Other Forms of Social Media:
Starbucks employs various other forms of social media to enhance its service and customer engagement.
Social media has helped Starbucks address recurring customer requests, such as offering free wireless internet.
Starbucks has used social media to introduce new products, including a fruit-infused drink, in response to customer suggestions.
Starbucks' social media presence spans more than 70 countries and continues to expand.
Starbucks' effective use of social media platforms like MSI, Facebook, and Twitter highlights its commitment to engaging with customers, listening to their suggestions, and co-creating products and services to meet their needs.
Mobile Marketing Research (MMR)
Definition:
MMR refers to marketing research, like surveys, conducted or administered on mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, phablets, and IoT devices.
Opportunities of MMR:
The rapid growth of mobile device usage and social media presents significant opportunities for MMR.
Nearly 60% of people in the United States use cell phones as their primary means of communication.
Globally, there are over 2 billion smartphone users, with a majority of their time spent in mobile apps.
Mobile Internet usage has surpassed desktop usage.
Conducting MMR:
MMR can be conducted through international survey platforms, mobile services of access panels, or specialist providers.
Platforms include Confirmit, Research Now, MobileMeasure, and Locately.
Advantages of MMR:
Offers reach, scale, and affordability similar to traditional research methods.
Potential for reaching a broader audience, obtaining faster results, reducing costs, and collecting high-quality responses.
Respondents can answer at their convenience on user-friendly interfaces.
Location technologies, like GPS, enable surveys to reach target audiences at specific locations.
Effective in developing economies where mobile phones are primary information and communication devices.
Disadvantages of MMR:
Surveys must be concise with typically no more than 15 questions and take less than 15 minutes.
Limited questions and engagement potential compared to other survey modes.
Issues with survey design and respondent engagement.
Challenges with using video in mobile research due to streaming and rendering issues.
Sample representativeness may be a concern since non-mobile device owners are excluded.
Costs for incentives and intensive respondent recruitment may be high.
Respondents may incur costs for mobile Internet usage.
Technical difficulties and issues related to data protection, anonymity, and compatibility.
MMR is unlikely to replace traditional methods but can complement and enhance findings in various projects.
The use of MMR is on the rise due to advances in technology and the increasing use of mobile devices, making it a valuable tool for marketing research, especially in specific situations and target populations.
Case Study: Mobile Platform Helps L'Oréal Launch New Product
Background:
L'Oréal was introducing a new product with a unique formulation and packaging.
They wanted to understand consumer comprehension of its use and application.
Solution:
MobileMeasure (mobile-measure.com) employed its mobile survey platform for data collection.
The study spanned four days and took place in the privacy of consumers' homes.
MobileMeasure gathered media recordings of actual product usage, ensuring noninvasive data collection.
Respondents were instructed to upload photos and videos demonstrating their use of the new product.
Diary entries were required from respondents during the product placement period.
Outcome:
L'Oréal was provided with a comprehensive view of consumers' real product usage.
The data collected included both quantitative and rich qualitative feedback.
The insights gathered through this mobile survey contributed to the successful launch of the new product.
This case exemplifies the power of mobile survey platforms in collecting real-time, actionable data that aids companies like L'Oréal in developing and launching products effectively. Mobile surveys, with their ability to capture visual and textual data, offer an enhanced understanding of consumer behavior.
Ethical Considerations in Marketing Research
Background:
Marketing research often involves commercial, for-profit organizations.
Four primary stakeholders are involved in marketing research: the researcher, the client, the respondent, and the public.
Ethical issues can emerge when the interests of these stakeholders conflict or when responsibilities are not upheld.
Examples of Ethical Issues in Marketing Research
Researcher Conduct:
When researchers don't follow appropriate procedures.
Example: Biased sampling, data manipulation, or dishonest reporting.
Client Misrepresentation:
When clients misrepresent research findings in their advertising.
Example: Exaggerating product benefits based on biased research.
Respondent Rights:
Violations of privacy and consent, especially when collecting sensitive data.
Example: Collecting personal information without informed consent.
Public Interest:
Conflicts between research findings and the public good.
Example: Suppressing research results that reveal harmful product effects.
Resolution:
Ethical dilemmas should ideally be resolved through honorable behavior.
Marketing research associations, like the American Marketing Association, offer codes of conduct to guide ethical behavior and address ethical issues.
Ethical considerations are paramount in marketing research to ensure the integrity and credibility of the research process and protect the rights and interests of all stakeholders involved. Violations of ethical norms can erode trust and credibility in the field.

 Knowt
Knowt