Chapter 13: RNA and Protein Synthesis
13.1 RNA
The Role of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
@@There are three main differences between RNA and DNA@@
- The sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose
- RNA is usually single-stranded and not double-stranded
- RNA contains uracil in place of thymine
Genes are made of instructions coded into DNA that tell cells how to build proteins
- The first step in decoding these instructions is to copy part of the base sequence from DNA into RNA
- RNA then uses these instructions to direct the making of proteins, which help to determine an organism’s characteristics
@@The three main types of RNA are messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA@@
- Messenger RNA carries instructions for making proteins from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm
- Ribosomal RNA forms an important part of both subunits of the ribosome
- Transfer RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome and matches them to the coded mRNA message
RNA Synthesis
- Most of the work of making RNA takes place during transcription, the synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template, or pattern
- The order of the RNA bases complements the base sequences of the DNA
- In eukaryotes, RNA is made in the cell’s nucleus, and then it moves to the cytoplasm to help make proteins
- During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to put together nucleotides to make a strand of RNA
- The enzyme binds only to promoters, regions of DNA that have specific base sequences
- Promoters are signals in the DNA that show RNA polymerase exactly where to begin making RNA
- In RNA editing, bits and pieces called introns are cut out and discarded from these RNAs; the remaining pieces, called exons, are then spliced back together
13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
The Genetic Code
- The genetic code is a code for making proteins; @@it is a collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino acid into a protein during protein synthesis@@
- The genetic code is read three “letters” at a time
- Each “word” is three bases long and corresponds to a single amino acid
- Proteins are made of long chains of amino acids called polypeptides
- Up to 20 different amino acids are found in polypeptides
- The shape and function of a protein are determined by its amino acids and their sequence
- RNA contains four different bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U), which are like the letters of a language called the genetic code
- Each word in the genetic code is three “letters,” or three bases; each three-base set is called a codon that specifies one amino acid
- There are 64 possible three-base codons in the genetic code, though most amino acids can be specified by more than one codon
