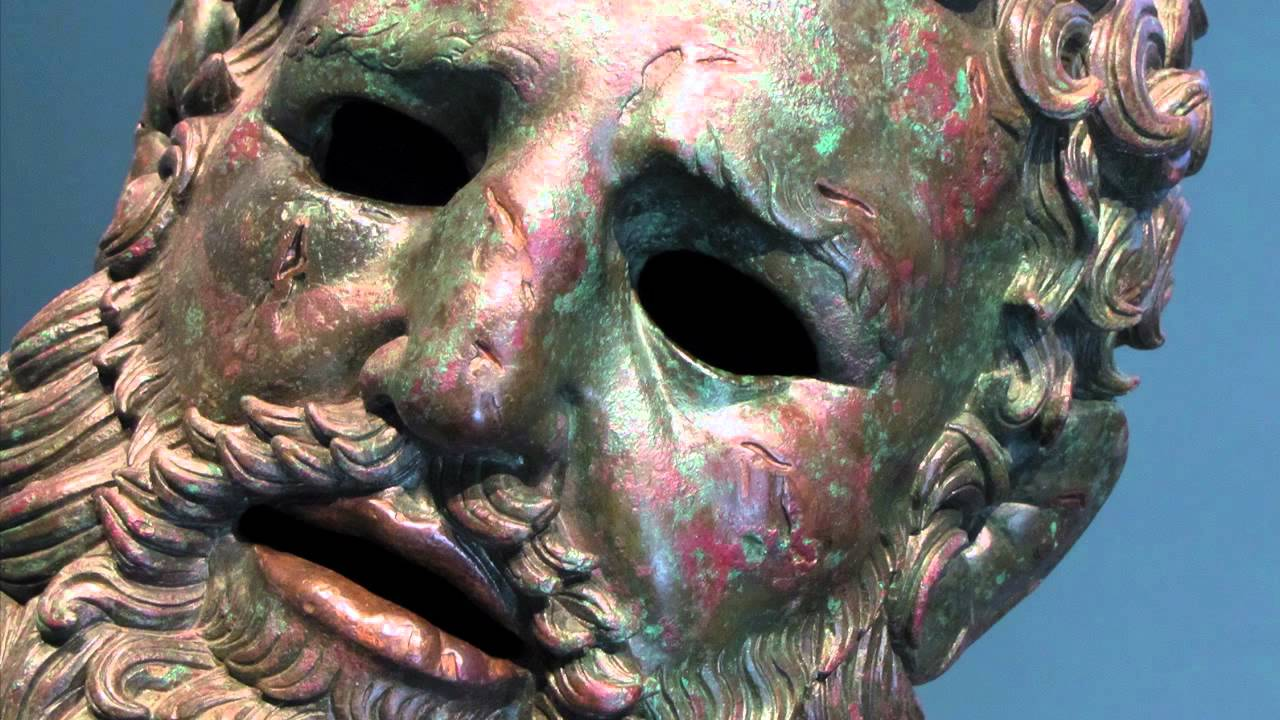Hellenistic - AP History notes (emotion, drama, naturalism) 😱🎭🌿
About Hellenistic
Beings after the death of Alexander the Great.
- divided his kingdom into 3 parts.
Main focus:^^emotion, drama, naturalism.^^
Hellenistic: mixture of different styles.
Key words (Hellenistic)
Architecture:
- Columnade
- Frieze
- wet drapery
Artistic:
- high relief
- gigantomosy
- foreshortening
- mosaic
- teserae shard
Altar of Zeus (Pergamon, Turkey) ⚡
Located in Pergamon, Turkey. Dedicated to the god Zeus. ^^Commissioned^^ ^^by King Attalos.^^
Main inspiration for the West front altar:
- Attalos I vs. Gauls ⚔
- ^^Defeat of the Persians (Pergamenes over the Persians)🏆^^
- Battle between Gods and Giants 🌬
Narrative: Attalos defeated the Gauls/Persians; temple is meant to celebrate the victory.
