Neuro Midterm Study Guide
Midterm Study Guide Fall 2023
SLP 5152 Clinical Neuroscience for Speech Language Pathology
1. Exam is made up of: 35 Questions overall: 4 Matching, 4 True/False, 26 Multiple Choice, and 1 Ranking/Ordering
2. You should study your draw it to know it labeling of anatomy!
Practice Labeling Printed Pictures
3. Review Ch. 3 and describe how neuronal development occurs.
All 6 phases and General idea of the sequence
4. How is the CNS developed and form what structure?
- CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- The brain is made up of 4 structures:
1. Brainstem – controls basic life functions ex: heartbeat, breathing
- Medulla
- Pons
- Midbrain
2. Cerebellum – coordination and precision of fine motor movement
3. Diencephalon
- Thalamus – relay station for sensory fibers
- Subthalamus – regulates and coordinates motor function.
- Hypothalamus – regulates body functions ex: temperature.
- Epithalamus – regulates genital development, sleep-wake cycle, and optic reflexes.
4. Cerebral Hemispheres – control higher cortical functions ex: cognition and language, planning and motor function
and interpreting sensory experiences.
5. What are the different forms of Glial Cells in chapter 4. (p. 67)
Astrocytes, Oligodendrogilia and Schwannn cells, Microglia, and Satellite cells? IS it involved with the CNS or involved in the PNS
6. Terms you should know: Define and describe the following (include being able to identify if applicable and describe the function/role):
a. Ventricles What is the functions of the ventricles? Do we need to know disorders of the ventricles? What they do and what they might supply
4 ventricles:
- First and Second are Right and Left - look like horseshoes
- Third - like a misshaped donut
- Fourth - like a diamond
b. Lobes of the brain
- Frontal Lobe - Cognitive functions (ex: reasoning), speech, and expressive language
- Parietal Lobe - Touch perception and interpretation
- Temporal Lobe - Receptive language and long-term memory
- Occipital Lobe - Visual perception and interpretation
c. The different parts of the brainstem (for Ex. Midbrain, Pons, Medulla)
d. Prefrontal Cortex
- Functions of the prefrontal cortex include cognition (executive control), personality, decision making, social behavior, self-awareness, planning, problem solving. Plays role in behavior, memory and judgment. Connected to Association cortices of other lobes, Hypothalamus, Medial Thalamus, Amygdala. Receives information regarding sensation, motivation, and emotion through these connections. Integration of info from connections leads to development of goal-oriented behavior
- Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC)
- Cognitive Association Cortex. Motivation, executive function, monitoring, response selection and inhibition. Control of Executive Functions: Attention, Working Memory, Set-Shifting, Planning Organizing, Problem Solving, Decision-Making. Language Functions: 1. Regulating spontaneous speech narrative discourse and verbal fluency. 2. Bilinguals: May aid in resolving conflicts from language inteference and to inhibit the language not being used.
- Orbitofrontal Prefrontal Cortex (OFC)
- Learning and decision making, Judgement for reward/punishment, Adaptive learning, Regulate social behavior - inhibiting socially inappropriate responses (aggression, sexual behavior), Reward value of stimuli - determine emotional value of information, Impulse control and response inhibition- inhibit or facilitate actions triggered by drives and appetites.
- Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex (VLPFC)
- Involved in judgement, emotion suppression, dual-tasking, and conflict resolution. Important in working and episodic memory - encodes and retrived memories for tasks, judgments, and making decisions. Role in motor inhibition (ex: stopping suddenly in traffic)
e. Neuropathology - The study of nervous system diseases
f. Neuroanatomy - The study of nervous system’s structure
g. Neurophysiology - The study of how neurons function
h. Anatomy - The study of structure
What more should we know about these fibers? (p. 160)
i. Projection Fibers
- The 1st of 4 basic fiber connections for communication in the cerebral hemispheres
- Project from the cerebral cortex to subcortical structures.
j. Commissure Fibers Did you mean Callosal Fibers????? And thalamocortical fibers
k. Association Fibers.
