Apicomplexa (Sporozoa)
Coccidia Sporozoa - Apicomplexa & Microsporidia
Sporozoa
Lack means of locomotion
Life cycle alternates between sexual and asexual stages
Definitive hosts – sexual reproduction
Intermediate hosts – asexual reproduction
Two host life cycle
Terms
Sporogony
- Sexual reproduction of spores and sporozoites
Schizogony (human host)
- Asexual multiplication
Paroxysm
- Toxic material are released form ruptured RBC (allergic response).. shaking chills, high fever, sweating
Coccidia
Pathogenic blood coccidia
- Plasmodium sp. – malarai
- Babesia microti
- Toxoplasma gondii – toxoplasmosis
Pathogenic intestinal coccidia
- Sarcocystis sp.
- Cystoisospora belli
- Cryptosporidium parvum
- Cryptosporidium hominis
- Cyclospora cayetanensis
Pathogenic Blood Coccidia 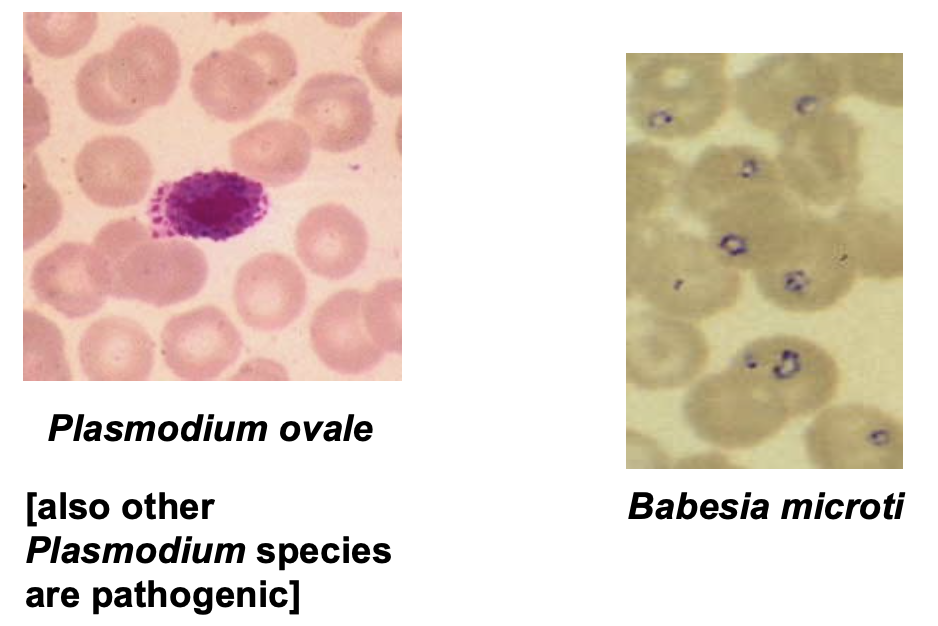
Plasmodium species
P. falciparum
P. vivax
P. ovale
P. malariae
Epidemiology
Causes malaria – one of the most common protozoal diseases in the world – kills 1-2 million/yr
Transmission: by Anopheles mosquito, blood transfusions, or transplacentally
Malaria
Symptoms
- Splenomegaly, chills, fever, sweats, anorexia, joint pain
- Leukopenia, normocytic anemia, and hemolytic anemia
Diagnosis
- ID of species-specific ring forms, gametes, and schizonts on giemsa blood sains (thick and thin smear)
Diagnostic Procedures
Thick Blood Smears
Thin Blood Smears
* Examine at 40x and oil immersion!
