Chem Units 1-3 Final
unit 1 Measuring Matter & Energy
vocab
calorie - energy required to raise the temp of one gram of water by one degree Celsius
Mass- measure of the amount of matter in an object
Weight - force exerted on an object by Earth’s gravitational pull
derived units - combining SI units into compound units
Density - ratio of mass & volume
potential energy - stored energy associated with position, shape or condition of an object
Kinetic energy - energy associated with the motion of an object
energy transfer - passing from one object to another
temperature - average kinetic energy of the particles that make up a sample of matter
conversion factors - ratios relating the value of one unit measure to another
accuracy - closeness of a measurement to the correct or accepted value of the quantity measured
precision - closeness of measurements of the same quantity made in the same way
significant figures - measurement consist of all the digits known with certainty + the first estimated digit
captive zeros - zeros appearing between nonzero digits
leading zeros - zeros that precede nonzero digits
trailing zeros - zeros at the end of a number
matter - anything that takes up space and has mass
physical property - property that can be measured/observed without changing the identity of matter
Density
Solubility
Conductivity
Magnetic attraction
State of matter (gas, liquid, solid)
Melting and boiling points
Viscosity (aka thickness)chemical properties - only observed after the identity of a substance changes
extensive property - property that depends directly on the amount of a substance present
intensive property - property that does not depend on the amount of a substance present
So matter…it has different states: the classic gas solid and liquid what are the diffs?
Solid: | Liquid: | Gas: |
|
|
b/c of speed difference they can flow/take diff shapes |
| ← IT'S A GAS Particles have so much energy → broken apart → electrically charged |
MEMORY TIP:
✲ The faster the particles move the easier it is to walk through the substance. So you cannot walk through a solid because the particles can only vibrate. You can walk through water because the particles are quicker, however it's still a challenge, but with gas since the particles are exponentially faster than particles of a solid you can walk through them with ease.
Intensive: | Extensive: |
Does not depend on the amount of substance present | Depends on the amount of substance present |
types of extensive properties
mass, volume (changes based on size/ amount)
types of intensive properties
density, melting point, boiling point, and conductivity (does not depend on amount)
pure substance - fixed composition
mixture - blend of two or more kinds of matter
homogeneous mixtures/solutions - uniform mixtures
heterogeneous mixtures - mixtures that are not uniform throughout
filtration - separate a solid with larger particles from a liquid with smaller particles
Centrifugation - separate certain solid components. The centrifuge spins rapidly, causing the solids to settle at the bottom of the test tube.
paper chromatography - used to separate dyes or pigments. The different substances move at different rates on the paper.
pure substances
pure substances are ALWAYS homogeneous
compounds - substances with constant composition that can be broken down into elements by chemical processes
elements - cannot be decomposed by chemical or physical means
systems
model - pattern, plan, rep or description designed to study the behavior of matter
system - set of interacting, interrelated or interdependent components that form a complex whole
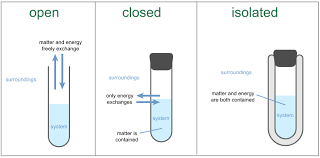
open system - energy and matter flow in and out freely
closed system - little to no exchange of matter but energy may be exchanged
isolation system - neither matter or energy can flows in or out
Engineering process
criteria - goals for the solution
constraint - limitations of the design
delimiting
the process of defining the constraints of the solutionTechniques to separate mixtures
tradeoff - exchange for one thing in return for another
multiscale modeling - rep a system using various scales
practice Q’s
Which of the following are chemical changes?
wooden logs burning to form ash
hydrogen and oxygen forming from water
An example of a pure substance is
carbon dioxide
A mixture is homogeneous if it has a uniform composition. A mixture is
heterogeneous if its composition is not uniform. A mixture can often be separated by techniques such as evaporation or filtration.
A group of chemical engineers are developing a medication to treat a disease. Which statement describes a possible constraint for the medication?
The cost of producing the medication will be kept as low as possible.
The density of a liquid substance in a container is an intensive physical property of the substance, so it can be used to help identify it. The volume of the substance is an extensive property, so it cannot be used in identification because it changes with the amount of the substance present.