- The 3rd basic fiber
- Connect cortical structures in the same hemisphere.
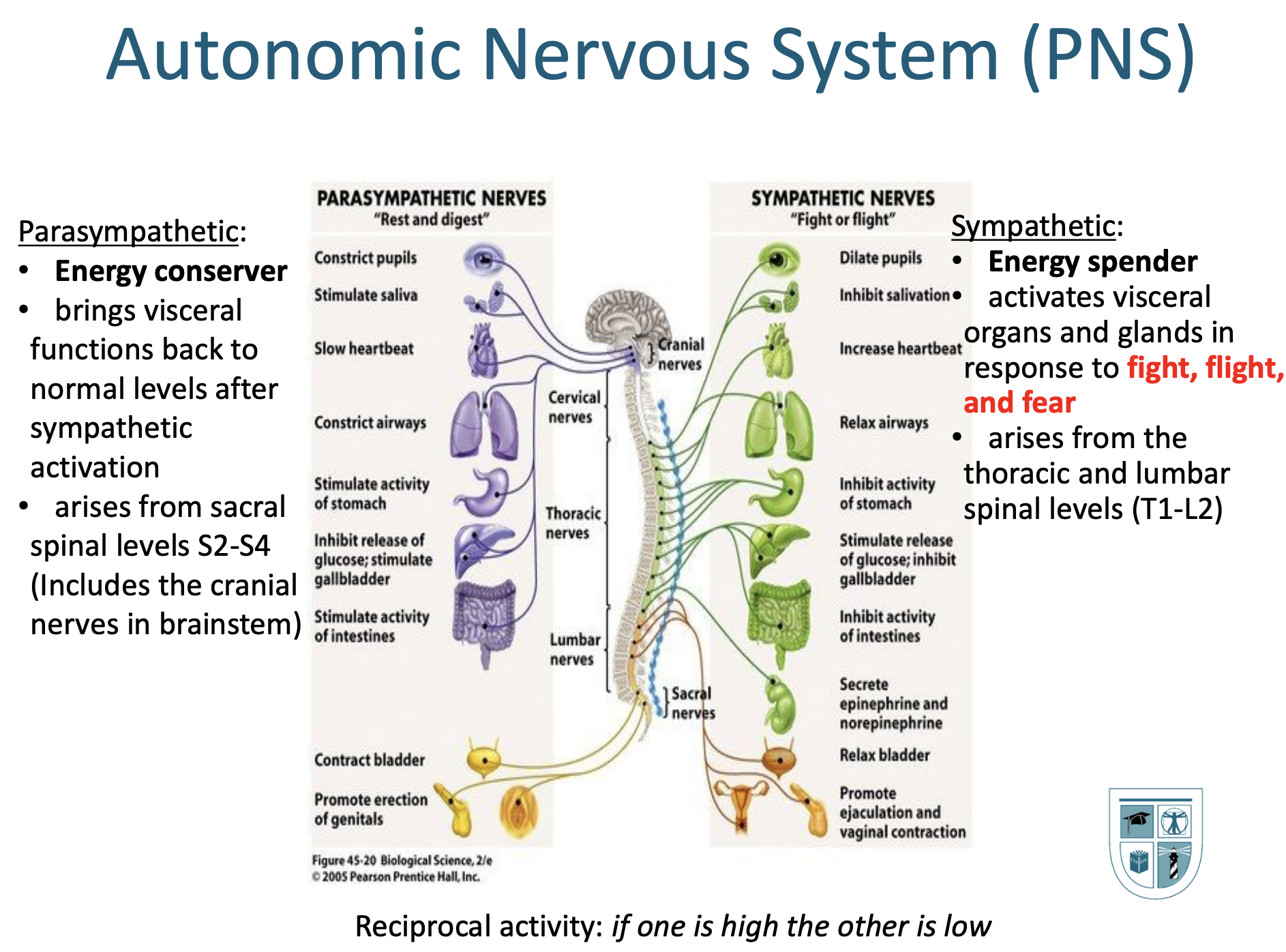
l. The CNS vs. the PNS Do you want us to know the parasympathetic features vs. the sympathetic? The picture from the powerpoint? Know pic and recognized which goes with which nervous system.
m. Cerebral Spinal Fluid
- Located in all ventricles and found in the subarachnoid space of the meninges
- The Choroid plexus (structure located in each ventricle) produces CSF each day
- Moves between ventricles via the interventricular foramen and the cerebral aqueduct.
