2025 Cisco 300-410 dumps online share
Share the latest information you need to know for the Cisco 300-410 exam and provide the latest exam questions and answers
300-410 ENARSI Overview
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (300-410 ENARSI) v1.1 is a 90-minute exam that certifies a candidate's knowledge for implementation and troubleshooting of advanced routing technologies and services including Layer 3, Virtual Private Network (VPN) services, infrastructure security, infrastructure services, and infrastructure automation.
300-410 ENARSI v1.1 Exam Topics
To earn your CCNP Enterprise certification you must pass the 350-401 ENCOR exam and an eligible concentration exam of your choice, such as 300-410 ENARSI. Passing this exam also earns you the Cisco Certified Specialist - Enterprise Advanced Infrastructure Implementation certification. You will be tested on your knowledge of:
Layer 3 Technologies (35%)
VPN Technologies (20%)
Infrastructure Security (20%)
Infrastructure Services (25%)
2025 Cisco 300-410 dumps exam questions online share
Question 1:
Refer to the exhibit. The branch router is configured with a default route toward the Internet and has no routes configured for the HQ site that is connected through interface G2/0. The HQ router is fully configured and does not require changes.
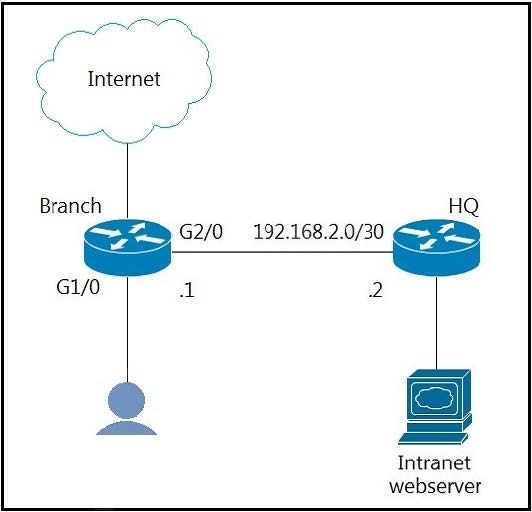
Which configuration on the branch router makes the intranet website (TCP port 80) available to the branch office users?
A. access-list 101 permit tcp any any eq 80 access-list 102 permit tcp any host intranet-webserver-ip ! route-map pbr permit 10 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 192.168.2.2 route-map pbr permit 20 match ip address 102 set ip next-hop 192.168.2.2 ! interface G2/0 ip policy route-map pbr
B. access-list 100 permit tcp host intranet-webserver-ip eq 80 any ! route-map pbr permit 10 match ip address 100 set ip next-hop 192.168.2.2 ! interface G1/0 ip policy route-map pbr
C. access-list 100 permit tcp any host intranet-webserver-ip eq 80 ! route-map pbr permit 10 match ip address 100 set ip next-hop 192.168.2.2 ! interface G2/0 ip policy route-map pbr
D. access-list 101 permit tcp any any eq 80 access-list 102 permit tcp any host intranet-webserver-ip ! route-map pbr permit 10 match ip address 101 102 set ip next-hop 192.168.2.2 ! interface G1/0 ip policy route-map pbr
Correct Answer: D
The ACL 101 matches all HTTP pakects while the ACL 102 matches TCP packets destined to Intranet webserver. These packets will be sent to HQ router. If amatchcommand refers to several objects in one command, either of them should match (the logical OR algorithm is applied). Forexample, in thematch ip address 101 102 command, a route is permitted if it is permitted by access list 101 or access list 102.
Question 2:
Refer to the exhibit.