- Special codons tell the cell where to start and stop translating RNA
- The codon AUG acts as the “start” codon for protein synthesis
- Translation continues until one of three different “stop” codons is reached; then, translation stops and the polypeptide is complete
Translation
Translation is a process by which the sequence of bases of an mRNA is converted into the sequence of amino acids of a protein; it is the decoding of an mRNA message into a protein
In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the cell’s nucleus
After transcription, mRNA leaves the nucleus, and translation takes place in the cytoplasm; the figure below shows this process:
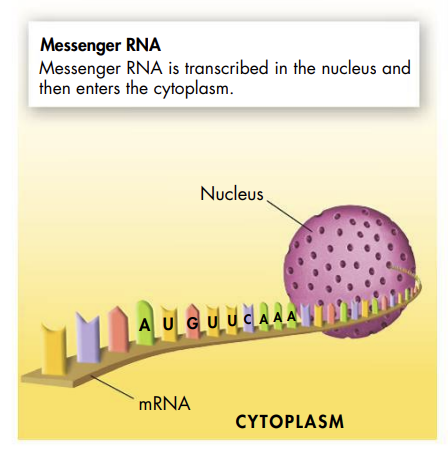

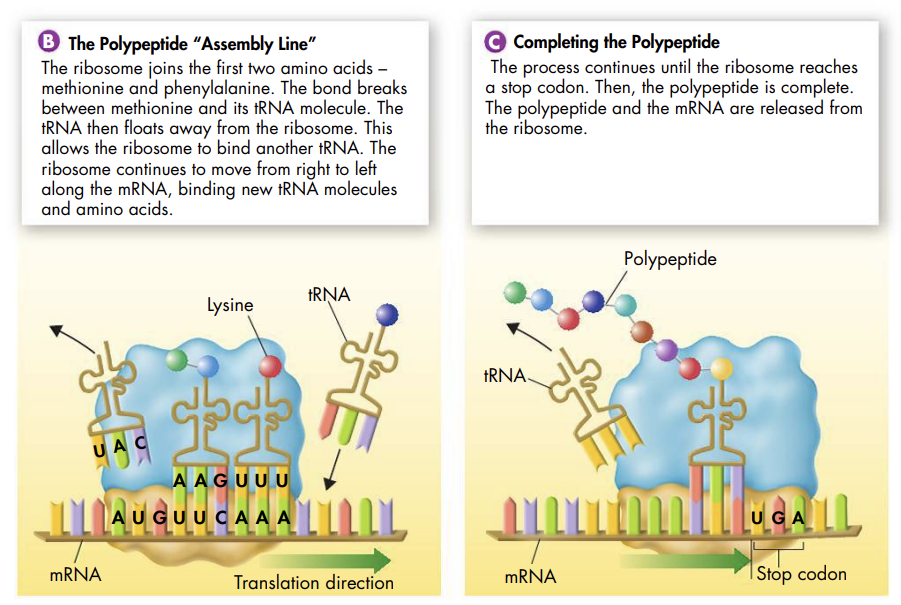
An anticodon is a group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to the three bases of a codon of mRNA
@@All three kinds of RNA are put to work in the ribosome during translation@@
- The mRNA molecule carries the coded message that directs the process
- The tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acid for each codon on the mRNA
- The rRNA and many proteins make up the ribosomes
The Molecular Basis for Heredity
- Basically, proteins are tiny tools, each one designed to build or run a part of a living cell
- Molecular biology tries to explain living organisms by studying them at the molecular level; it uses molecules like DNA and RNA as tools to understand living things
- The central dogma of molecular biology is that information is transferred from DNA to RNA to protein
- Though there are many exceptions to this “dogma,” it is a useful rule that helps to explain how genes work
- Gene expression is the way DNA, RNA, and proteins are involved in putting genetic information into action in living cells
13.3 Mutations
Types of Mutations
Sometimes cells make mistakes in copying their own DNA by inserting the wrong base or skipping a base as a strand is put together
- These variations are called mutations, or, changes in genetic information that can be inherited
@@All mutations fall into two basic categories@@
- Mutations that make changes in a single gene are known as gene mutations
- Mutations that make changes in whole chromosomes are known as chromosomal mutations
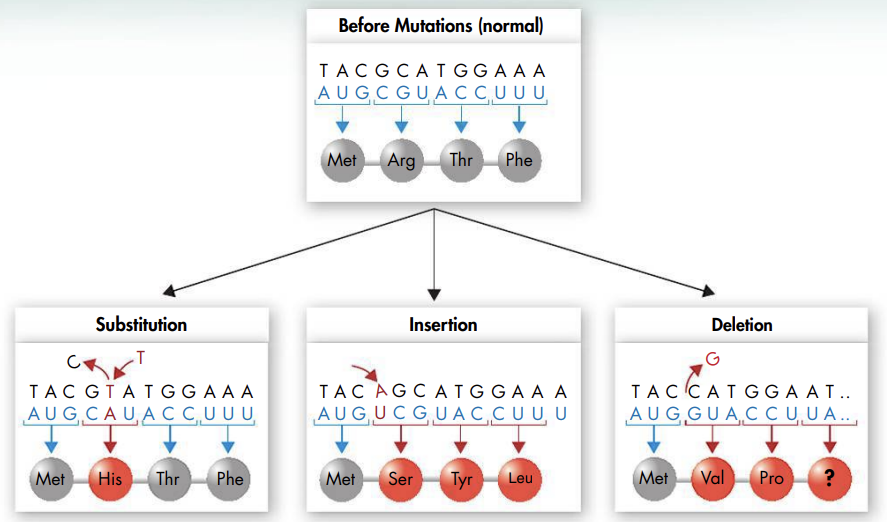
@@Gene mutations that involve changes in one or a few nucleotides are known as point mutations@@
- Point mutations happen at a single point in the DNA sequence and include substitutions, insertions, and deletions; they usually happen during replication
- In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base
- Substitutions usually affect a single amino acid, and sometimes they have no effect at all