Plasmodium falciparum
Malignant malaria
tropics
36 to 48 hrs paroxysms
Infect RBCs (normal size)
Hemolytic anemia – blackwater fever
Diagnostic form are trophs (multiple ring forms) and crescent gametocytes in RBCs
Maurer’s clefts or dots (red)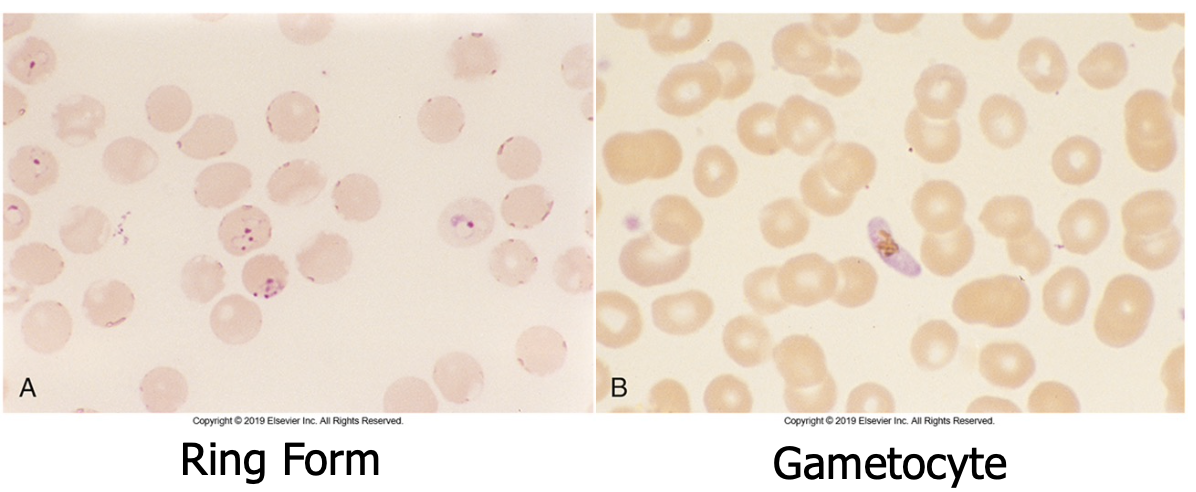
P. malariae
Quraan malaria
Paroxysms every 72 hrs
Tropics
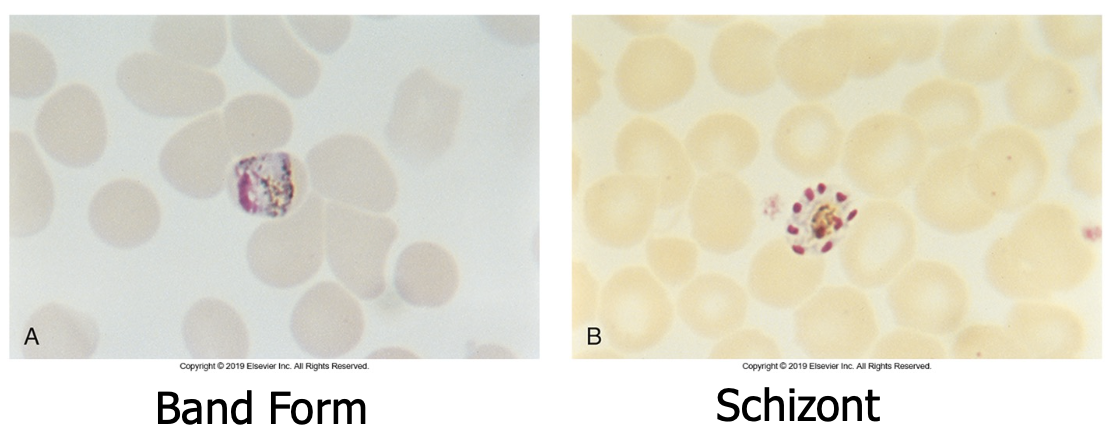
Diagnostics forms are trophozoite band forms and schizonts (6-12 merozoites that form a rosette)
Color plate:
Plasmodium vivax
Tropics
Tertian malaria
Most prevalent
Paroxysms every 48 hrs
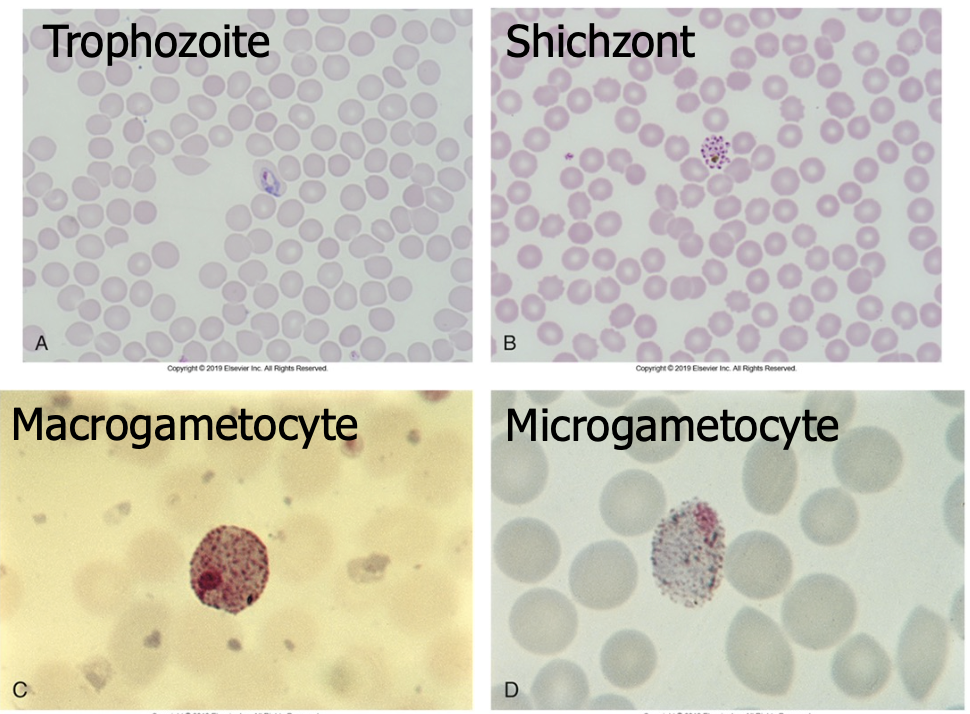
Diagnostic stages are ring forms infecting young RBCs, schuffner’s dots, and schizonts with 12 to 24 merozoites