An engineer is developing a process to separate a pure substance from a chemical reaction mixture. Which of the following would be considered a constraint on the engineering design process for the separation technique?
The budget for the process is $100 000
A student determines the density of a substance as 1.536 g/mL. The accepted value of the density is 1.446 g/mL. What is the percentage error in the student's value?
The percentage error is 6.224 %.
A hot metal block is placed into a beaker of cold water. Explain what happens to the thermal energy of the system.
What is scientific notation, and why it is useful for reporting scientific measurements?
A block of ice is placed outside on a hot summer day. Describe the changes in particle motion and the corresponding changes in energy as the ice melts and eventually becomes water vapor.
what is chemistry? - study of the composition of matter, the physical and chemical changes that matter undergoes, and the energy absorbed or released during those changes.
conversions
1g=1000mg
1cm=10mm
1L=1000mL
Smallest to largest:
nanogram, microgram, milligram, centigram, kilogram, megagram
percentage error
value experimental-value accepted/value accepted x 10
how to know which percent error is most accurate
smallest = more accurate
Volume
L x W x H
Accuracy
closeness to the true value
Precision
closeness to other answers trying to find the true value
Density
amount of mass per volume an object contains
Magnetic attraction
the ability of a substance to be attracted to a magnet
Solubility
the amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given amount of another substance
State of matter
solid, liquid, gas, plasma, Bose-Einstein condensate
Physical change (salt dissolving in water)
Change occurs without a change in the substance's chemical composition at a molecular state
plasma (most of universe)
gas in which the particles have so much energy that they broke apart and became electrically charged
Chemical properties of sodium in water
faster than sodium, more smoke, flame
Chemical properties of potassium in water
reacts so fast it can be explosive
Chemical properties are only observed
when one attempts to change the identity of the substance
Chemical change
particles of a substance are rearranged, resulting in a change in chemical composition
Reactants
substance undergoing the change
Products
the new substance found produced by chemical reaction
vocab
HEAT
Thermodynamics - relationship between heat and other forms of energy, how it can be transferred and transformed
Temperature - avg. KE of particles in a substance; property of all states of matter
Thermal equilibrium - when two systems with different temperatures reach the same temperature, resulting in no transfer of energy
zeroeth law - if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they are in thermal equilibrium
heat transfer - thermal energy is transferred
law of conservation of energy - energy cannot be created or destroyed
heat capacity - The ratio of the energy needed to change the temperature of a system compared to its change in temperature; depends on mass & type of material; extensive property
specific heat capacity - intensive property; the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one kelvin; (cal/g•°C)
The high specific heat capacity of liquid water makes it useful for absorbing excess energy in industrial processes
MASS
molar mass - mass of one mole of a substance
22.4L
6.022×10²³ particles
avogadros law - equal particle numbers result from equal pressure, temperature, and volume
PHASE CHANGES
phase change - transition between different states of matter (melting, vaporization, condensation)
vaporization - change from liquid—>gas
evaporation
particles at the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to become a gas
condensation
gas—>liquid
sublimation - solid—> gas (skips liquid state)
deposition - gas—>solid (skips liquid stage)
triple point - all 3 states coexist
open system - energy and matter flow in and out freely
closed system - little to no exchange of matter but energy may be exchanged
isolation system - neither matter or energy can flows in or out
BEHAVIOR OF GASES
internal energy - state of a substance
ex: temperature
volume - amount of physical space occupied by a gas
pressure - force exerted by gas particles colliding on surfaces
barometers - instruments used to measure air pressure
(STP) - standard temperature and pressure - standard conditions for measuring molar volume of a gas
ideal gas - hypothetical gas used to describe behavior of real gases
(KMT) - Kinetic molecular theory
describes properties of ideal gases
constant motion/negligible forces between particles
elastic collisions - no net loss in KE
momentum and KE are conserved
pressure vs volume (inverse) —> volume (up) = pressure (down)
temperature is constant
volume vs temperature (direct) —> volume (up) = temperature (up)
ENERGY TRANSFER
conduction - transfer of thermal energy by the collision of particles when objects or substances are in contact
conduction misc. bigger temp diff. conduction happens at higher rate + materials w/ low conductivity make good insulators
convection - cycling of air due to the differences in densities; occurs in gases & liquids
if convection natural = natural convection
if convection not natural = forced convection
Thermal radiaton - thermal energy is transferred through waves such as visible light, infrared radiation, and other types of electromagnetic waves. CAN FEEL COOLER B/C OF THERMAL RADIATION NOT JUST HOTTER
diffusion - Gases spread out spontaneously and mix with other gases in a process
entropy - show how disordered a system is (most to least disordered gas, liquid, solid)
increase entropy = increase energy
Second law of thermodynamics - all real processes increase the entropy of the universe
smaller system can be made more ordered by using energy from the outside, creating greater entropy in the larger system
energy flows from the higher temperature system to the lower temperature system aka energy flows from higher energy to lower energy objects or particles
computational model - computer performs this analysis or provides a way to model the behavior of matter
Work - transfer of energy to a system by the application of force that causes the system to move in the direction of the force
energy is defined by ability/capacity to do work
Heat engine - energy is transferred to the system in the form of heat. system transforms that energy to do work on its surroundings
The amount of work that a heat engine can do on its surroundings cannot be more than the amount of energy transferred to the heat engine.