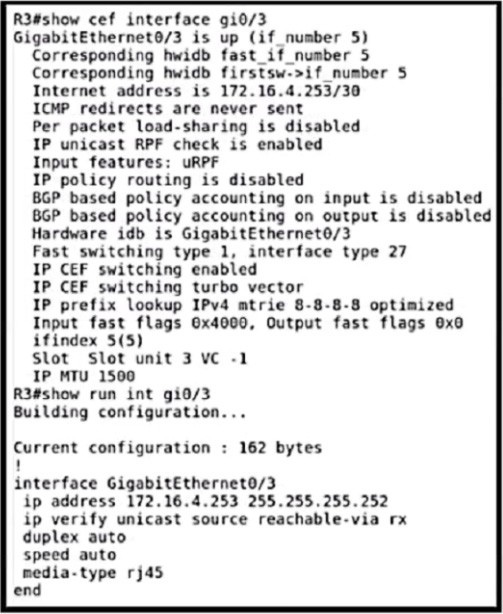
An engineer implements uRPF to increase security and stop incoming spoofed IP packets. Same asymmetrically routed packets are also blocked after the configuration. Which command resolves the issue?
A. ip verify unicast source reachable-via any
B. ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx
C. ip verify unicast reverse-path
D. ip verify unicast reverse-path any
Correct Answer: A
Question 3:
Refer to the exhibit.
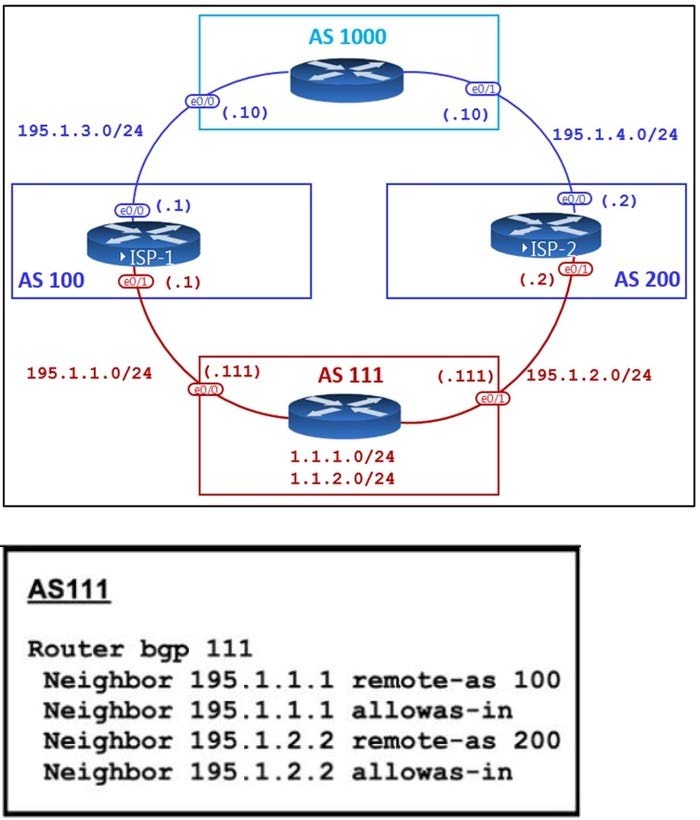
AS111 is receiving its own routes from AS200 causing a loop in the network. Which configuration provides loop prevention?
A. router bgp 111 neighbor 195.1.1.1 as-override no neighbor 195.1.2.2 allowas-in
B. router bgp 111 neighbor 195.1.2.2 as-override no neighbor 195.1.1.1 allowas-in
C. router bgp 111 neighbor 195.1.1.1 as-override neighbor 195.1.2.2 as-override
D. router bgp 111 no neighbor 195.1.1.1 allowas-in no neighbor 195.1.2.2 allowas-in
Correct Answer: D
A router discards BGP network prefixes if it sees its ASN in AS-Path as a loop prevention mechanism. The "allowas-in" feature allows routes to be received and processed even if router detects its own ASN in AS-Path.
Question 4:
A network engineer is investigating a flapping (up/down) interface issue on a core switch that is synchronized to an NTP server. Log output currently does not show the time of the flap. Which command allows the logging on the switch to show the time of the flap according to the clock on the device?
