Unit 6 - Energy Resources and Consumption
6.1 Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Resources
Learning Objective
- Identify differences between nonrenewable and renewable energy sources
Renewable v. Non-Renewable
Renewable energy sources CAN be replenished naturally, at or near the rate of consumption
- Depletable renewables can run out if over used
- ex. biomass (wood, charcoal, ethanol)
- Nondepletable renewables do not run out if overused
- ex. solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal
Nonrenewable energy sources CAN’T be easily replaced or regenerated and exist in fixed amounts
- Fossil fuels: fossilized remains of ancient biomass that take millions of years to form
- ex. coal, oil, natural gas
- Nuclear energy is generated from uranium or other radioactive fuels
Rate of Consumption
The rate of consumption is the rate of use of an energy source.
- Must be below or at the rate of regeneration for renewables so to avoid depletion
- Fossil fuels will run out because they’re rate of consumption is faster than their rate of regeneration
PRACTICE FRQ
Explain whether or not biomass is a renewable energy source. Justify your answer.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
This is an explain question so you can answer with either side of the argument as long as you can justify it.
- ex. biomass is a renewable energy source because the fuel source, such as trees/plants/animal waster can be continually regenerated without depletion
- ex. biomass is not a renewable energy source because it can be harvested and used at a rate that is faster than it regenerates, eventually depleting it
- ex. biomass is a potentially renewable energy source, if it is consumed near or below the rate which it regenerates
These are all correct because they sufficiently justify their argument.
6.2 Global Energy Consumption
Learning Objective
- Describe trends in energy consumption
Developed v. Developing Countries
Developed nations use more energy on a per capita (per person) basis, but developed nations use more energy in total because of their higher populations.
- The avg. US resident uses 5x as much energy as the world avg.
Developing nations are still industrializing and their populations are still growing rapidly.
- Their energy consumption will also increase on a per person basis as their economies industrialize and residents achieve higher standards of living
Most Used Energy Sources
Fossil fuels are by far the most common fuel source globally. Its many byproducts have many uses.
- Oil → Gasoline → Main fuel for vehicles
- Coal → Main fuel for electricity generation
- Natural Gas → Secondary fuel for electricity generation and main fuel for heating
Hydroelectric energy (dams used to create electricity) is the second largest energy source.
- Water spins a turbine which generates electricity
Nuclear energy is the third largest source of energy.
- Uranium fission releases hear to turn water into steam to turn a turbine to generate electricity
Increases in Consumption
Development leads to increases in energy consumption. Many residents of less developed nations depend on subsistence fuels
- biomass that they can easily gather/purchase
- ex. wood, charcoal, dried animal manure
- can drive deforestation
Economic development → affluence (wealth) → higher per capita GDP → energy use
- As developing nations develop, fossil fuel consumption will increase
- Oil → Gas for vehicles
- Coal & Natural Gas → electricity
- electricity demand for homes and manufacturing will increase
Factors that Affect Energy Source Use
Availability: Fossil fuel use depends on discovered reserves and accessibility of these reserves