Color plate:
Plasmodium ovale
Rare, West Africa
Ovale malaria
Paroxysms every 48 hrs
Diagnostics forms are ring forms, oval RBcs, schuffner’s dots, schizonts (8 to 12 merozoites)
Color plate:
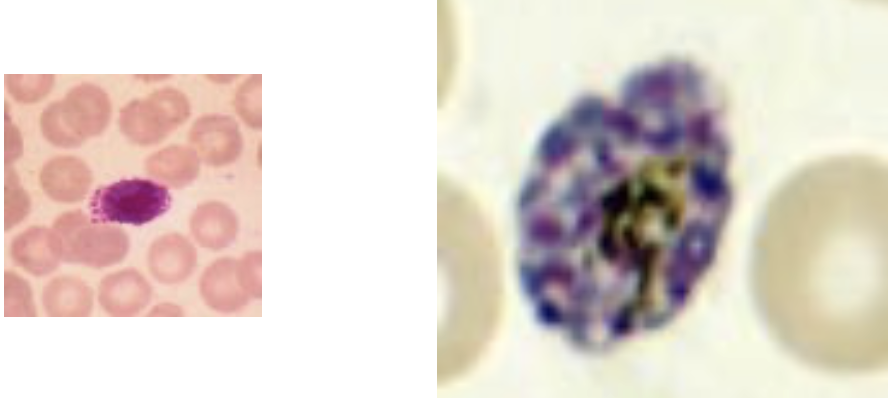
Plasmodium Summary
P. falciparum
- Multiple ring forms (double dot chromatin)
- Young and old RBC infected
- Mauer’s dots
- No schizont observed; gametocytes observed
P. malariae
- Single ring form (signet ring)
- Old RBCs infected
- Troph form band actress RBC
- Schizont: 6-12 merozoites
P. vivax
- Single ring form
- Young RBC infected (retic)
- Schuffner’s dots
- Schizont: 12-24 merozoites
Babesia species
Tick transmitted human infection and transfusion
Cases in the U.S.