A. service timestamps log uptime
B. clock summer-time mst recurring 2 Sunday mar 2:00 1 Sunday nov 2:00
C. service timestamps log datetime localtime show-timezone
D. clock calendar-valid
Correct Answer: C
By default, Catalyst switches add a simple uptime timestamp to logging messages. This is a cumulative counter that shows the hours, minutes, and seconds since the switch has been booted up
Question 5:
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer configured R2 and R5 as route reflectors and noticed that not all routes are sent to R1 to advertise to the eBGP peers. Which iBGP routers must be configured as route reflectors to advertise all routes to restore reachability across all networks?
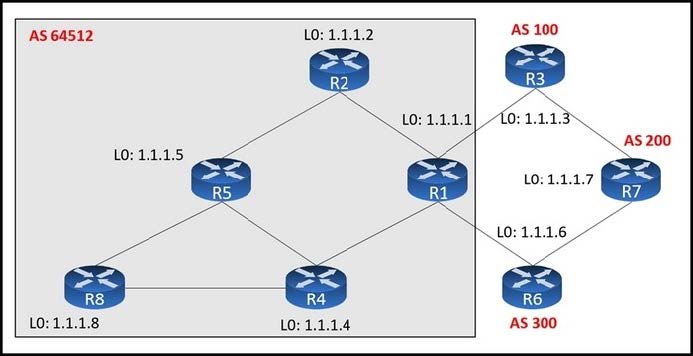
A. R1 and R4
B. R1 and R5
C. R4 and R5
D. R2 and R5
Correct Answer: C
When R2 and R5 are route reflectors (RRs), routes from R4 and R8 are advertised to R5 and R5 advertises to R2. But R2 would drop them as R2 is also a RR. Thereforesome routes are missing on R1 to advertise to eBGP peers.
Good reference: https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/emea/docs/2015/pdf/TECRST-2310.pdf
Route reflectors (RR) must be fully iBGP meshed so we cannot configure RR on both R1 and R5.
Question 6:
Company A recently acquired Company B and the network infrastructures are being merged. Both organizations used non-overlapping globally unique network addressing but different Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs). Initially, multiple WAN links will connect the two organizations. Company A will maintain its core routing protocol, and Company B\'s routing protocol will be the edge routing protocol. Two-way redistribution will be used to ensure full network routing capability.
What additional routing configuration should be performed to prevent routing loops and suboptimal routing?
A. Manually configure static routes.
B. Manually configure default routes.
C. Manually adjust the administrative distances.
D. Manually adjust the local preference attribute.
Correct Answer: C
When routes are being redistributed from the core into the edge and from the edge into the core, the administrative distance (AD) associated with external routes should be modified. This lessens the possibility of sub-optimal routing when
multiple routing protocols advertise different paths to the same network. The AD associated with the externally advertised routes should be higher than the internal IGP\'s AD. To change the AD for an entire routing protocol, use the distance
command. An example and the command syntax are shown below:
router(config)#router rip
router(config-router)#distance 125
The complete syntax of the distance command is:
distance weight [address mask [ access-list-number | name]
The weight parameter is the AD, which can be a number from 10 to 255. Note that distances 0 through 9 are reserved for system use.
To change only the AD for selected networks, use an access list with the distance command as shown below:
router(config)# access-list 5 permit 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
router(config)# access-list 5 permit 11.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
router(config)# access-list 5 permit 12.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
router(config)# router rip
router(config-router)# distance 220 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 5
The 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 portion included with the distance command could hold an address/mask combination for a single address, but it is more common to use an access list.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify redistribution between any routing protocols or routing sources
References:
Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Routing: Protocol-Independent Command Reference > distance (ip) Cisco > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > What Is Administrative Distance? > Document ID: 26634
Question 7:
Examine the following diagram:
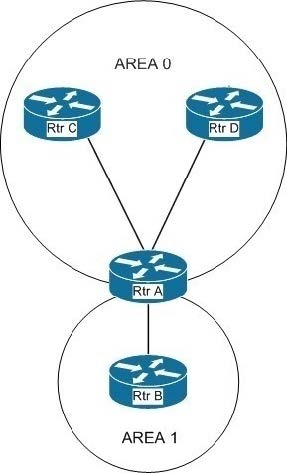
Which of the following actions will make area 1 a totally stubby area? (Choose all that apply. Each correct answer is part of the solution.)
