Transport in Animals (2.25-2.29)
Circulatory system: System of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one way flow of blood
Fish have a single circulation and a 2 chambered heart
- Every 1 circuit of the body blood passes through the heart once
- ==Body→Heart→Gills→Body==
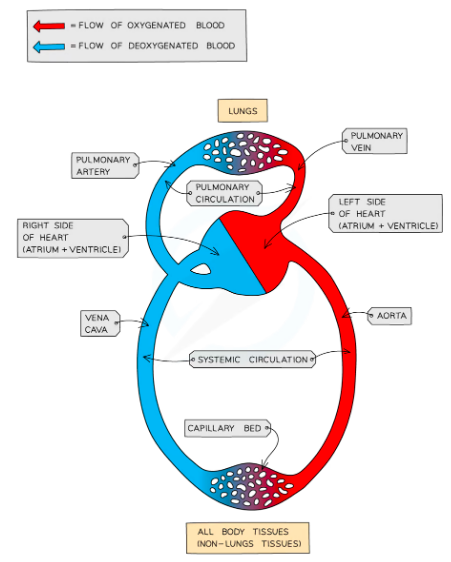
Mammals have double circulation and a 4 chambered heart
Every 1 circuit of the body blood passes through the heart twice
- RIGHT- recieves deoxygenated blood from body (atrium) pumps to the lungs (ventricle)
- LEFT- revieves deoxygenated blood from lungs (atrium) pumps to body (ventricle)
- ==Body→Heart→Lungs→Heart→Body==
Advantages of double circulation
Blood travelling through capillaries loses pressure so will travel slow
Returning blood to the heart allows the pressure to be raised again
Cells are supplied with oxygen and glucose faster and more frequently for respiration
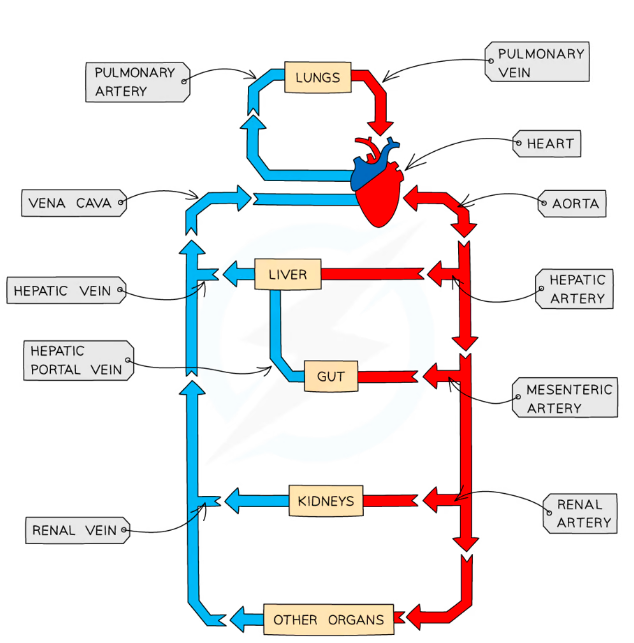
Veins: Carry blood towatds the heart
- Main vein is the vena cava
Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart
- Main artery is the aorta
- The pulmonary artery carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
- The pulmonary vein carries blood from the lungs to the left atrium
Septum: Muscle wall that seperates two sides of the heart preventing the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Ventricles: Have a thicker muscle wall than the atria because they pump blood at higher pressure
- Left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall compared to right because it pumps blood to entire body at high pressure
- Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs for gas exchange
Atria: The right and left atrium contracts to pump blood into the right and left ventricles respectively
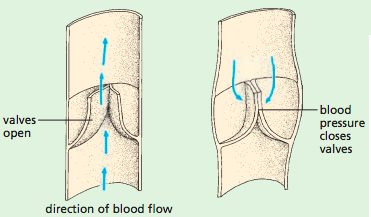
Valves: Prevent the backflow of blood and ensure one way flow
- The aterioventricular valves separate the atrium and ventricles on both sides of the heart.
