respiratory system for leen 😙
Function: The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, in the body.

inhalation/exhalation respiratory system:
Inhalation (Breathing In):
The diaphragm contracts (moves downwards).
The intercostal muscles (between ribs) also contract, expanding the rib cage.
The chest cavity increases in volume.
Air pressure inside the lungs decreases (becomes lower than outside air).
Air rushes in through the nose/mouth → trachea → bronchi → lungs → alveoli.
💨 Oxygen enters the body during this process.
Exhalation (Breathing Out):
The diaphragm relaxes (moves upward).
The intercostal muscles relax, and the rib cage moves down and in.
The chest cavity decreases in volume.
Air pressure inside the lungs increases (becomes higher than outside).
Air is pushed out from the lungs → bronchi → trachea → nose/mouth.
💨 Carbon dioxide is removed from the body during this process.
🫁 Structures and Their Functions
Structure | Function |
|---|---|
Nose / Nasal cavity | Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air using hairs and mucus |
Pharynx | Passage for air from the nose to the larynx |
Larynx (Voice box) | Contains vocal cords; also protects the trachea from food entering |
Trachea (Windpipe) | A tube that carries air to and from the lungs |
Bronchi | Two main branches from the trachea that lead to each lung |
Bronchioles | Smaller branches of the bronchi inside the lungs |
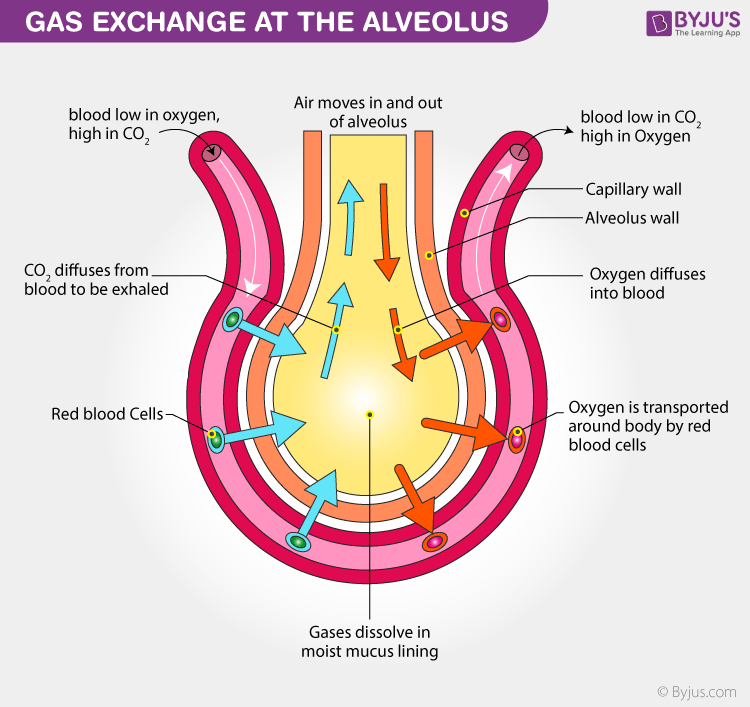
Alveoli | Tiny air sacs where gas exchange happens (O₂ in, CO₂ out) |
Diaphragm | Dome-shaped muscle that controls breathing by contracting and relaxing |
Intercostal Muscles | Help expand and contract the rib cage during breathing |
Lungs | Main organs where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released |
🫁 Adaptations of Alveoli
Adaptation | How it Helps |
|---|---|
Large surface area | Increases space for oxygen and carbon dioxide to exchange |
Thin walls (one cell thick) | Allows quick diffusion of gases (short distance to travel) |
Surrounded by capillaries | Easy access to blood for oxygen to enter and CO₂ to leave |
Moist lining | Gases dissolve in moisture, which helps them diffuse more easily |
Elastic walls | Expand and recoil to help push air in and out during breathing |
Rich blood supply | Maintains a strong concentration gradient for continuous gas exchange |