- Altar was commissioned by King Attalos.
Key words:
Architecture:
- Columnade
- Frieze
- Frieze sculptures
- Ionic capital (not Doric)
- gigantomachy
- ^^metope (contains statues)^^
Artistic:
- Power and authority
- high relief
Athena Battling Alkyoneos (Athens, Parthenon) ⚔
Narrative: Athena is taking Alkyones by the hair and dragging him, placed across the stairs of the Altar of Zues. Alkyones is humiliated by Athena.
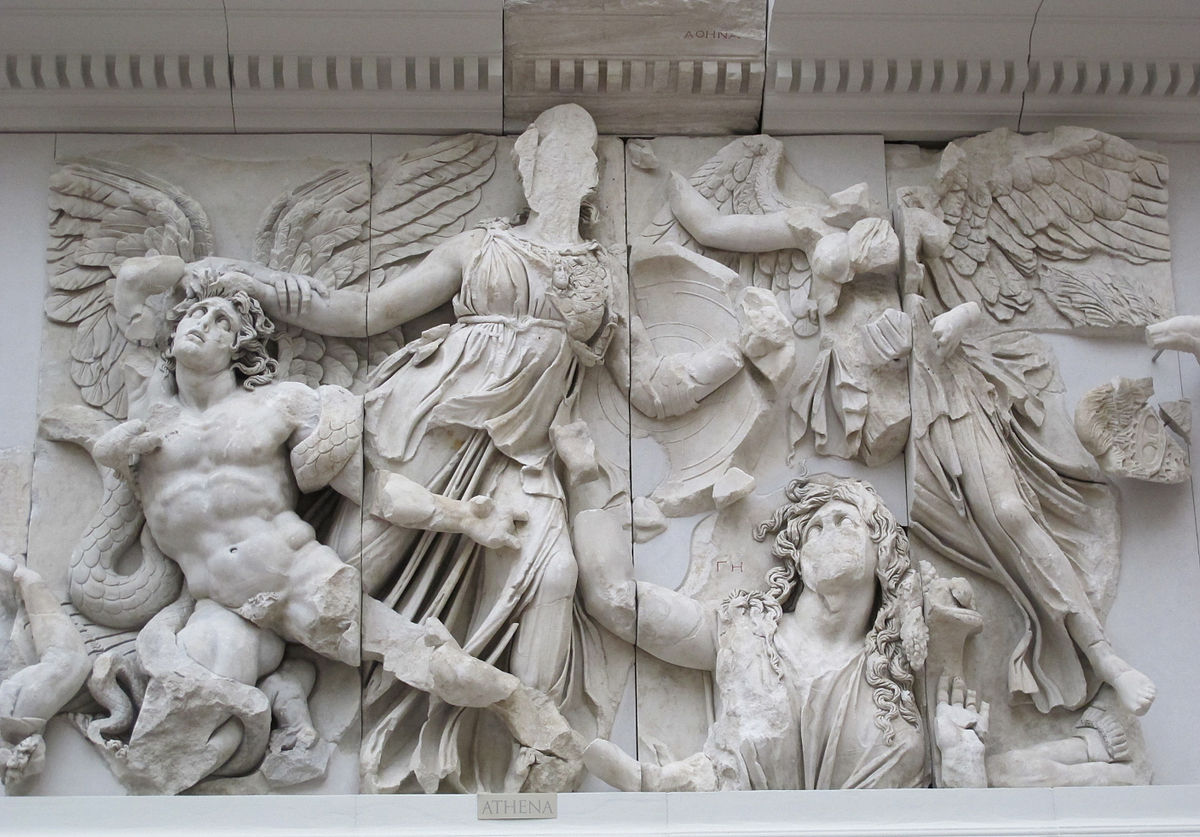

Key characters:
- Athena and Athena Nike
- Alkyoneos the giant
- Gaia the earth Goddess (mother of Alkyones)
Key words:
Architecture:
- ^^gigantomachy^^
- ^^gigantomy^^ scene
- overlapping
- wet drapery
Artistic:
- high-relief
- laurel crown (Given by Athena Nike to Athena)
- power and authority
The Alexander Mosaic (Pompeii, Italy - Battle of Issus) 🐎⚔
A decorative/utilitarian mosaic art piece depicting Alexander the Great in the chaotic battle of Issus 📮 on a chariot.