- 4 Major functions:
- Functions as a water cushion for protection
- Lightens the weight of the brain
- Reduces waste by removing metabolic waste from nervous system
- Helps transport nutrients and hormones to the brain
n. Posterior Cerebral Artery – what part of the brain does it supply and what is that responsible for?
o. Anterior Cerebral Artery - what part of the brain does it supply and what is that responsible for?
p. Middle Cerebral Artery - what part of the brain does it supply and what is that responsible for?
q. Central Nervous System
r. Peripheral Nervous System
7. Know the types of cerebral vascular accidents. Describe a Transient Ischemic Attack and what makes it different than a CVA), Ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic.
8. Know the directional terms
Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
Sagittal | Right and Left (Lateral) | Cut Apple |
Coronal | Front and Back (Frontal) | Sliced Bread |
Transverse | Upper and Lower (Horizontal) | Hamburger Layers |
Superior (or cranial) | From a high position | The brain is superior to the heart. |
Inferior (or caudal) | From a low position | The heart is inferior to the brain. |
Anterior (or ventral) | Toward the stomach | The sternum is anterior to the heart. |
Posterior (or dorsal) | Toward the back | The spine is posterior to the stomach. |
Medial | Toward the body’s midline | The heart is medial to the ribs. |
Lateral | Away from the body’s midline | The ribs are lateral to the heart. |
Proximal | Point nearest limb’s attachment | The shoulder is proximal to the elbow. |
Distal | Point farthest from limb’s attachment | The ankle is distal to the knee. |
Peripheral | Toward the outer surface | The cell’s wall is peripheral. |
Central | Toward the center | The cell’s nucleus is central |
Ipsilateral | Same side | Canadians drive ipsilateral as Americans |
Contralateral | Opposite side | Brits drive contralateral to Americans |
9. Know your Cranial Nerves (by Roman Numeral – CN I, CN II and so on) and the role of each nerve.
10. Review your Neuron Table – know your neuron structures and generally what each is structure is responsible for in the Action Potential process ???????? know parts of neuron and be able to label it and what do the dendrites do? what do the axons do, ect. Know the general roles and understand the idea of action potential. What sparks? what keeps it going? where does the signal come together?
Part of the Neuron: Primary Function: Action Potential Involvement
- Dendrites Receives signals and pass them toward the cell body Chemical transmission occurs
- Nucleus Part of the cell that contains DNA which is the genetic code that regulates the maintenance of the cell and production of new cells Keeps the cell alive and active
- Cell body (soma) Maintains the neuron’s structure, contains the nucleus and other important structures, provides energy Chemical transmission occurs
- Axon Sends signals away from cell body Chemical transmission occurs
- Nodes of Ranvier Helps to facilitate the propagation of electrical signals down the axon due to the signal jumping from one node to the next. - Small molecular ion gates open when neurotransmitters attach - Opening of gates causes sodium to rapidly and passively transport into the neuron - Sudden change in polarity triggers action potential - Where depolarization occurs
- Myelin sheaths Covers axons and aids in neural transmission Speeds up action potential
- Axon hillock Controls initiation of electrical impulse based on inputs from other neurons or environment Action potential initiated here
- Vesicles Hold neurotransmitters until stimulated to release them Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles and received by the correlating neuron
- Terminal buttons Sends signal to other neurons Once it reaches the end of the axon, the action potential signals the terminal buttons to release neurotransmitters
11. Be familiar with the layers of the meninges.
Afferent transports TO CNS efferent goes OUT