- use of fossil fuels varies heavily with availability
Price: Fossil fuel prices fluctuate dramatically wit discovery of new reserves or depletion of existing ones
- Fracking opens new natural gas reserves, increasing availability, decreasing price, increasing use
Government Regulation: government can mandate certain energy source mixes
- ex. 25% renewable by 2025
They CANNOT directly raise or lower prices of energy sources
- ex. raise gas to $10/gallon
They CAN use different strategies to discourage or encourage certain energy usage
- ex. increase taxes to discourage companies from building fossil fuel power plants
- ex. rebates or tax credits to encourage companies building renewable energy power plants
PRACTICE FRQ
From 2005 to 2018, the annual investment in renewable energy sources in the United States increased from $11.4 billion to $46.5 billion. Calculate the percent change in renewable energy investment in the US from 2005 to 2018.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
This kind of question is worth 2 points. 1 for the correct setup and another for the correct answer with the correct units. To calculate percent change you do:
(Old number - New Number)/New Number x 100
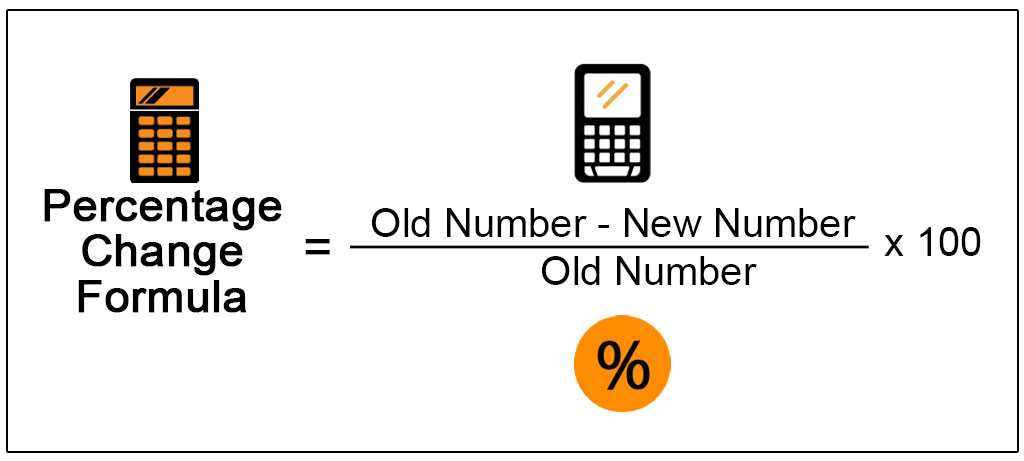
- ex. (46.5 x 10^9 - 11.4 x 10^9)/11.4 x 10^9 x 100 = 307.9% increase
Experts estimate that for the US to reach 100% renewable energy in 2050, it will require $7.8 trillion. Calculate the percent change this would represent from the 2018 investment level of $46.5 billion.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
This kind of question is worth 2 points. 1 for the correct setup and another for the correct answer with the correct units. See picture above for how to do percent change.
- ex. (7.8x10^12 - 46.5 x 10^9)/46.5 x 10^9 x 100 = 16,674% increase
6.3 Fuel Types and Uses
Learning Objective
- Identify types of fuels and their uses
Subsistence Fuels
Subsistence fuels are biomass fuel sources that are easily accessible (can be found and gathered by hand). These are often used in developing countries as a home heating or cooking fuel.
- Wood and charcoal are two of the most common fuel sources in developing nations
- Wood is free/cheap to cut down and utilize as fuel
- can cause deforestation and habitat loss
- Charcoal is made by heating wood under low oxygen conditions for a long time
- Peat is another common fuel source that can be dried and used as a biomass fuel source
- Peat is partially decomposed organic matter (often ferns or other plants) found in wet, acidic, ecosystems like bogs and moors
Coal Formation
Coal is a common nonrenewable energy source. It formed by pressure from overlying rock and sediment layers which compact peat into coal over time.
There are also different types or “ranks” of coal. These are ranked in order of density, quality, and carbon content.
In order from highest to lowest
Anthracite → Bituminous → Lignite
- the deeper a coal reserve is buried, the more pressure from overlying rock layers and the energy becomes more dense
Because higher energy density means more energy released upon burning of the fuel source, anthracite is the most valuable form of coal.
How does it generate energy?
- Coal is burned to heat water into steam which turns a turbine that generates electricity
More dense coal → hotter/longer fire → more steam → more electricity
Note: The US is proven to have the largest coal reserves
Natural Gas
Decaying remains of plants and animals (mostly marine life) are buried under layers of rock and converted by pressure into oil (petroleum) and natural gas over time.