Fever, chills, sweats, fatigue
Hemolytic anemia, spleen and liver disease
“Maltese cross formation” ring forms
Color plate: 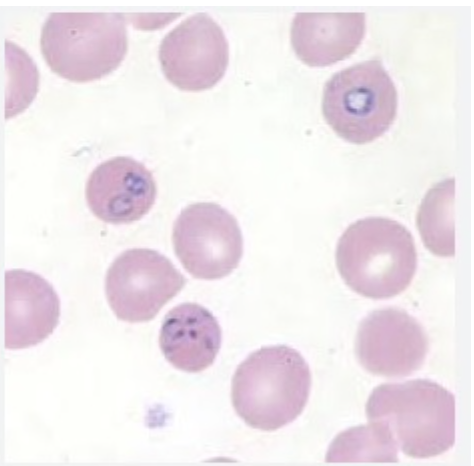
Pathogenic Intestinal Coccidia
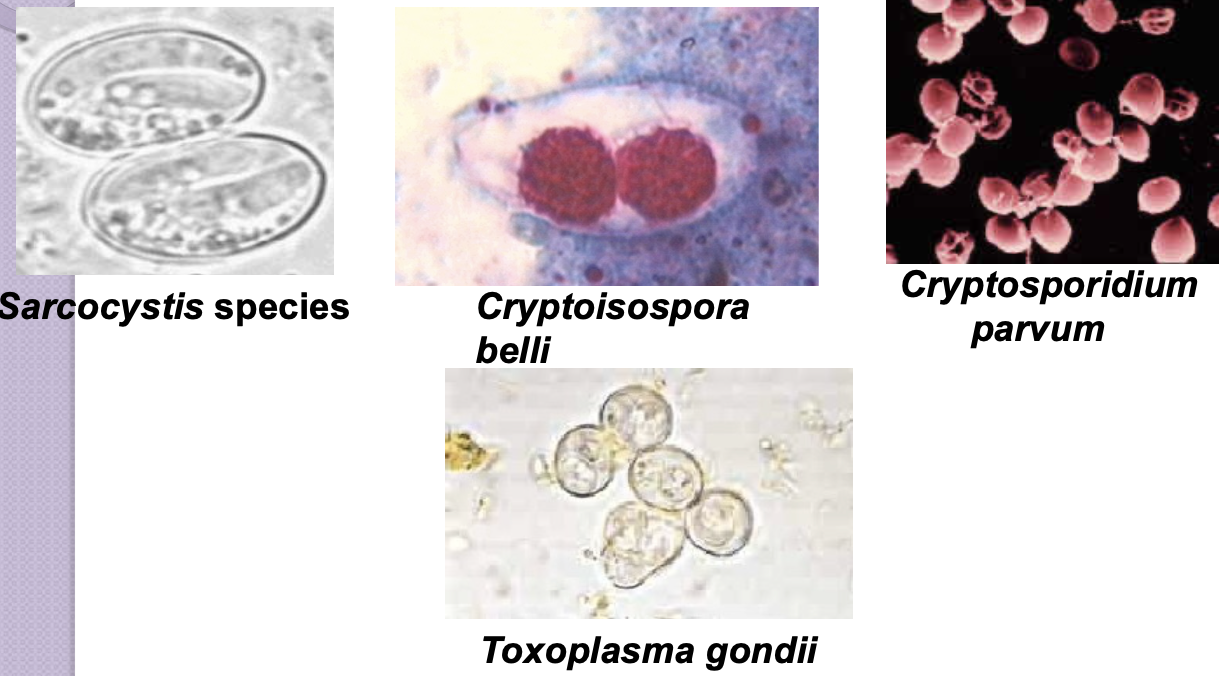
Toxoplasma gondii
Definitive host is the domestic cat
Oocysts are shed in cat feces and human become infected via contaminated food, drink, or hand to mouth transmission (cat litter)
Caution for pregnant females
Blood transfusions and organ transplant
Causative agent of toxoplasmosis
Clinical infections:
- Adults
- Asymptomatic mostly
- Mimics Mono
- Children
- Rarely: rash myocarditis, encephalomyelitis, hepatitis, retinochoroiditis (blindness)
- Immunocompromised and congenital are most at risk
Toxoplasma gondii Lab Diagnosis
Encysted tachyzoites in many tissues of the body
- Biopsy materials
Serology
- Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs)
- Titer rise
- Histology
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans
PCR
Cryptosporidium parvum & Cryptosporidium hominis
Common infection of cattle, rodents, and fowl
Transmission: ingestion of fecal-contaminated food or water (not killed by chlorine)
Symptoms: abdominal pain and diarrhea, sever in immunocompromised (HIV+)
Diagnosis
- acid -fast oocyst in feces, ID of organisms in biopsies, serologic tests, Mutli-plex PCR
Cystoisospora belli (Isospora belli)