gas does work on its surroundings when its temperature increases
engine - device that transforms energy into mechanical force or motion
Geothermal energy - Energy from underground sources
dry steam plant - uses steam from an underground geothermal source to turn a turbine
binary cycle power plant - transfers energy from geothermal water to another liquid
perpetual motion machine - hypothetical machine that can perform work without any input of energy
spontaneous - not requiring an outside source of energy to proceedpractice Q’s
EARTH AND SPACE STUFF
tectonic plates
pieces of Earth’s very thin and rigid outer shell
types of chemistry
Physical
the study of the properties and changes of matter and their relation to energy
Analytical
the study of the composition of substances
theoretical
the studies of chemical structure and its dynamics
inorganic
the study of non organic substances
organic
the study of most carbon based compounds
biochemistry
the study of the chemistry of living things
unit 2 Heat & Energy in the Earth System
vocab
Thermodynamics
the relationship between heat and other forms of energy and the ways energy can be transferred and transformed (flow of energy in a system)
Internal energy
The total kinetic and potential energy of all particles in a system (ex: thermal)
Changing mass or speed
effects kinetic energy
Changing mass, charge, or moving system in field
effects potential energy
Adding or removing energy
effects internal energy
Volume
amount of physical space occupied by gas (cm^3)
Pressure
the amount of force exerted per unit area of a surface (Pa or N/m^2 or psi)
barometer
Used to measure atmospheric pressure
Temperature
average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance
Thermal equilibrium
when two systems have the same temperature so no energy transfer occurs
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
If two thermodynamic systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other
Avogadro's number
6.022 x 10^23 The number of gas particles in exactly one mole of a substance
STP
standard temperature and pressure (by convection gases are analyzed at 1 atm of pressure and 273.15K)
As pressure decreases
volume increases (inverted relationship)
as temperature increases
pressure increases (directly related)
as temperature increases
volume increases (directly related)
Why does condensation form?