Natural Gas is mostly methane (CH4) and is found on top of trapped oil (petroleum) deposits
- forms when oil is trapped in a porous, sedimentary rock, underneath a harder, impermeable rock layer that doesn’t let the gas escape
Natural Gas is also considered the cleanest of the fossil fuels since it produces the fewest air pollutants and the least amount of CO2 when burned)
- produces about half as much CO2 as coal when burned
- produces virtually no particulate matter (ash/soot)
- produces far less SOX, NOX, than coal or oil and NO MERCURY
Crude Oil (Petroleum)
Crude oil is decaying organic matter that is trapped under rock layers and compressed into oil over a long period of time.
It is extracted by drilling a well through the overlying rock layers to reach the underground deposit and then pumping liquid oil out under pressure. It can also be recovered from tar sands (combination of clay, sand, water, and bitumen).
- Bitumen is a thick, stick, semi-solid form of petroleum (not liquid)
Note:
- Extracting and using oil from tar sands is extremely energy and water intensive.
- Lots of water needs to be heated (requiring energy) to create steam that’s piped down into the tar sand to melt the bitumen into a liquid that can flow up a pipe.
- Lots more water is used to separate the oil from all of the impurities (sand, clay) at the refinery.
Saudi Arabia has been the largest exporter for the past 4 decades.
Fossil Fuel Products
Crude Oil (petroleum) is converted into lots of different products through the process of fractional distillation.
In order to make its byproducts, crude oil is burned in a furnace and vapor passes into a column where different hydrocarbons are separated based on their boiling points.
Hydrocarbons with lower boiling points gather at the top of the column while higher boiling points gather at the bottom.
Different hydrocarbons are used for different products such as:
- petroleum gas
- gasoline (fuel for cars - 20lbs of CO2 released per gallon)
- Naptha (used to make plastic)
- Jet Fuel
- diesel fuel
- motor oil
- bitumen (asphalt for roads)
PRACTICE FRQ
Natural gas is considered to be a better fossil fuel for the environment than coal is. Explain two environmental benefits of using natural gas as a fuel compared to using coal.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
This is another explain question, so you have to make a valid argument and justify it. For this question in particular the benefits in your argument have to be environmental not economic.
- ex. fewer SOX produced, less acid rain as a result
- ex. fewer NOX produced, less acid rain and less photochemical smog
- ex. Harmful mining techniques are avoided so less environmental damage
- ex. fewer particulates released (soot) must connect this to an environmental problem caused by particulate matter
- less CO2 produced must connect CO2 to an environmental problem
6.4 Distribution of Natural Energy Resources
Learning Objective
- Identify where natural energy resources occur
Fossil Fuel Reserves
Coal ~100-150 years
- US
- Russia
- China
- Australia
Natural Gas ~50-60 years
- Russia
- Iran
- Qatar
- US
- Saudi Arabia
Crude Oil and Petroleum Products ~50 years
- Venezuela
- Saudi Arabia
- Iran
- Canada
- Iraq
Fracking and Shale Gas
Hydraulic fracturing otherwise known as fracking is a method of natural gas extraction that has extended access to natural gas.
- Fracking natural gas from shale rock increases and extends supply of natural gas
Shale Gas Reserves
Fossil fuels are non-renewable and will eventually run out but short-term economic profit still drives its extraction and use.
- discovered but unharvested reserves represent economic benefits to countries
Tar Sands
Tar sands are bitumen deposits where crude oil can be recovered but with higher water and energy inputs.
- Just like fracking, tar sands extraction extends the world’s supply of crude oil
Canada (Alberta region) is the world’s largest tar sands reserve.