This art piece was discovered in the House of Faun, Pompeii.
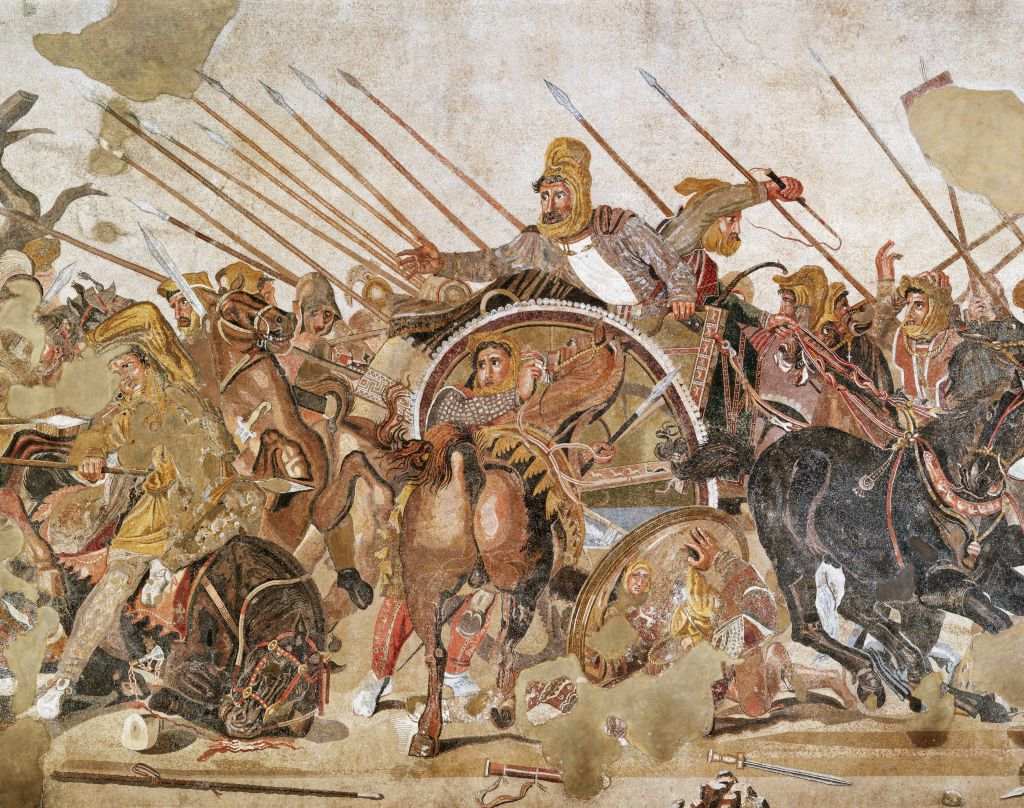

Commissioned/created by citizens of ^^Pompeii.^^
meant to be placed in a home as floor/wall tiles.
shows strong demonstrations of emotion.
Narrative: Alexander and his army is charging towards Darius III on a chariot. Darius’ army is also battling Alexander’s soldiers.
celebrates the victory over the Persians and the Battle of Issus 📮.
Key words:
Artistic:
mosaic
^^Tesserae^^ ^^(shards)^^
prespective
ground
^^foreshortening^^
foreground; middle ground; background ^^(Advanced perspective)^^
decorative / utilitarian
^^crowded composition^^
^^House of Faun, Pompeii^^
\
Key characters:
- Darius III
- Alexander the Great
- Charioteer
other facts:
first depictions of crowded composition
new words; advanced perspective, crowded composition
use of mosaic and tesserae again (used back in the Standard of Ur)
Nike of Samothrace (Victory of Samothrace, Greece) 🏆🥇
This 12 ft contrapposto wet-drapery marble sculpture was found with no head or arms. Patrons and artist is N/A.
