
Unit 3 (Internationalism)
Incentives vs Sanctions
Incentives- offering closer relations, if certain conditions are met
Sanctions- Cutting off relations(trade) until the hostile “problematic behaviour” of a certain state stops
Incentives
Generally, when countries that receive help become economically successful and self- sufficient, the world can become a safer place
When economically unstable nation-states are offered trade opportunities, or opportunities to become more economically stable, they can be more inclined to cease actions that are viewed a problematic to other countries(for example, human rights abuse)
Sanctions
Countries try to promote peace in other countries by imposing economic sanctions
This includes cutting off trade and other economic ties with a country with efforts to force them to follow a particular behaviour
It is viewed as a more favourable alternative to harsher measures (such as declaring war)
Can be not as effective if other countries continue to trade with “problematic” nation-states
Also seen as more harmful to citizens rather than the government
Questions
What are your thoughts on sanctions?
Do you believe they help to promote peace?
Are sanctions ethical?
Peacekeeping
Peacekeepers are sent to conflict zones only after a ceasefire has been negotiated
Peacekeepers then set up a buffer zone (Area where no fighting occurs)
Peacekeepers protect humanitarian workers who provide food, shelter and medical aid
They are ONLY allowed to use force in self defense
**Peacekeepers MUST follow these guidelines:
- Consent: Respecting the sovereignty of the host country
Impartiality: Peacekeepers must not take sides
Self-defense: Peacekeepers may use force only to defend themselves
Questions
What are your thoughts on Peacekeeping?
Do you believe they help to promote peace?
What are some cons with peacekeeping?
Questioning the Role of Peacekeeping
**Sometimes problems do occur with peacekeeping:
Opposing sides may start to fight again, with peacekeepers in the middle of conflict
Peacekeepers can sometimes be attacked
Diplomats may not be able to reach a resolution, causing peacekeepers to stay indefinitely
Opposing sides sometimes start killing civilians, peacekeepers are to stay out of it
In the 1990s several peacekeeping mission failures caused people to question its effectiveness as a foreign policy tool
This resulted in the belief that peacemaking is more effective than peacekeeping
Peacemaking: Ending armed conflict and human rights abuses
Peacemakers are not required to remain neutral. They may shoot to kill and enter a country without being invited
Questions
If you were a peacekeeper, which aspect do you think you would find hardest?
Respecting the sovereignty of the host country
Not taking sides
Using force to only defend yourself
Questions
Why do country’s have laws and courts?
Why would it be ideal for country’s to share the same laws?
International Law and Agreements
The foreign policies of various countries can sometimes conflict
To help resolve the disputes between countries, a large body of international laws and agreements have been developed
Some international laws stem from trade agreements between two or more countries |
|---|
Some are based in international treaties and UN resolutions |
Some are based on UN conventions or agreements |
The UN’S International Court of Justice (The World Court) interprets laws and tries to settle disputes peacefully
HOWEVER, not every country recognises the World Court
For example, the U.S refuses to recognise this court
Foreign Aid and Internationalism
Countries promote internationalism by providing foreign aid
Every year, developed countries give billions of dollars to developing countries for humanitarian and other purposes (medical supplies, food, clothing, etc.) -Foreign aid donors can ensure that they provide effective help through coordinating their work
The Red Cross and similar organizations have workers “on the ground”
These workers are involved with communities and know where and what kind of aid is needed most
The 0.7 Per Cent Solution
In 1969, former Canadian prime minister Lester B. Pearson wanted to aim to build a peaceful world
Pearson issued a challenge to the richest countries in the world -The challenge called for them to spend 0.7 % of their gross national income (GNI) on foreign aid *GNI refers to to the total value of good & services produced per year, both inside and outside a countries borders
UN members were committed to the goal, however in 2006 Canada gave only 0.33% of its GNI as foreign aid
What are your thoughts about Canada not giving the expected 0.7%? Was this a justifiable action?
Climate Change (The Kyoto Protocol)
Established in 1997 is an international attempt to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Canada and other developed countries that sign this agreement agreed to reduce their emissions by 20% by 2020
Canadian government had said that in order to do this, it would cost the economy and Canadians $51 billion.
Questions
What are your views on countries attempts to address climate change?
Is the Kyoto Protocol effective? Yes or No?
The spread of diseases
The spread of diseases from one person to another-across international borders has been a global issue for a long time
Throughout history, health care workers and hospitals had trouble helping people who fell ill -The World Health Organization (WHO) tries to stop the spread of deadly diseases -They focus on identifying, monitoring and controlling international health threats
Questions
Is an organization such as WHO needed to control 21st-century pandemics?