PRACTICE FRQ
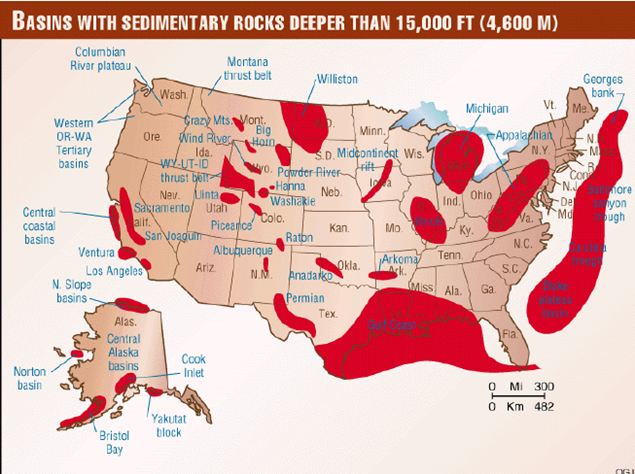
Identify a region of the United States that is likely to be a large producer of natural gas.
Describe the geological features associated with natural gas reserves.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
This question has two parts each worth 1 point. The first point for identifying any of the correct regions.
- ex. southern Alabama/Mississippi/Texas/Alaska/Michigan/Louisiana/West Virginia/Pennsylvania/Western California/North Dakota/Wyoming/Gulf-coast Region/Midwest Region
The second point is for describing the geological features associated with natural gas reserves.
- ex. natural gas forms in areas where sedimentary rock is found beneath an impermeable rock layer above
- ex. natural gas is found in semi-permeable sedimentary rock layers such as shale
- ex. natural gas is found trapped in the cracks/space of semi-permeable sedimentary rock layers
6.5 Fossil Fuels
Learning Objective
- Describe the use and methods of fossil fuels in power generation.
- Describe the effects of fossil fuels on the environment.
Fossil Fuel Combustion
Reaction between oxygen (O2) and fossil fuels (hydrocarbons) that releases energy as heat and produces CO2 and H2O as products.
Remember: Combustion is a step in the CARBON cycle. Hydrocarbons (fossil fuels) are burned to release energy and the carbon stored in them reacts with O2 in the air to form CO2
- Methane (natural gas), gasoline, propane, butane, coal are all fossil fuels (hydrocarbons) that release energy in the same way
- Wood and biomass work the same, carbon is burned and reacts with O2 to form CO2 and give off energy
Fossil Fuels to Generate Electricity
- The #1 source of electricity production globally is coal, followed by natural gas
The steps of electricity generation are the same no matter what you’re burning to produce the initial heat.
Heat → Water into Steam → Steams turns a turbine → Turbine powers generator → Generator produces electricity
Coal, oil, natural gas, biomass, and trash can all be burned to drive this same process and create energy. Even nuclear energy works similarly with nuclear fission producing the initial heat.
Environmental Consequences: Coal
Coal and its extraction cause habitat destruction to clear land for mining and produces pollutants and releases CO2. (Greenhouse gas → Global Warming)
- Releases more CO2 than any other fossil fuels when burned for electricity generation
- Releases particulate matter (soot, ash) which can irritate respiratory tracts of humans/animals
- produces toxic ash contaminated with lead, mercury, and arsenic
- taken to landfills or stored in ash ponds, both can leak into ground/surface waters or into soil
- releases SOX and NOX (sulfur and nitrogen) which irritates respiratory systems and contribute to smog and acid rain
Generating Energy
Coal is ~30% efficient as a fuel source for generating electricity (30% of energy from the bonds in the hydrocarbon are converted to electricity)
- Natural gas is ~60% efficient when it’s burned to generate electricity
Much of the energy “lost” or not converted into electricity escapes as heat
Cogeneration: when the heat produced from the electricity generation is used to provide heat (air and hot water) to a building
- CHP (Combined Heat and Power) systems are close to 90% efficient (much better than coal/natural gas alone)
Oil/Petroleum Extraction
Extracted by drilling a well through the overlying rock layers to reach the underground deposit and then pumping liquid oil under pressure.
Can also be recovered from tar sands.