The stuff inside the system takes energy from the outside of the system (bottle ex)
Avogadro's law
the equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure have equal numbers of particles
1 mol of any gas at STP
22.4 L
Molar mass
the mass of one mole of a substance
KE = 1/2mv^2 (kinetic energy of a gas depends on mass and speed)
As gas density increases
speed and movement of the particles decreases
kinetic molecular theory
explains the properties of an ideal gas, constantly moving particles, mostly empty space with limited contact, do not exert much force on each other, no loss of kinetic energy after collision, gas temp is directly proportional to KE
Ideal gas
hypothetical gas in which the particles ave no volume and no attractions for each other (low temp high pressure, gases attract less in low temperatures due to slower speeds)
vaporization
boiling or evaporation turning liquid to gas
sublimination
when a solid turns directly to gas (dry ice)
deposition
gas directly to solid (frost)
triple point
the pressure and temperature conditions where all three states may exist
In lower pressures
less energy must be added or removed to change somethings state
Thermal pollution
temperature increase in a body of water caused by human activity (heat dissolves oxygen)
Thermal energy
total kinetic energy of the particles in a substance (depends on amount and temp)
Law of conservation of energy/ 1st law thermodynamics
Energy can not be created or destroyed
When two or more objects are in thermal equilibrium
energy is no longer transferred between them (energy between both objects is equal)
heat capacity
the ratio of energy needed to change the temp of a system compared to its change in temp (extensive, depends on amount of energy)
Heat capacity of a system depends on
mass and material
Specific heat capacity
intensive property of a substance that represents the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1K
High heat capacity
absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before changing temperature
Specific heat capacity can vary with
pressure (cp is for heat capacity with standard pressure)
Calorimeter
calculates the specific heat capacity of a substance
conduction
Form of heat transfer where heat energy is directly transferred between molecules through direct contact
Thermal conductivity
The rate at which a system transfers energy via conduction (depends on type of material and temp difference between object and heat source, greater temp difference = higher rate)
Low thermal conductivities
air (things with low thermal conductivity makes good insulators) (solids are best conductors, liquids, then gas)
Convection
when a space is heated, the warmer gas with more kinetic energy rises, making the air less dense, and the cooler denser air will sink, pushing the warm air upward (occurs in liquid and gas)
natural convection
when convection is driven by natural forces like a difference in densities
forces convection
when something like a fan causes the liquid or gas to move
Thermal radiation
a mode of energy transfer that occurs when thermal energy is transferred through waves such as visible light, infrared radiation, and other types of electromagnetic waves (does not require medium like the other two)
diffusion
when gases spread out spontaneously and mix with other gases to eventually fill up a space (bromine in container of air)
Entropy
how disordered a system is
States from highest to lowest entropy
Gas, liquid, solid (low organization of particles to high)
Entropy is directly related to
energy
second law of thermodynamics
All natural processes increase entropy, meaning that energy will always be lost to surroundings.
third law of thermodynamics
As the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, and entropy reaches its lowest possible value.
zeroth law
If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
work
the transfer of energy onto a system (application of force that moves energy into the direction of that force)
heat engine
a system that transfers energy in the form of heat that transforms that heat energy to do work
(1st law) the change in total energy depends on energy lost or gained by the system and work done or by the system
triangle U = Q+W (technically minus because any energy transfer or work will be negative)
triangle U
change in internal energy
Q
energy absorbed
W
work (work and heat are measured in J)
As temp of a gas increases
volume (space gas takes up) increases , so gas does work on its surroundings when temp is increased
tectonic plates
pieces of the lithosphere that move around on top of the asthenosphere
Rocks closest to the mid ocean ridge are______ and as you move from the ridge rocks get _____ implying that crust is being ______ at mid ocean ridges
youngest, older, produced
Why do the properties of rock change as temperature and pressure increases?
The particles in the rock are excited due to the temp increase, loosening them and they become more flexible, it changes states into magma
As most solid materials undergo melting, the particles in the material ____ thus the material ______ and its density ______ therefore this position of the material will ____ relative to the surrounding material.