Or should countries be left to take action on their own?
Internationalism Behaviour
Poverty can lead to hunger, malnutrition and starvation
850 million people in the world do not have access to food
In November 1996, the UN organized the First World Food Summit
Delegates from 185 countries and the EU met in Rome
They vowed to reduce hunger by half the number by 2015
Questions
How effective is the international approach to address world hunger?
Is this achievable?
Questions
What do you think people’s behaviours are motivated by?
Needs vs Wants
Needs | Wants |
|---|---|
Things that people must have to survive. Needs include food, water, shelter and health. | Things that people desire. Wants are not necessary to survive. Someone may, for example want a cellphone or a tattoo. BUT they can survive without one. |
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs
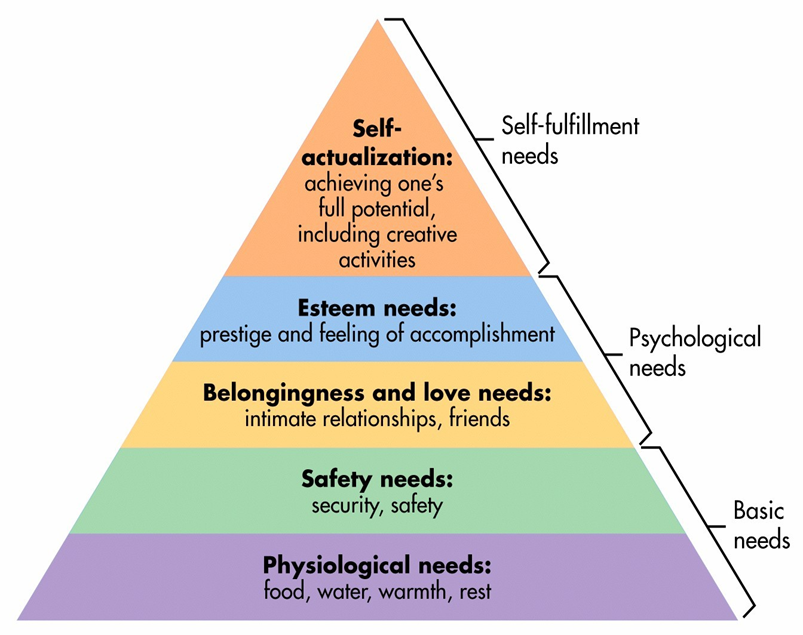
Abraham Maslow-Psychologist*- studied people’s needs.
Believed that people see basic needs as most important.
Noted that once people had their basic needs met, they were motivated to try to meet their needs at other levels.
Believed that people would make their way up to each level until they became fulfilled, happy human beings
Needs & Motives of Successful Nation-States
The behaviours of nations and nation-states is also motivated by the collective needs & wants of the country’s people
The actions of a responsible government serve the national interest
Many nation-states, ESPECIALLY with democratic governments are MOTIVATED to achieve and maintain:
ECONOMIC STABILITY
PEACE & SECURITY
SELF-DETERMINATION
HUMANITARIANISM
Unit 3 (Internationalism)
Incentives vs Sanctions
Incentives- offering closer relations, if certain conditions are met
Sanctions- Cutting off relations(trade) until the hostile “problematic behaviour” of a certain state stops
Incentives
Generally, when countries that receive help become economically successful and self- sufficient, the world can become a safer place
When economically unstable nation-states are offered trade opportunities, or opportunities to become more economically stable, they can be more inclined to cease actions that are viewed a problematic to other countries(for example, human rights abuse)
Sanctions
Countries try to promote peace in other countries by imposing economic sanctions
This includes cutting off trade and other economic ties with a country with efforts to force them to follow a particular behaviour
It is viewed as a more favourable alternative to harsher measures (such as declaring war)
Can be not as effective if other countries continue to trade with “problematic” nation-states
Also seen as more harmful to citizens rather than the government
Questions
What are your thoughts on sanctions?
Do you believe they help to promote peace?
Are sanctions ethical?
Peacekeeping
Peacekeepers are sent to conflict zones only after a ceasefire has been negotiated
Peacekeepers then set up a buffer zone (Area where no fighting occurs)
Peacekeepers protect humanitarian workers who provide food, shelter and medical aid
They are ONLY allowed to use force in self defense
**Peacekeepers MUST follow these guidelines:
- Consent: Respecting the sovereignty of the host country
Impartiality: Peacekeepers must not take sides
Self-defense: Peacekeepers may use force only to defend themselves
Questions
What are your thoughts on Peacekeeping?