- Open when atria contract, close when ventrcles contract
- Semilunar valves are found within the pulmonary arteries and the aorta
- Open when ventricles contract, close when atria contract
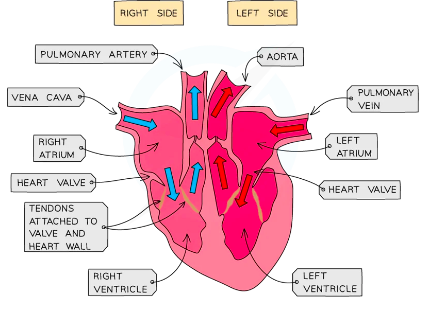
- Deoxygenated blood flows from the body to the right atrium through the vena cava
- Once the R.A is filled it contracts and the tricuspid valve is pushed open
- Blood is pushed into the right ventricle
- The right ventricle contracts (semilunar valve opens) blood is pushed through semilunar valves into pulmonary artery
- Blood travels to lungs and gas exchange takes place
- Oxygenated blood returns to left atrium through pulmonary vein
- Passes through bicuspid valve into left ventricle
- Muscle wall contracts strongly to push blood out into aorta through semilunar valves (prevent backflow of blood) to the body at high pressure
Heart activity and Electricity
- Heart activity can be measured by:
- Using an ECG (electrocardiogram)
- Measure pulse rate
- Listening to sounds of valves closing (stethescope)
- During exercise heart rate increases and may take time to return to normal
- It is important so enough blood is taken to working muscles to provide enough glucose and oxygen for increased respiration and theres fast waste removal
- After exercise heart continues to beat fast to ensure all excess waste is removed
- ‘Oxygen debt’ built up due to anaerobic respiration of muscles to be repaid following exercise through aerobic respiration of lactic acid in the liver
- Anaerobic Respiration: Glucose→Lactic acid
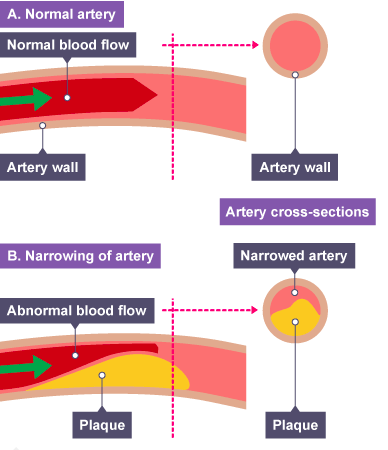
Coronary Heart Disease
- ==Muscle cells in the heart need their own supply of blood to deliver oxygen and glucose==
- Blood is supplied by coronary arteries
- If the coronary arteries become blocked by fatty tissue deposites (cholesterol build up)
- ==Poisonous wastes build up and the heart muscles are deprived of oxygen and glucose==
- Arteries are not elastic so they can not stretch to accomodate blood forced through
Coronary heart disease
Partial blockage of coronary arteries creates restricted blood flow to heart muscle cells; angina
Complete blockage leads to a heart attack; cells in the area of the heart cannot respire/ contract