spread apart, expands, decreases, rise
P waves (primary waves)
longitudinal waves (slinky) that make vibrations in the direction of travel, forming areas of compression and distillation, travels through solids, liquids, and gases
S waves (secondary waves)
transverse waves (right angles), their vibrations are at right angles to the direction of travel, only travels through solids
Lithosphere and athenosphere
includes the crust: the outermost layer, mostly solid rock, tectonic plates move leading to volcanic activity
lower mantle
mostly solid, mantle convection causes the plate movement above
outer core
liquid
inner core
solid under extreme pressure (density increases as you go deeper)
seismograph
instrument that detects and records seismic waves
seismograms
the recordings made by seismographs that identifies the waves produced by earthquakes
solid chunks of mantle picked up to the surface in volcanic eruptions
mantle xenoliths
meteorites
have a similar composition to earth layers, metallic meteorites containing mostly iron which may have a similar makeup to earths core
Scientists use ______ to infer what is happening deep inside earth by conducting lab experiments to observe how rocks behave under high pressures and temps
diamond anvils, and for the solid inner core, computer models
Most energy transfer within earth happens due to
convection (mostly in athenosphere and lower mantle prompting plate movement)
Earth's core is hotter than the mantle so we can assume heat is transferred from the core to the mantle via
conduction
When two plates move toward each other and one plate is much denser than the other, the ____ plate sinks beneath the other into the athenosphere. This forces the less dense rock in the athenosphere to rise
denser
Energy flows from the core towards the surface due to ____ differences
temperature
Energy moves through the lower mantle and athenosphere as rock flows due to _____ differences. This type of energy transfer is called ____
density, convection
Wherever particles of different temps come into contact ______ transfers energy from warmer to cooler particles. It can be assumed that this occurs in the lower mantle, athenosphere, and lithosphere because they are all _____
conduction, solid rock
mantle convection
the pattern of motion in which mantle rock is colder and denser and sinks, pushing up warmer and less dense rock
Subduction
when tectonic plates move towards each other and the denser plant sinks into the mantle beneath the lesser dense plate. this forms deep sea trenches, and the subducted plate melts to form volcanic magma
slab pull
the gravitational force on the subducting edge of the plate, pulling the rest of the plate along with it
slab suction
when subducting plates indirectly exert a force on the overriding plate. As the subducting slab descends it pulls the overriding plate towards itself.
Mid oceanic ridges
mid ocean mountain ranges that can be thousands of meters higher than the sea floor where gravity pulls new formed rock from eruptions downhill, producing an outward force called ridge push (negligible in plate motion)
other factor that contributes to speed and direction of plates
friction
earthquakes mostly occur at
oceanic trenches that run along the boundaries where denser oceanic edges or lithosphereic plates sink beneath less dense plates
geophysicist
Studies processes that change and shape the Earth with electrical, seismic, and magnetic techniques
seismologist
studies earthquakes and seismic waves and how they relate to geology and earth as a whole
marine geophycisists
use different technologies to map the sea floor and understand the area beneath it
diamond anvil
crushes sample rocks between two diamonds, sometimes uses lasers, simulates temps and pressures materials may experience closer to the core
Conduction occurs
the transition in between the different layers of the earth, wherever there is solid rock through and through such as the inner core, lower mantle (sometimes/ oobleck), and lithosphere
convection occurs
In the more liquid or moldable layers such as the outer core, sometimes lower mantle, and athenosphere
layers in order
lithosphere, athenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core
intensive/extensive in the earth
Intensive
does not depend on the amount of a substance present, temp, pressure, density, boiling and melting points
extensive
depends on the amount of a substance present, mass, volume, energy, heat capacity
geothermal energy
Geothermal power plant
a plant that uses Earth's internal heat to generate electricity
turbine
part of generator that produces electrical energy
dry steam plant
uses steam from underground geothermal sources to turn a turbine (steam to turbine)
flash steam plant
draws liquid from geothermal source, uses pressure to convert it into steam to drive a turbine (liquid to steam to turbine)
binary cycle power plant
transfers energy from geothermal water to another liquid. Liquid is then converted to steam to drive the turbine (underground water to other body of water to steam to turbine)
geothermal energy
energy from an underground source
geothermal heat pump
uses stable underground temperatures to warm and cool homes depending on the season
How do geothermal pumps work
when its cold out thermal energy from the ground heats the pipes to transfer that energy to the house, vice versa when it is cold
practice Q’s
How is the stability of a gaseous system affected by changes in the system?
How is energy transferred within and between systems?
How do energy and matter cycle in earths interior
You have two flasks of water. You place a thermometer in the first flask and leave it until the temperature no longer changes. The temperature reads 100 °C. When you move the thermometer to the second flask and again leave it, it also reads 100 °C.
The thermometer and the second flask of water are in thermal equilibrium.
The zeroth law states that the two flasks are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
Choose the correct statement as it relates to the energy of a system and a heating curve.
A known number of moles of gas is placed in a flexible container. What will happen if some of the gas is removed from the container while the pressure and temperature are kept constant?
The volume will decrease.
The kinetic-molecular theory states that ideal gas molecules do which of the following?
are in constant, rapid, random motion
Two substances have the same temperature. The particles of Substance A have a slower average speed than the particles in Substance B. What can you say about the molar masses of the two substances?