Environmental Consequences: Tar Sands
- Habitat destruction to clear land for roads, drilling equipment, digging through ground surface to reach deposits (biodiversity loss)
- Ground or nearby surface water depletion (H2O needed for steam and for washing impurities from bitumen and refinery)
- Water Contamination: tailing ponds (holes dug for storing wastewater) can overflow and run into nearby surface waters, or leach into ground water
- benzene (carcinogen) salts, acids, hydrocarbons, bitumen
- all toxic to plant and animals
- CO2 released by machinery during extraction, transport, refinement
Environmental Consequences: Crude Oil/Petroleum
Possibility of spill (either from tanker ships or pipelines breaking)
- spills in water = crude oil covering sun, clogging fish gills, suffocating many ocean animals, sticking to bird feathers
- spills on land = toxic to plant roots, surface or ground water contamination (with hydrocarbons/crude oil)
Habitat loss or fragmentation when land is cleared for roads, drilling equipment, and pipelines
Fracking (Hydraulic Fracturing)
Used to extract natural gas from sedimentary rock
Vertical well is drilled down to sedimentary rock layer, then turns horizontally into the rock layer
- Perforating gun cracks (fractures) the rock layer around horizontal wells, making it more permeable
- Fracking fluid (water, salt, detergents, acids) is pumped into well at very high pressure to crack the rock even more and allow natural gas to flow out
- natural gas is collected at surface and shipped for processing/use
- flowback water (used fracking fluid) flows back out well and is collected and stored in containers or ponds nearby
Environmental Consequences: Fracking
Habitat loss and fragmentation, CH4 release
Possibility of well leaking and contaminating groundwater with fracking fluid (salt, detergent, acids) or hydrocarbons
- ponds can overflow or leach into ground and contaminate surface or ground waters with fracking fluid (salt, detergent, acids)
- can be toxic to plants and animals that rely on these water sources
Depletion of ground or surface waters nearby (as they’re drawn from for fracking fluid)
- Increased seismic activity (earthquakes) linked with wastewater injection wells (storing fracking fluid deep underground)
PRACTICE FRQ
Explain one environmental consequence of tar sands petroleum extraction.
Explain a different environmental consequence of hydraulic fracturing.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
This question has two points up for grabs. This is the criteria to get those points.
a. 1 pt. for any of the following explanations
- Large volume of water required for tar sands petroleum extraction can lead to \n depletion of nearby surface or groundwater sources
- Tar sands petroleum extraction results in more CO2 emissions than standard \n petroleum extraction, contributing further to climate change/global warming
- Tar sand petroleum extraction can lead to habitat destruction as nearby land is cleared \n for mining/transport roads
b. 1 pt. for explaining a different consequence than in part (a)
- Fracking fluids can leak from pipe/well and contaminate groundwater sources with methane/salt/benzene/detergents/acids
- Used fracking fluid can leak or overflow from tailing ponds, contaminating surface or groundwater with salt/benzene/detergents/acids
- Large volume of water required for fracking can lead to depletion of nearby surface or groundwater sources.
6.6 Nuclear Energy
Learning Objective
- Describe the use of nuclear energy in power generation
- Describe the effects of the use of nuclear energy on the environment
Nuclear Fission and Radioactivity
A neutron is fired into the nucleus of a radioactive (unstable) element, such as Uranium.
- Nucleus breaks apart and releases lots of energy (heat) + more neutrons that break more nuclei apart, releasing more energy (chain reaction)
Radioactivity refers to the energy given off by the nucleus of a radioactive isotope (Uranium-235)
- Radioactive nuclei decay, or breakdown and give off energy (radiation) even without fission; nuclear fission just releases tons of energy all at once
- Radioactive Half-Life = the amount of time it takes for 50% of a radioactive substance to decay (breakdown)
- Ex: 1/2 life of Cobalt-60 isotope = 5.27 yrs.
- In 5.27 yrs. 1/2 of a Co-60 sample would be gone (decayed)
Generating Electricity
Same electricity generation process as with fossil fuels, just uranium fission to heat water into steam.