- An insertion adds a new base to the DNA sequence, and a deletion removes a base from the DNA sequence
- The effects of these changes can be dramatic; after a change, the sets shift in every codon that comes after the mutation
- Insertions and deletions are also called frameshift mutations because they shift the “reading frame” of the genetic code; this change can alter a protein so much that it cannot do its job
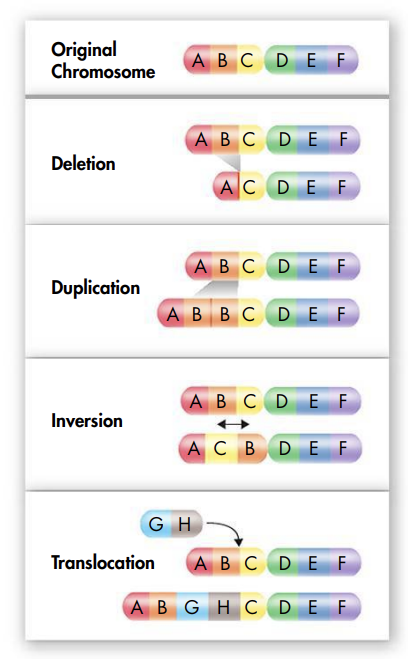
@@A chromosomal mutation is a change in the number or structure of chromosomes@@
- There are four types of chromosomal mutations: deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation
- Deletion happens when part or all of a chromosome is lost
- Duplication happens when an extra copy of all or part of a chromosome is made
- Inversion happens when parts of a chromosome change direction
- Translocation happens when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another one
Effects of Mutations
- Some mutations are caused by mutagens, chemical or physical agents in the environment
- Chemical mutagens include some pesticides, tobacco smoke, and pollutants
- Physical mutagens include X-rays and ultraviolet light
- Sometimes the cell can repair the DNA, but when the cell cannot fix the DNA, the sequence changes become permanent
- @@Mutations can help or harm organisms, though most mutations have little or no effect on genes@@
- Some of the changes made by mutations can help an organism or species; these mutations make genes with functions that are useful to organisms in different environments
- For example, the condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes is called polyploidy; polyploid plants are often larger and stronger than diploid plants
- Some of the most harmful mutations make big changes in protein shape or gene activity; the proteins made by these mutations can get in the way of biological activities
- @@Mutations are important because they promote genetic variation@@
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation
@@Most bacteria transcribe only the genes they need at any one time@@
- For example, some genes produce enzymes used to digest certain types of food molecules; if these food molecules are not present, there is no need for these enzymes
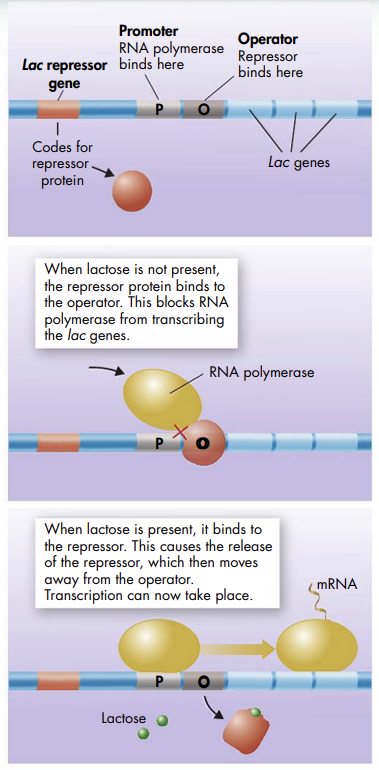
One way bacteria control making proteins is through operons; an operon is a group of adjacent genes that share a common operator and promoter and are transcribed into a single mRNA
- For example, in the case of the lac operon, when lactose is not present, the repressor protein binds to the operator, blocking RNA polymerase from transcribing the lac genes
- When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, causing the release of the repressor, which then moves away from the operator; transcription can then take place
