AP Biology - Evolution Chapter 22-26
Notes of things I don’t understand….
Chapter 24.3 - Hybrid Zones
When species with incomplete reproductive barriers come into contact with each other, they could form a hybrid zone.
Can lead to hybridization when they breed
1) Reinforcement of Barriers: Hybrids are less fit than their parent species and natural selection will strengthen barriers to reproduction
Barriers stronger in sympatric populations than allopatric populations
2) Fusion of Species (Weakens Reproductive Barriers): the 2 species mate and form hybrids and the hybridizing species will fuse into a single species
Some much gene low occurs that the gene pools of both species become increasingly alike
3) Stability: Hybrids continue to be produced because the hybrids survive or reproduce better than the parent species
Stability can also happen even when Hybrids are selected against
Chapter 25.5 - Molecular
Evo-Devo: slight genetic differences can produce major morphological differences between species
Genes that alter rate, timing, and Spatial pattern
Heterochrony: evolutionary change in the rate or timing of developmental events
Relative growth rates of different body parts —> changes can alter the adult form
Increased growth rates of finger bones led to the wings of bats, slowed growth of bones led to the loss of hind limbs in whales
Paedomorphosis: development of reproductive organs are greater than that of other organs
Causes the production of animals that look different from their ancestors
Changes in Spatial Pattern
Master Regulatory Genes (Homeotic Genes) - where basic features will develop
Hox genes - provide positional info
Changing locations of Hox genes/how they are expressed can lead to changes in morphology
Changing in Gene Sequence
New genes arise after gene duplication events
Altering the expression of a developmental gene
Changes in Gene Regulation
May have fewer harmful side effects than a change to the sequence of the gene
Stickleback fish
Phylogenics vs. Cladistics
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history and can be represented by a phylogenetic tree
A clade is a type of phylogenetic tree. It is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all of its descendants
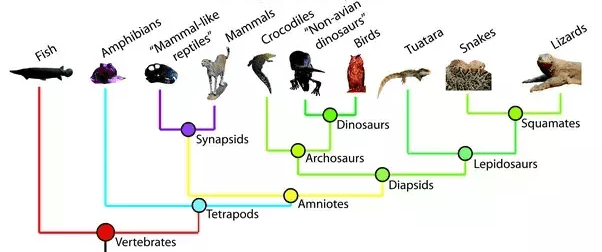
Cladistics is a way to compare traits in related species to determine ancestor-descendant relationships

Chapter 25.1 - Conditions for the Origin of Life
Produce simple cells through 4 main stages
1) The abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules like amino acids and nitrogenous bases
2) The joining of the small molecules into macromolecules, like proteins and nucleic acids
3) The packaging of these molecules into protocells (droplets with membranes that have a different internal chemistry from the surroundings)
4) the origin of self-replicating RNA that made inheritance possible
The Abiotic Synthesis of small organic molecules
First atmosphere had little oxygen, lots of water vapor and compounds released by volcanic eruptions. The cooling of Earth caused the water vapor to condense into oceans and a lot of the hydrogen escaped into space
Oparin and Haldane: Earth’s early atmosphere was a reducing/electron-adding environment and the energy came from lightning and UV radiation. The ocea was a solution of organic molecules/”Primitive soup”
Millery and Urey: recreated early conditions of life and create amino acids
Organic compounds could have been formed in hydrothermal vents/alkaline vents or brought to earth by meteorites
The Abiotic Synthesis of macromolecules
Synthesis of RNA monomers from precursor molecules.
Dripping solutions of amino acids/RNA nucleotides onto hot sand/clay/rock could produce polymers
Protocells
DNA replication needs a supply of nucleotide building blocks and enzymes. The necessary conditions may have been met in vesicles (fluid-filled compartments enclosed by membrane-like structure)
Abiotically produced vesicles can have simple reproduction and metabolism, and maintain and internal chemical environment
Vesicles can form when lipids are added to water and adding things like montmorillonite can increase the rate of vesicle self-assembly.
Self-Replicating RNA
RNA was mostly likely the first genetic material
Can take on a variety of 3D shapes
Can act as a catalyst - Ribozyme
Learning Module:
In order for speciation to occur, gene flow between populations must be interrupted.
One species with a diploid number of 6 and another with a diploid number of 12 —> come together and form a hybrid with a diploid number of 18 (haploid numer of 9 —> 6/2 + 12/2)
Morphological species concept distinguishes species by body shape and other structural features
Gene flow does not contribute to allopatric speciation because allopatric speciation requires interrupted gene flow
Biological species concept: a species is a group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable, fertile
Mechanical Isolation prevents individuals of closely related species from copopulating successfully
It is clear that speciation has occurred when the gene pool changes establish reproductive barriers between two populations
After the Permian and Cretaceous mass extinctions, the percentage of marine organisms that were predators increased
Geological Eras: Paleozoic ,Mesozoic, Cenozoic
Genetic Drift does not contribute to adaptive radiations
Vesicles are an internal structure that appears in eukaryotic cells and were present in more ancient prokaryotic cells.
The known fossil record is biased in favor of species that existed for a long time
In order for life to evolve on land, there had to be adaptations that facilitated the reproduction and the prevention of dehydration
Neutral Theory: Darwinian selection does not influence a lot of evolutionary change in genes and proteins because many of these changes to not effect fitness
Systematics is a discipline within taxonomy (the scientific naming and classification of organisms)
Systematics: classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationships
Horizontal gene transfer can occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Genes are transferred from one genome to another through exchanging transposable elements/plasmids, viral infection, and fusions of organisms
Using molecules as clocks to time evolutionary events
Nucleotide substitutions in a gene occur at a relatively constant rate
Orthologous genes: a gene in different species that evolved from a common ancestor by speciation (similar genes in different species)
The more differences between genes, the longer ago the species diverges
Paralogous genes: genes present in a particular organism that are related to each other through a gene duplication event (related genes within the same organism)
mtDNA to explore more evolutionary events
Sister taxa on a phylogenetic tree are defined as groups that share an immediate common ancestor and are each other’s closest relatives
An outgroup is a species or group of species from an evolutionary lineage that is known to have diverged before the lineage that includes all the species under study (the ingroup).
Polytony: A branch point on a phylogeny from which more than 2 descendant groups emerge
Phylogenetic trees are constructed to reflect the evolutionary relationships among organisms