Heat → Water into Steam → Steams turns a turbine → Turbine powers generator → Generator produces electricity
U-235 stored in fuel rods, submerged in water in reaction core; heat from fission turns H2O → steam
- Control rods: lowered into reactor core to absorb neutrons and slow down the reaction, preventing meltdown (explosion)
- Water pumps: brings in cool water to be turned into steam and also cools reactor down from overheating
- Cooling tower: allows steam from turbine to condense back into liquid and cool down before being reused (this gives off H2O vapor)
Nonrenewable but Cleaner
Nuclear energy is nonrenewable because radioactive elements like Uranium are limited. But, nuclear energy is clean than fossil fuels.
- No air pollutants (particulate matter, SOX, NOX) or CO2/CH4 released when electricity is generated; mining of uranium and plant construction still release GHGs
- Only gas released from generating electricity is water vapor
Other drawbacks of nuclear energy include possibility of meltdown and radioactive contamination
- Spent Fuel Rods: used fuel rods remain radioactive for millions of years and need to be stored in lead containers on site at nuclear powerplants
- Mine tailings: leftover rock and soil from mining may have radioactive elements that can contaminate water or soil nearby
- Water Use: nuclear powerplants require lots of water and can deplete local surface or groundwater sources
- Thermal Pollution: hot water from powerplant released back into surface waters can cause thermal shock (decreased O2 and suffocation)
Nuclear Meltdowns
Three Mile Island (US)
- partial meltdown due to testing error, radiation released but no deaths or residual cancer cases
Fukushima (Japan)
- an earthquake and tsunami triggered cooling pump failure that lead to a meltdown (explosion of reactor core) and widespread radiation release
Chernobyl (Ukraine)
- stuck cooling valve during test lead to complete meltdown (explosion of reactor core), several deaths, and widespread radiation release
These are the 3 most famous nuclear meltdowns.
Environmental Consequences: Nuclear Energy
Genetic mutations and cancer in surrounding people, animals, and plants due to radiation released from reactor core
- Contaminated soil: radiation can remain in soil and harm plants and animals in the future (genetic mutations)
- Radiation Spread: radiation can be carried by the wind over long distances, affecting ecosystems far from the meltdown site
PRACTICE FRQ
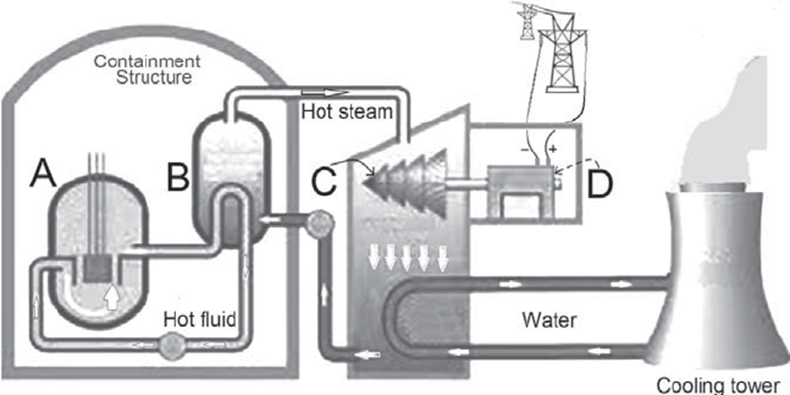
Identify and describe one letter in the diagram that is common to both nuclear and fossil fuel electricity production. Identify and describe one letter in the diagram that is found ONLY in nuclear power plants.
HOW TO GET RIGHT
a) 1 pt. for any of the following
- Structure B is a boiler/steam generator where water is heated into \n steam
- Structure C is a turbine that is spun/turned/rotated by steam
- Structure D is a generator/electric generator that produces electricity \n when powered/turned/driven by a turbine
b) Only letter A may earn points in part (b)
- Structure A is a nuclear reactor/reactor core/nuclear fuel rod(s) where uranium or other radioactive elements undergo fission and release heat/energy