A. execute the area 1 stub no-summary command on RouterA
B. execute the area 1 stub no-summary command on RouterB
C. execute the area 1 stub command on RouterB
D. execute the area 1 stub command on RouterA
E. execute the area 0 stub-no summary command on RouterA
F. execute the area 0 stub no-summary command on RouterB
G. execute the area 0 stub command on RouterB
H. execute the area 0 stub command on RouterA
Correct Answer: AC
You should execute the area 1 stub no-summary command on RouterA and the area 1 stub command on RouterB. A totally stubby area is one that only keeps local area routes in the link-state database (LSDB), plus a default route that leads
out of the area. To make an area totally stubby, the area border router (ABR) should be configured with the area 1 stub no-summary command and all other area routers should be configured with the area 1 stub command. The diagram in the
scenario indicates that RouterA is the border router. You should not run any of the commands that refer to area 0. This would affect a different area than the requirement stated in the scenario.
None of the other combinations of actions will create a totally stubby area.
If you run the area 1 stub command on both RouterA and RouterB, it will create a stub area. A stub area differs from a totally stubby area in that a stub area will allow updates about areas in the same OSPF domain.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify network types, area types, and router types
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > What Are OSPF Areas and Virtual Links? > Define a Totally Stub Area
Question 8:
DRAG DROP
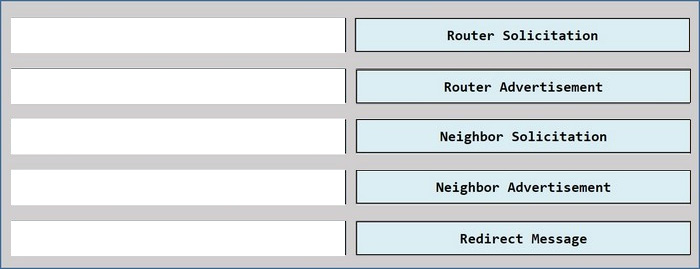
Drag and drop the ICMPv6 neighbor discovery messages from the left onto the correct packet types on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Question 9:
Refer to the exhibit.
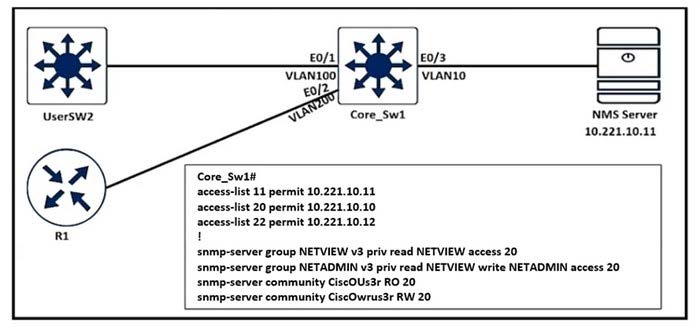
An engineer configured SNMP communities on the Core Sw1, but the SNMP server cannot obtain information from Core_Sw1. Which configuration resolves this issue?
A. snmp-server group NETVIEW v2c priv read NETVIEW access 20
B. access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.11
C. access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.12
D. snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN access 22
Correct Answer: B
The SNMP server configuration ties ACL 20 to the list of allowed SNMP servers that can pull data from the switch. The IP address of the NMS server needs to be added to this ACL.
Question 10:
Router R1 has been configured with a default route like this:
R1#(config) ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.2.3.1
You want to redistribute this route into OSPF but when you configure the redistribute static command under the OSPF process the default route is not present. What will create a default route in the OSPF routing process?