Do you believe they help to promote peace?
What are some cons with peacekeeping?
Questioning the Role of Peacekeeping
**Sometimes problems do occur with peacekeeping:
Opposing sides may start to fight again, with peacekeepers in the middle of conflict
Peacekeepers can sometimes be attacked
Diplomats may not be able to reach a resolution, causing peacekeepers to stay indefinitely
Opposing sides sometimes start killing civilians, peacekeepers are to stay out of it
In the 1990s several peacekeeping mission failures caused people to question its effectiveness as a foreign policy tool
This resulted in the belief that peacemaking is more effective than peacekeeping
Peacemaking: Ending armed conflict and human rights abuses
Peacemakers are not required to remain neutral. They may shoot to kill and enter a country without being invited
Questions
If you were a peacekeeper, which aspect do you think you would find hardest?
Respecting the sovereignty of the host country
Not taking sides
Using force to only defend yourself
Questions
Why do country’s have laws and courts?
Why would it be ideal for country’s to share the same laws?
International Law and Agreements
The foreign policies of various countries can sometimes conflict
To help resolve the disputes between countries, a large body of international laws and agreements have been developed
Some international laws stem from trade agreements between two or more countries |
|---|
Some are based in international treaties and UN resolutions |
Some are based on UN conventions or agreements |
The UN’S International Court of Justice (The World Court) interprets laws and tries to settle disputes peacefully
HOWEVER, not every country recognises the World Court
For example, the U.S refuses to recognise this court
Foreign Aid and Internationalism
Countries promote internationalism by providing foreign aid
Every year, developed countries give billions of dollars to developing countries for humanitarian and other purposes (medical supplies, food, clothing, etc.) -Foreign aid donors can ensure that they provide effective help through coordinating their work
The Red Cross and similar organizations have workers “on the ground”
These workers are involved with communities and know where and what kind of aid is needed most
The 0.7 Per Cent Solution
In 1969, former Canadian prime minister Lester B. Pearson wanted to aim to build a peaceful world
Pearson issued a challenge to the richest countries in the world -The challenge called for them to spend 0.7 % of their gross national income (GNI) on foreign aid *GNI refers to to the total value of good & services produced per year, both inside and outside a countries borders
UN members were committed to the goal, however in 2006 Canada gave only 0.33% of its GNI as foreign aid
What are your thoughts about Canada not giving the expected 0.7%? Was this a justifiable action?
Climate Change (The Kyoto Protocol)
Established in 1997 is an international attempt to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Canada and other developed countries that sign this agreement agreed to reduce their emissions by 20% by 2020
Canadian government had said that in order to do this, it would cost the economy and Canadians $51 billion.
Questions
What are your views on countries attempts to address climate change?
Is the Kyoto Protocol effective? Yes or No?
The spread of diseases
The spread of diseases from one person to another-across international borders has been a global issue for a long time
Throughout history, health care workers and hospitals had trouble helping people who fell ill -The World Health Organization (WHO) tries to stop the spread of deadly diseases -They focus on identifying, monitoring and controlling international health threats
Questions
Is an organization such as WHO needed to control 21st-century pandemics?
Or should countries be left to take action on their own?
Internationalism Behaviour
Poverty can lead to hunger, malnutrition and starvation
850 million people in the world do not have access to food
In November 1996, the UN organized the First World Food Summit
Delegates from 185 countries and the EU met in Rome
They vowed to reduce hunger by half the number by 2015
Questions
How effective is the international approach to address world hunger?
Is this achievable?
Questions
What do you think people’s behaviours are motivated by?
Needs vs Wants
Needs | Wants |
|---|---|
Things that people must have to survive. Needs include food, water, shelter and health. | Things that people desire. Wants are not necessary to survive. Someone may, for example want a cellphone or a tattoo. BUT they can survive without one. |
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs

Abraham Maslow-Psychologist*- studied people’s needs.
Believed that people see basic needs as most important.
Noted that once people had their basic needs met, they were motivated to try to meet their needs at other levels.
Believed that people would make their way up to each level until they became fulfilled, happy human beings
Needs & Motives of Successful Nation-States
The behaviours of nations and nation-states is also motivated by the collective needs & wants of the country’s people
The actions of a responsible government serve the national interest
Many nation-states, ESPECIALLY with democratic governments are MOTIVATED to achieve and maintain:
ECONOMIC STABILITY
PEACE & SECURITY
SELF-DETERMINATION
HUMANITARIANISM
 Knowt
Knowt