The molar mass of Substance A is greater than Substance B.
A puddle of water on a sidewalk evaporates in the hot afternoon sunshine. Complete the statement to describe what is happening.
Before the phase change, thermal energy is absorbed by the water, causing its temperature to increase
A scientist is testing the properties of a gas. Before he performs his experiment, he wants to make claims about the way the gas will behave in different situations. Then, he will compare his claims to his results. Complete each of the claims based on evidence you gathered in this lesson.
When the temperature of a gas is held constant, if pressure increases then the volume decreases
When the volume of a gas is held constant, if pressure increases then the temperature increases
When the pressure of a gas is held constant, if temperature increases then the volume increases
Solid carbon dioxide changing state to gaseous carbon dioxide is an example of
sublimation
How are evaporation and boiling alike, and how are they different? In your answer, discuss differences in energy and differences in temperature.
Describe kinetic-molecular theory and how it applies to the transfer of energy as an ideal gas is heated.
During an investigation, you place a gas in a glass syringe and use a movable plunger to keep the gas inside. You then slightly warm the syringe and the gas inside, causing the gas to expand. You then observe the plunger moving slightly outward. Explain the changes you observed in the system in terms of the kinetic-molecular theory.
What happens to a cup of water if you place it in a freezer?
The water transfers thermal energy to the freezer, decreasing the water's internal energy.
During an investigation, you connect two containers by a thin tube. A stopcock keeps the tube closed. One container is empty, and the other contains a gas. What will happen if you open the stopcock to connect the containers?
The entropy of the gas will increase, and it will spread out to fill both containers.
When a hot piece of metal is placed in water, thermal energy is transferred from the
metal to the water. The average kinetic energy of the particles in the metal
decreases, while the average kinetic energy of the water molecules
increases. This results in a decrease in temperature of the metal and an increase in temperature of the water. According to the first law of thermodynamics, the overall change in energy must be zero.
unit 3
vocab
PROPERTIES
Elements - pure substances (single type of atom)
Not physically/chemically broken down into another element
NOT BROKEN DOWN/SIMPLIFIED INTO OTHER ELEMENTS
SIMILAR PROPERTIES LIKE OTHER ELEMENTS
Metals - good conductors of heat/electricity/shiny
Bent into thin sheets (ductile)
Solid at room temp
Ex: magnesium, zinc, copper
Nonmetals - poor conductors of electricity/heat
Nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine —> gases at room temp
Brittle/dull —> solids at room temp
Ex: carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, iodine
Metalloids - metal/nonmetal
Solid at room temp
Semiconducting
Ex: boron, silicon
Reactivity - how readily an element combines with other elements
Noble gases - no reactivity/combining with other elements
SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
Electrons - negatively charged
Nucleus - positively charged center of the atom
Protons - positive charge equal to electrons negative charge (magnitude)
Neutrons - mass of a proton/no charge
ENERGY
Electromagnetic spectrum - radiation traveling in waves identified by wavelengths
Wavelength - distance between 2 crests
Shorter wavelength—>more energy - violet
Longer wavelength—>less energy - red
Visible light - rainbow
Absorbing energy - raised energy levels
Releasing energy - returning to normal levels
Orbits - circling the nucleus in paths
Fixed energy
Ground state - lowest energy/closest to nucleus
Excited state - further from the nucleus
ELECTRONS CANNOT BE ON SEPARATE EMISSION LINES
cant have 2 differing energy levels
ORBITALS
Orbital - 3D region around nucleus indicating electron location
Filled based on amount of electron energy
Increase - more filled/stable
Decrease - less filled
1s - 2 electrons/1 sub shell
Shells - 1-7 electrons based on level
S - 1 orbital
P - 3 orbitals
2s + 2p - 8 electrons
2: 2s
6: 2P
ELECTRON CONFIGURATION