A. Use the redistribute static subnets command.
B. Create a default metric for the static default route.
C. Use the default-information originate command under the OSPF process.
D. Change the static default route to use an Administrative Distance (AD) greater than 110.
Correct Answer: C
Question 11:
SIMULATION Tasks A network is configured with CoPP to protect the CORE router route processor for stability and DDoS protection. As a company policy, a class named class-default is preconfigured and must not be modified or deleted. Troubleshoot CoPP to
resolve the issues introduced during the maintenance window to ensure that:
1.
Dynamic routing policies are under CoPP-CRITICAL and are allowed only from the 10.10.x.x range.
2.
Telnet, SSH, and ping are under CoPP-IMPORTANT and are allowed strictly to/from 10.10.x.x to the CORE router (Hint: you can verify using Loopback1).
3.
All devices ping (UDP) any CORE router interface successfully to/from the 10.10.x.x range and do not allow any other IP address.
4.
All devices run a successful traceroute (UDP) to any interface on the CORE router to/from the 10.10.x.x range, are under CoPP-NORMAL, and do not allow any other IP address traceroute is to be under CoPP-NORMAL (Hint: Traceroute port range 33434 33464).
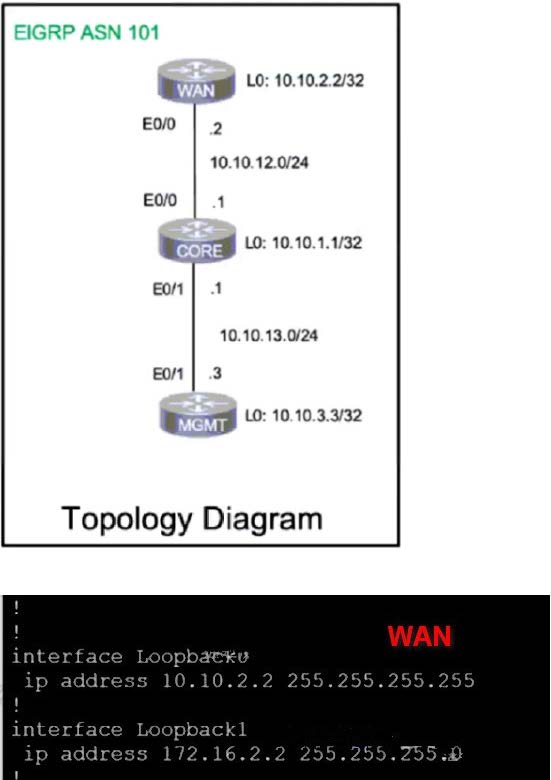
A. See the solution below in Explanation.
B. PlaceHolder
C. PlaceHolder
D. PlaceHolder
Correct Answer: A
>>> CORE
policy-mao CoPP class CoPP-CRITICAL police 1000000 50000 50000 conform-action transmit exceed-action transmit
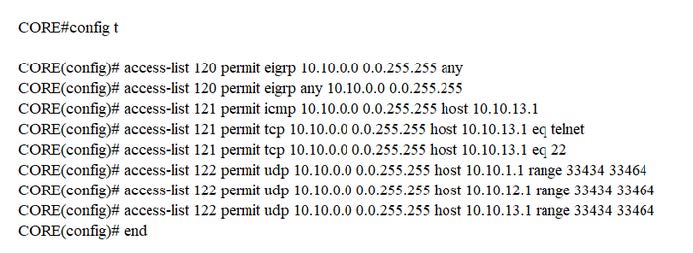
CORE# Copy run start >>> TESTING: CORE
Question 12:
Refer to the exhibit.
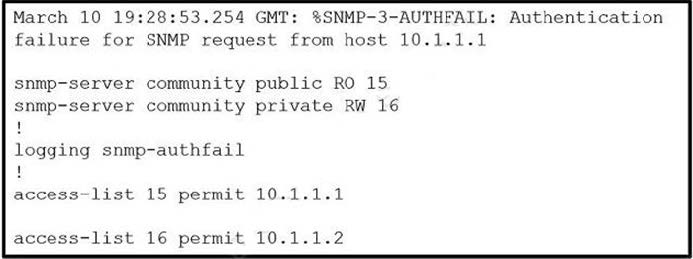
Which action resolves the issue?