- Other body tissues can not recieve their supply of oxygen and glucose
Risk Factors
- Poor Diet - high levels of saturated fats increase levels of cholesterol increasing chance of build up of plaque
- Stress- Hormones cause increase blood pressure
- Smoking- nicotine narrows blood vessels and increases blood pressure
- Age
- Genetics
- Gender- more common in males
Treatment
Aspirin: Dilutes blood and so reduces blood clotting
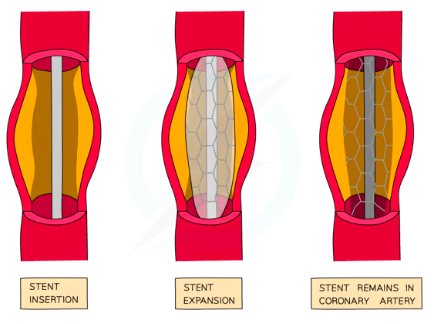
Angioplasty: Catheter threaded through the groin up the blocked vessel
Balloon inserted into catheter pushed up blocked vessel and inflated
Flattens plaque against wall of artery clearing blockage
Stent inserted to keep artery clear
Sometimes coated with drug to prevent further build up
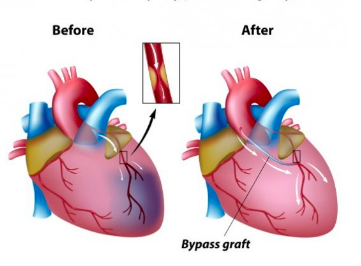
Coronary bypass surgery: Piece of blood vessel is taken from patients lef or arm
Used to create new passage to cardiac muscle BYPASSING the blocked area
Blood vessels
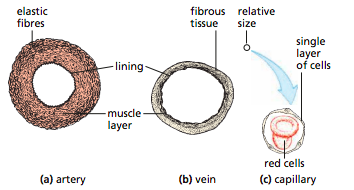
Arteries:
- Carry oxygenated blood at high pressure away from the heart
- Thick muscular walls containing elastic fibres that expand and relax
- To withstand high pressure of blood and maintain blood pressure as it recoils after blood passes
- Narrow lumen to maintain high pressure
- Blood flow is fast
Veins:
Carry blood at low pressure towards the heart
Carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary veins)
Thin walls
Large lumen to reduce resistance to blood at low pressure
Have valves that prevent the back flow of blood as its under low pressure
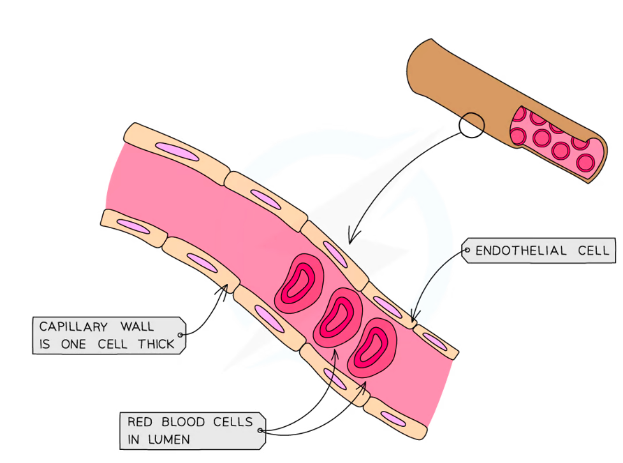
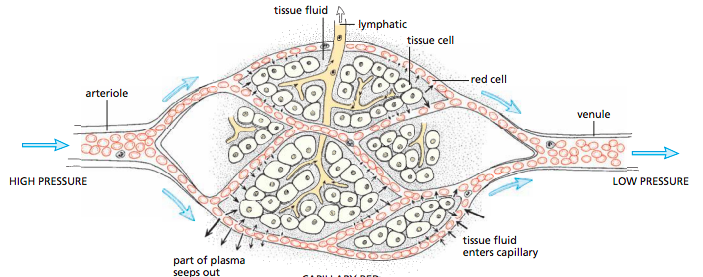
Capillaries
Carry blood at low pressure
Both oxygenated and deoxygenated
One cell thick walls for easy diffusion in and out
‘Leaky’ walls allow blood plasma to leak out and forn tissue fluid surrounding cells
Connects arteries and veins
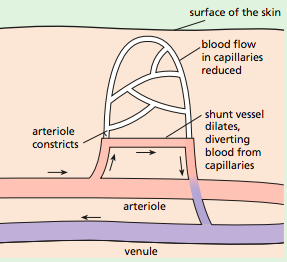
Arterioles: Smaller branches of an artery that eventually form capillaries
- Arterioles have muscular/elastic walls that can constrict & dilate in order to regulate blood flow.
Venules: Small vessels formed from the joining of the capillaries and combine to form a vein.