Opportunistic pathogen
- Acute infections are clinically indistinguishable from C. parvum
- Most serious in immunocompromised patients
- Symptoms
- Low-grade fever, headache, diarrhea, and colicky abdominal pain
- Oocyst
- Elliptical or oval in shape
- 20 to 33 um long by 10 to 19 um wide
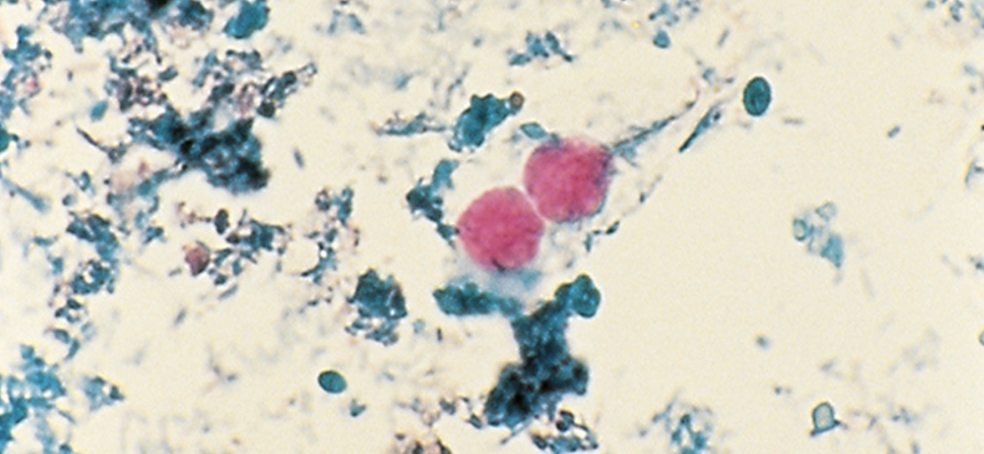
Cyclospora cayetanensis
Transmission
- Contaminate food & water
- Humans are the only known host
Symptoms
- Diarrhea alternating with constipation
- Anorexia, abdominal cramping, vomiting, low-grade fever, and nausea
- Self-limiting infection
- Opportunistic pathogen in immunocompromised host
Microsporidia
The phylum Microspora are often referred to as fungal-related parasites. A vast majority of these organisms are in the process of recategorization and are routinely referred to as ”Microsporidia.” Officallt they have been recategorized as fungi but almost all literature discusses them in the realm of parasites, and so shall we.
Microsporidia Diagnosis
Transmission
- Soil contaminated with spores from fevers or urine
Symptoms
- Diarrhea, cramps, loss of appetite, and fatigue
- Occasionally dehydration and weight loss
- Immunocompromised and HIV-positive patients
- Higher risk
Enterocytozoon bieneusi
- Intestinal and hepatobiliary infections
Encephalitozoon hellem
- Ocular infections
Encephalitozoon intestinalis
- Intestinal and disseminated infections