A. Configure host IP address in access-list 16.
B. Configure SNMPv3 on the router.
C. Configure SNMP authentication on the router.
D. Configure a valid SNMP community string.
Correct Answer: D
Looking at the configuration, it seems that there are two SNMP community strings configured, "public" and "private". However, the configuration does not specify which community string is being used by the host with IP address 10.1.1.1. The correct action to resolve this issue would be to configure a valid SNMP community string on the device from which the SNMP request is being made, and ensure that it matches the community string configured on the router.
Question 13:
Refer to the exhibit.The control plane is heavily impacted after the CoPP configuration is applied to the router. Which command removal lessens the impact on the control plane?
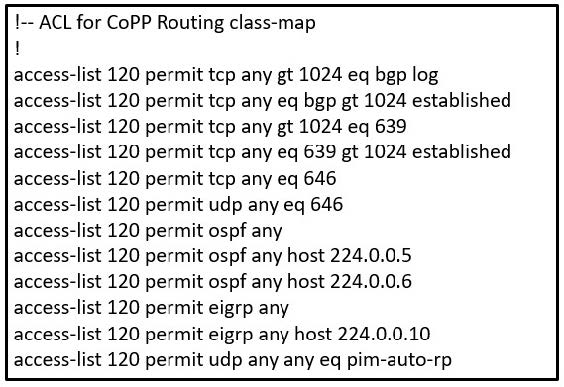
A. access-list 120 permit eigrp any host 224.0.0.10
B. access-list 120 permit ospf any
C. access-list 120 permit udp any any eq pim-auto-rp
D. access-list 120 permit tcp any gt 1024 eq bgp log
Correct Answer: C
Question 14:
After some changes in the routing policy, it is noticed that the router in AS 45123 is being used as a transit AS router for several service provides. Which configuration ensures that the branch router in AS 45123 advertises only the local networks to all SP neighbors?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Correct Answer: C
By default BGP advertises all prefixes to external BGP neighbors. This means that if you are multihomed (connected to two or more ISPs) then you might become a transit AS. For example, ISP 2 in AS 200 can send traffic to your router in AS 100 to reach ISP 3 in AS 300 because you advertised prefixes in ISP 3 to ISP 2.
This is what will be seen in the BGP routing table of ISP1:

Question 15:
The network administrator configured CoPP so that all SNMP traffic from Cisco Prime located at 192.168.1.11 toward the router CPU is limited to 1000 kbps. Any traffic that exceeds this limit must be dropped.
access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 161 ! class-map CM-SNMP match access-group 100 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP police 1000 conform-action transmit ! control-plane service-policy input PM-COPP
The network administrator is not getting the desired result for the SNMP traffic and SNMP traffic is getting dropped frequently. Which set of configurations resolves the issue?
A. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit tcp host 192.168.1.11 any eq 161
B. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit udp host 192.168.1.11 any eq 161 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP no police 1000 conform-action transmit police 1000000 conform-action transmit ! control-plane no service-policy input PM-COPP ! interface E 0/0 service-policy input PM-COPP ! interface E 0/1 service-policy input PM-COPP
C. no access-list 100 access-list 100 permit udp host 192.168.1.11 any eq 161 ! policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP no police 1000 conform-action transmit police 1000000 conform-action transmit
D. policy-map PM-COPP class CM-SNMP no police 1000 conform-action transmit police 1000000 conform-action transmit
Correct Answer: C
1000 kbps = 1 000 000 bits per second => bps is used in CoPP, so this value needs to be changed.
The ACL syntax for matching the interesting traffic:
access-list 100 permit udp host any eq 161 (or eq snmp)
https://community.cisco.com/t5/routing/acl-help/td-p/2788816/page/2
The Leads4pass 300-410 dumps exam material contains 925 latest exam questions and answers. Use https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html to download the complete material to help candidates successfully pass the Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) exam.
 Knowt
Knowt