- Conjectured to be a Masthead on a ship. (Victory monument).
- Made to celebrate naval battles on the island of Samothrace; is also apart of a ^^fountain.^^
- wet-drapery are moving against the strong wind in front of her, as well as her wings. Victory is ready to take off.
- There were many depictions of how Athena Nike would’ve posed in this sculpture.
- Athena Nike is symbolic of Victory. 🏆
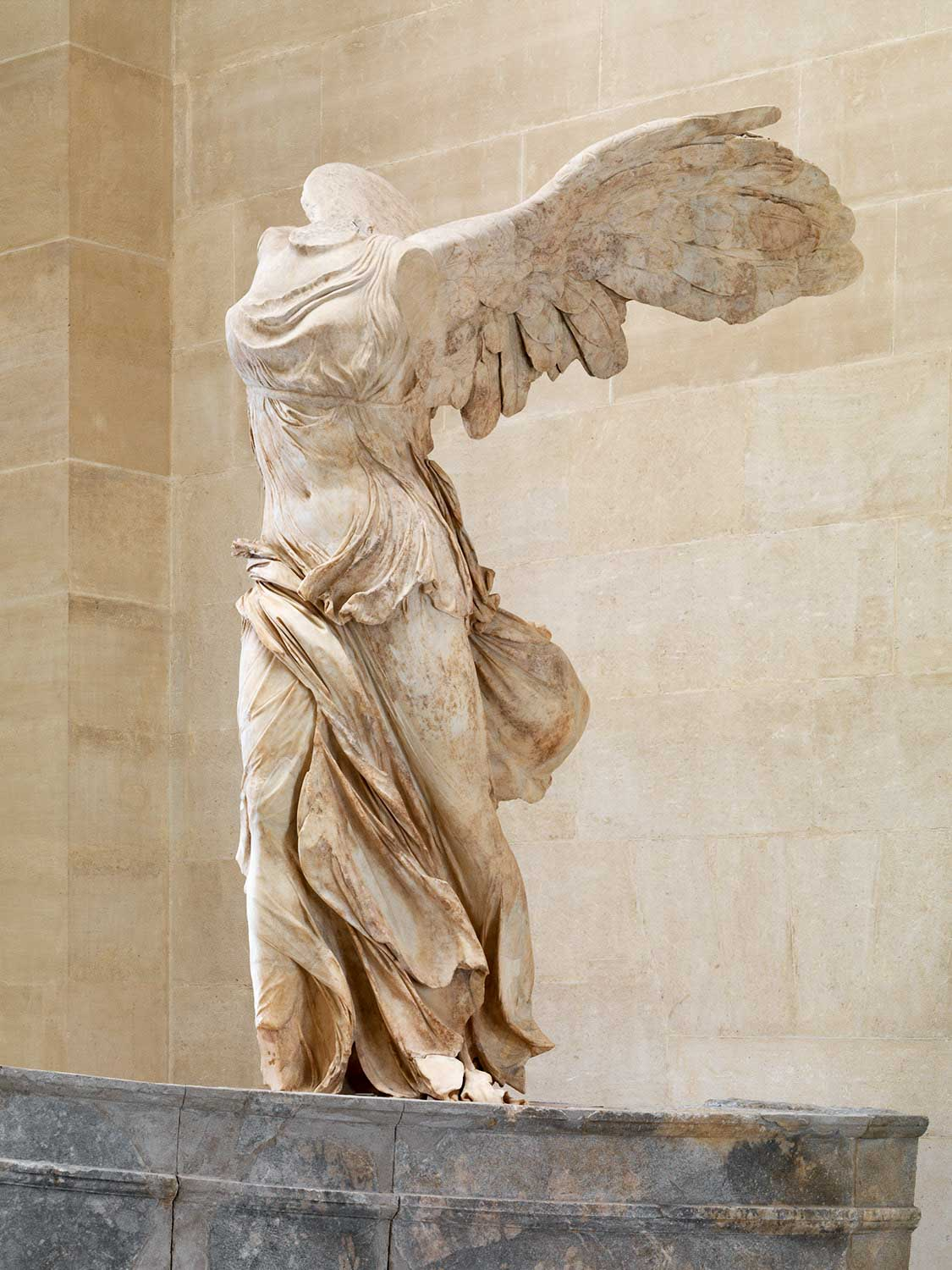

Narrative: The Nike of Samothrace was built to celebrate a naval battle at Samothrace.