Electron configuration - arrangement of electrons
1s orbital must be filled before moving onto the next orbital
1s
2s
2p
3s
3p
ELECTRON-DOT NOTATION
Valence electrons - outermost shell/level of nucleus
part of most chemical reactions
Place dot based on amount of valence electrons/level
Octet - full electron shell around the nucleus (8 valence electrons)
Carbon: 6 electrons —> 2 electrons in 1s, 2s, 2p (4 valence electrons as it does not have 8)
ATOMS
Protons # determines amount of electrons
Atomic # - # of protons
Neutral: proton=electron
Mass # - protons+neutrons in nucleus
Isotopes - different mass #’s/nearly identical chem. Properties
Unified atomic mass unit (u) - mass of one proton/neutron
1/12 mass of a common isotope —> 12u
MASS SPECTROMETRY
Mass spectrometry - measures mass of atoms
EXPERIMENTS
Cathode ray - discovered electrons
Deflection towards positive plate at large angles
Electron didn’t account for atoms mass
Plum pudding - electrons balanced in a mass of positively charged material
Additional mass of atom
Not accurate
Gold foil - alpha particles passed through foil/some deflected
Most of the atom was empty space
Found the nucleus/accounts for atoms mass
Flame test - produces flames of different colors
Light —> electromagnetic radiation
Wavelength - length of 2 crests
Shorter - more energy (violet)
Longer - less energy (red)
Released - returning to normal energy levels
Absorbed - raising energy levels/further from nucleus
Emission line - spectral lines of hydrogen atomic emission spectrum
Can’t jump between lines of energy
Absorb
Release
Interference - waves overlap —> add/cancel each other out
Double slit - light is diffracted interference occurs
Light behaves like a wave
Exploration 1: Making predictions using the periodic table
Dmitri Mendeleev —> organized periodic table
arranged by increasing atomic mass
left gaps for future elements based on predictions
Ex: predicted gallium and germanium
periodicity - repeating pattern of properties
(1913) Henry Moseley - atomic #
number of protons in an atom
periodic law - chemical/physical properties repeat with increasing atomic #
period: row
group: column
Properties
metals - solid at room temp, shiny, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat/electricity
nonmetals - less malleable, dull, brittle, less conductive
metalloids - semiconductors
noble gases - no charge/reactivity
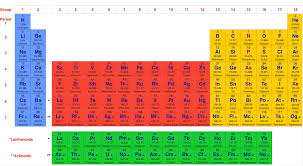
group 1 and 2 - alkali/alkaline earth metals
group 3 - 12 - transition metals
group 17 - halogens
group 18 - noble gases
patterns in chemical properties
valence electrons - outermost orbitals of an atom
most easily gained/lost
# of valence electrons influence location on periodic table
shells of noble gases:
all electrons paired
filled with electrons
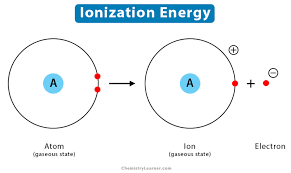
Exploration 3: Patterns in ionization energy
ionization energy - energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom
produces a charged atom - ion
force is greater on inner electrons
closer to the nucleus partially shield outer electrons from positive charge
repulsive force between them —> pushes outer electrons forward
valence electrons need less energy to break free
depends on net force keeping the valence electrons in the atom
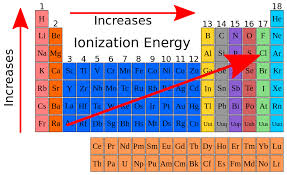
Shielding effect: less energy for ionization —> greater shielding effect in valence electron level of orbital
Exploration 4: Patterns in Atomic Size
Atomic radius - half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms
pico meters: 1×10^-12 meters
X-ray/spectroscopy
Electron cloud - area surrounding nucleus
Charge increases along a period
Decrease in atomic radii
Increase of atomic radii - down a group —> higher energy levels —> looser electrons being held in the nucleus
Metals - more reactive
larger atomic radius/outer electrons are loose—> greater attraction
Nonmetals - smaller atomic radius/tightly bound electrons
Exploration 5: Patterns in Electronegativity
compounds formed: gain/lose/share electron
Stronger atom attracts a smaller one more strongly
ex: a boy asks girl bc he has a crush
Electronegativity - measure of attraction for an atom it shares a molecule with
Larger radius - weaker attraction (distance=larger) —> more protons
Smaller radius - stronger attraction (shorter distance)


 Knowt
Knowt