Shunt vessels: Connect blood directly from arterioles to venules forming an alternative route dor blood flow
- Have walls that can construct & dilate in order to regulate blood flow \n
| Organ | Towards Organ | Awat from organ |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | Vena Cava, Pulmonary Vein | Aorta, Pulmonart Artery |
| Lungs | Pulmonary artery | Pulmonary vein |
| Kidney | Renal Artery | Renal Vein |
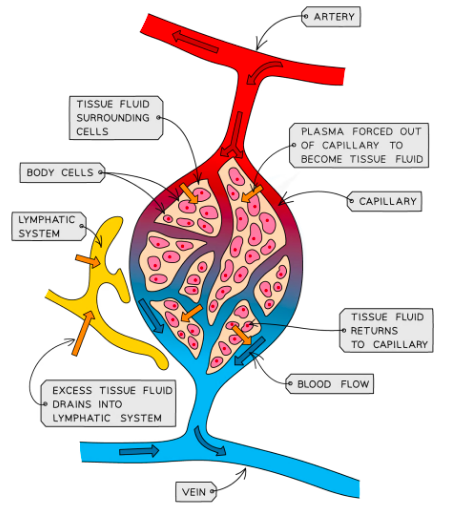
Lymphatic System
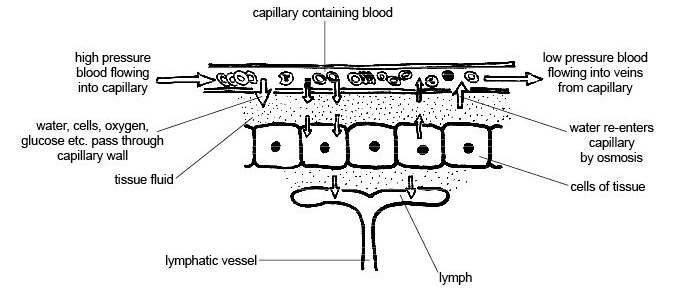
Walls of capillaries are thin; water dissolved substances can easily leak out of them
==Plasma is forced out of the capillary to become tissue fluid==
Cells exchange materials across membranes with tissue fluid
If fluid leaked out i smore than fluid returned
- The excess leaked fluid surrounding capillaries passes into lumphatic system (becomes lymphatic fluid)
Lymphatic system: Tubes which flow from tissues to heart
- The lymphatic system is composed of lymphatic vessels which carry “lymph” and lymph nodes which produce lymphocytes for immunity.
Blood
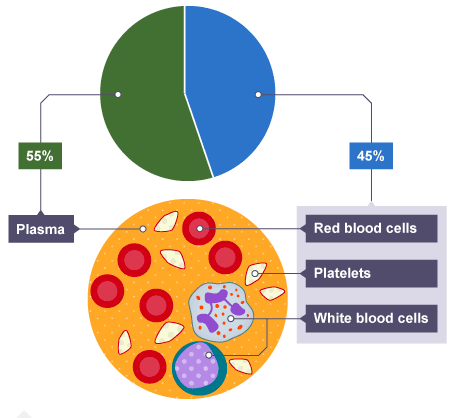
==Red Blood Cells:== Transport Oxygen from lungs→Respiring tissues
- Prepare Carbon dioxide for transport
- Small, biconcave in shape, flexible and have no nucleaus to create mre space for oxygen; can squeeze through capillaries
- ==Haemoglobin==- Iron containing pigment pick Oxygen and drops
==White Blood cells:==
- Phagocytes- defend against pathogenic organisms by phagocytosis
- Sensitive cell membrane detecs chemicals produced by pathogen
- Engulfes pathogen
- Releases digestive enzymes on pathogen
- Digested and excreted
==Multilobed nucleus and non granular cytoplasm==
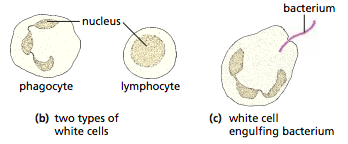
Lymphocytes: produces antibodies and antitoxins
==Large round nucleaus and clear non granular cytoplasm==
==Plasma:== Transporting carbon dioxide, digested food, urea, hormones and heat
==Plateles====:== Blood clotting
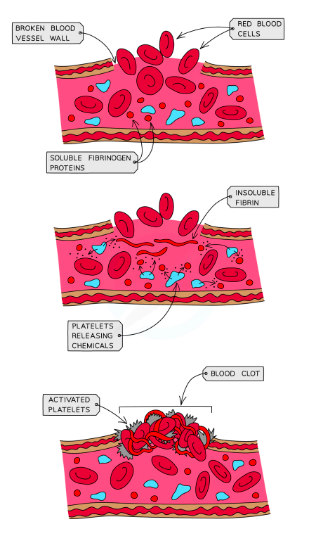
Blood Clotting
- Prevents continued blood loss
- Prevents entry of microorganisms
Process
- Skin broken; platelets arrive at site
- Platelets release chemicals that stimulate the conversion of ==soluble fibrinigen → Insoluble fibrin==, forming insoluble mesh trapping RBCs and froming a clot
- Clot dries and becomes a scab to protect wound