this statue was apart of a Double-Tier fountain to create the illusion that Nike is on a boat.
- Nike of Samothrace was found on a fountain of 2 tiers (low; water and rocks > top tier; Athena Nike)
Key words:
wet-drapery
conrtapposto
double-tier (fountains)
marble
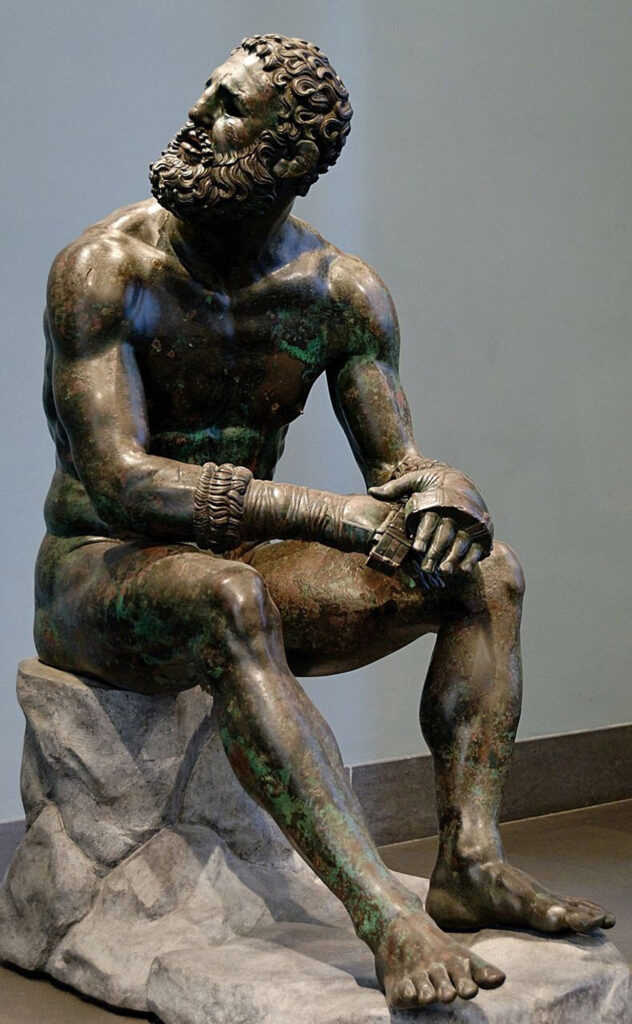
Seated Boxer (Quirinial - one of 7 hills, Rome) 🥊
- The bronze seated boxer sculpture depicts not of victory but of losing. Possibly an actual depiction of a real-life (famous?) athlete.
- Mostly inspired by the Lysippos (A statue that depicts a weary Hercules; Hercules is always depicted battling).
- All sections of the seated boxer is made from lost wax, then wielded together.
- Copper is used to depict blood, ear is in the shape of the cauliflower ears (type of boxing injury).
- Possibly a good luck charm for athletes. 🍀🥊
Key words:
lost wax
copper
bronze
stone
cauliflower ears
narrative: The seated boxer was a portrayal of a possibly real-life Greek athlete who lost a boxing match.
similar to the ^^superstition of rubbing a statue of^^ ^^Hercules for luck in battle;^^ the seated boxer also showed indications that people had been ^^rubbing it’s foot for luck.^^
- shows a lot of emotion, drama, and naturalism.