On one side of the operon’s three genes are two control regions
- The first is a promoter (P), the site where RNA polymerase can bind to begin transcription
- The other region is called the operator (O), a short DNA region, adjacent to the promoter of a prokaryotic operon, that binds repressor proteins responsible for controlling the rate of transcription of the operon
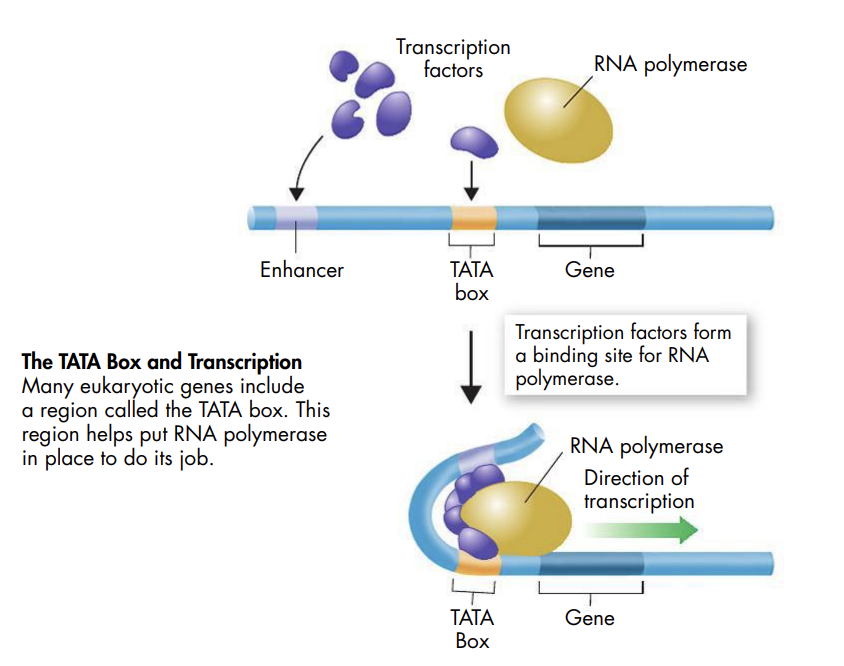
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
Transcription factors control the expression of eukaryotic genes by binding DNA sequences in regulatory regions
Complex gene regulation is what makes specialization possible
Using a silencing complex to block gene expression is called RNA interference (RNAi)
- MicroRNAs attach to mRNA molecules and stop them from passing on their protein-making instructions
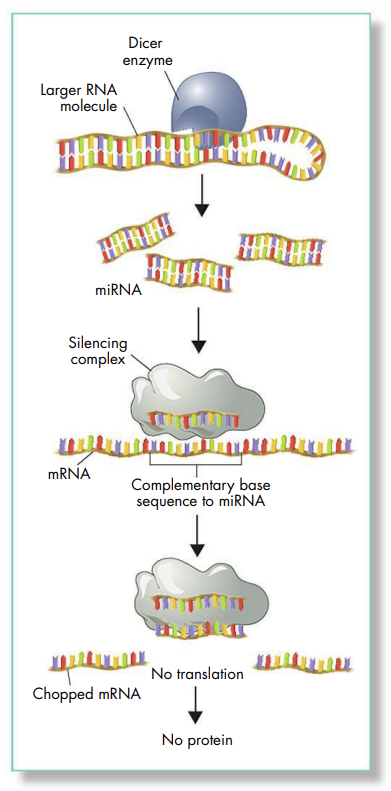
The discovery of RNAi has made it possible for researchers to switch genes on and off by inserting double-stranded RNA into cells
- RNAi technology may also provide a way for medical scientists to turn off genes from viruses and cancer cells; RNAi may provide new ways to treat, and maybe even cure, diseases
Genetic Control of Development
- Controlling gene expression helps shape the way a multicellular organism develops
- This kind of cell change and development is called cell differentiation
- Homeotic genes are a class of regulatory genes that determine the identity of body parts and regions in an animal embryo
- Mutations in these genes can transform one body part into another
- All homeotic genes share a similar DNA sequence, called the homeobox sequence
- Homeobox genes code for transcription factors that turn on other genes
- These genes are important in cell differentiation, as they control features such as the presence of wings or legs
- Other animals, including humans, also have Hox genes; so, nearly all animals share the same basic tools for building the different parts of the body
Environmental Influences
- @@In all kinds of organisms, environmental factors like temperature can change gene expression@@
- Metamorphosis is another example of how organisms can alter gene expression in response to environmental changes
- Metamorphosis involves a series of changes from one life stage to another and is usually regulated by factors inside and outside of the body
- Environmental changes are translated into hormonal changes
- The hormones act to regulate gene expression, which controls the speed of metamorphosis
- Temperature and population size can also affect the speed of metamorphosis
- @@Master control genes are like switches that trigger particular patterns of development and differentiation in cells and tissues@@