INTRO TO BIOCHEM
Bio= life
Chemistry = study of matter and the changes it undergoes
Biochemistry= the branch of science in which you study the chemical and physical processes that occur in an organism.
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is the study of Carbon compounds. (those that contain carbon-carbon bonds)
· Organic compounds are compounds composed primarily of a Carbon skeleton.
· All living things are composed of organic compounds.
Carbon
What makes Carbon Special? Why is Carbon so different from all the other elements on the periodic table?
o The answer derives from the ability of Carbon atoms to bond together to form long chains and rings.
· Carbon is able to form 4 covalent bonds (4 valence electrons) with other carbon or other elements.
· Carbon can covalently bond with up to four other atoms.
· Carbon can form immensely diverse compounds, from simple to complex.
Macromolecules of Biochem
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Polymers and Monomers
Each of these types of molecules are polymers that are assembled from single units called monomers.
Each type of macromolecule is an assemblage of a different type of monomer.
Monomers
Macromolecule | Monomer |
Carbohydrates | Monosaccharide |
Lipids | Not always polymers; Hydrocarbon chains |
Proteins | Amino Acids |
Nucleic Acids | Amino acids |
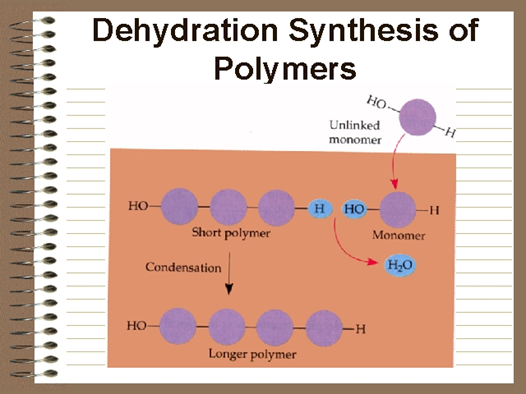
How do monomers form polymers?
In condensation reactions (also called dehydration synthesis), a molecule of water is removed from two monomers as they are connected together.
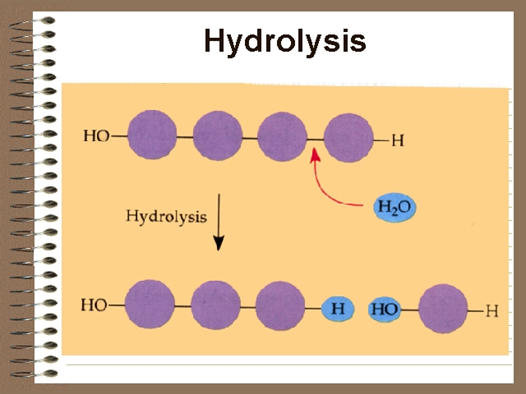
Hydrolysis
In a reaction opposite to condensation, a water molecule can be added (along with the use of an enzyme) to split a polymer in two.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, always in a ratio of 1:2:1.
Carbohydrates are the key source of energy used by living things.
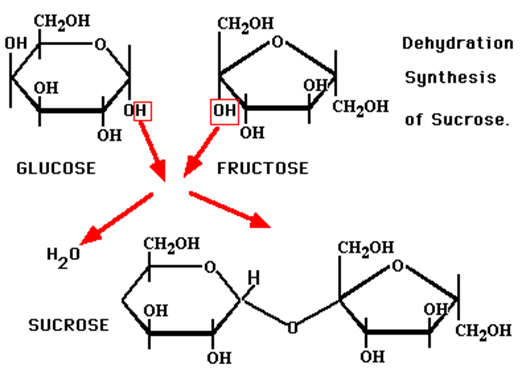
The building blocks of carbohydrates are sugars, such as glucose and fructose.
What do the roots mono-, di-, oligo-, and poly mean?
Each of these roots can be added to the word saccharide to describe the type of carbohydrate you have.
How do two monosaccharides combine to form a polysaccharide?
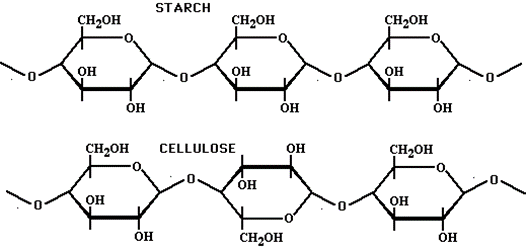
Polysaccharide
Lipids
Lipids are molecules that consist of long hydrocarbon chains. Attaching the three chains together is usually a glycerol molecule. Lipids are NONpolar.
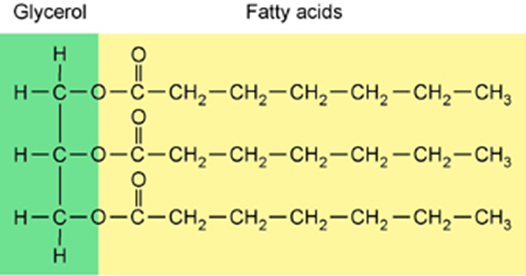
Saturated vs Unsaturated Fat
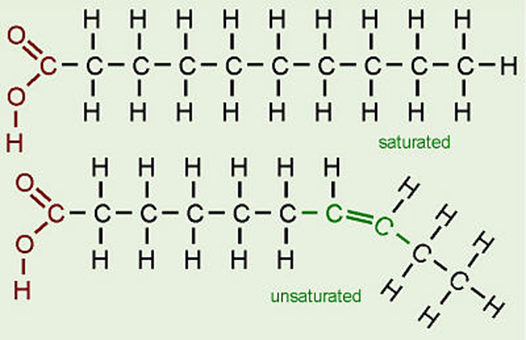
Saturated Fats: A type of fat with certain chemical properties that is usually solid at room temperature. Most saturated fats come from animal food products, but some plant oils, such as palm and coconut oil, also contain high levels. Eating saturated fat increases the level of cholesterol in the blood and the risk of heart disease.
Unsaturated fats: contain one or more double or triple bonds between the molecules. These fats are liquid at room temperature in oil form.
Proteins
Proteins have building blocks of structures called amino acids. Proteins are what your DNA codes make (we will talk about this in great detail in a month or so).
A peptide bond forms between amino acids by dehydration synthesis.
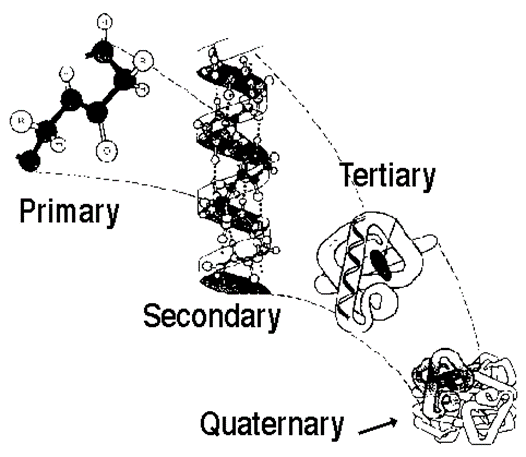
Levels of Protein Structure
Level | Description |
Primary | The amino acid sequence |
Secondary | Helices and Sheets |
Tertiary | Disulfide bridges |
Quaternary | Multiple polypeptides connect |
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are molecules that allow organisms to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next.
· Nucleic acids are macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production.
· Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides.
· Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group.
· DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
· RNA has ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A, G, C, and uracil (U).