Peripheral Nervous System
● PNS
○ Receive and process information from sense organs, and to bring about responses to the information received.
○ Along with the endocrine system, it coordinates all our voluntary and involuntary actions.
○ What is the PNS?
■ Consists of nerve fibres, which carry information to and from the CNS, and groups of cell nerve bodies (ganglia), which lie outside the brain & spinal cord.
■ Nerve fibres arranged into nerves which arise from the brain and spinal cord.
■ Cranial Nerves (12 pairs)
■ 12 pairs of nerves arising from the brain
■ Most are mixed nerves:
■ contain fibres that carry information to brain (sensory) & fibres that carry information away from brain (motor)
■ Few carry only sensory or only motor
■ Spinal Nerves (31 pairs)
■ 31 pairs arising from the spinal cord
■ All mixed nerves & each joined to spinal cord by 2 roots:
■ Dorsal root: contains axons of sensory neurons that have cell body in small swelling known as dorsal root ganglion
■ Ventral root: contains axons of motor neurons that have their cell bodies in grey matter of spinal cord
● Divisions of the PNS
○ The PNS can be divided into a number of divisions. We need to be able to compare the following divisions with one another:
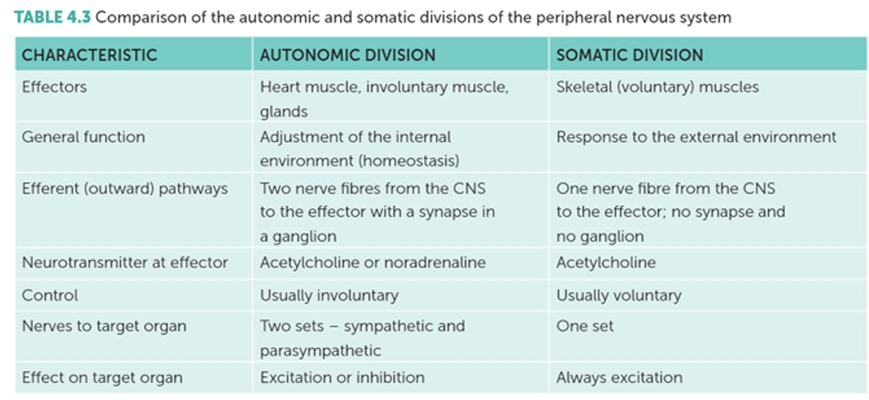
○ Afferent Division
■ Sensory division - Fibres that carry impulses into the CNS
■ Somatic sensory neurons: Carried by sensory nerve cells from receptors in skin & around muscles & joints
■ Visceral sensory neurons: Sensory nerve cells that take impulses from internal organs
■ Motor Division - Fibres that carry impulses away from CNS
■ Somatic division: Takes impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
■ Autonomic division: Carries impulses from the CNS to heart muscle, involuntary muscle & glands
○ Efferent Division
■ Motor Division - Fibres that carry impulses away from CNS
■ Somatic division:
Takes impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
■ Autonomic division: Carries impulses from the CNS to heart muscle, involuntary muscle & glands
■ Responsible for control of the body’s internal environment & is involved in many mechanisms to keep internal environment constant
■ Usually operates without conscious control
■ Regulated by group of nerve cells in Medulla Oblongata, Hypothalamus & Cerebral Cortex
■ Auto means ‘self’, nomo means ‘govern’ = Autonomic System is self governing
■ ANS Control
■ Nerve fibres of ANS make up part of spinal nerves & part of some of cranial nerves
■ Carry impulses to heart muscle, internal organ muscles & glands
■ 2 motor neurons involved in autonomic pathway.
■ One neuron has its cell body in the CNS, whilst the other has its cell body in a ganglion
■ 1 motor neuron in somatic pathway
■ Parasympathetic vs Sympathetic Division
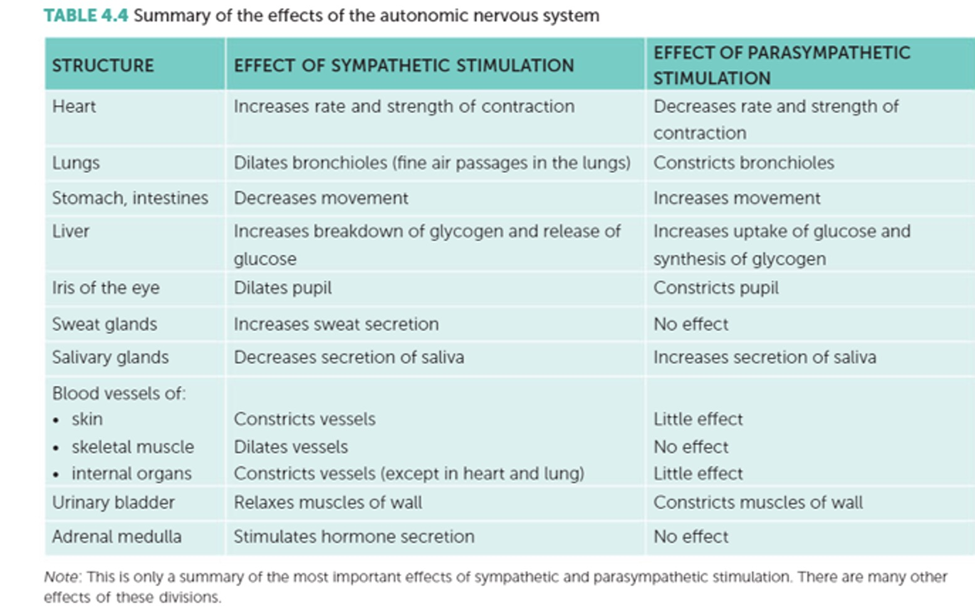
■ Parasympathetic: generally produces responses that maintain body during relatively quiet conditions. Nerve endings release acetylcholine
■ Sympathetic: produce responses that prepare body for strenuous physical activity. Fight-or-flight response. Nerve endings release noradrenaline
■ Under normal circumstances we are not aware of the activities of ANS
■ Right now your sympathetic & parasympathetic nerves are sending out impulses to the internal organs to maintain stability of body functions
■ Eg. Heart with only sympathetic input - rate of 100 beats per minute, parasympathetic stimulation keeps it down to around 70 to 80 beats per minute
■ In threatening situation, balance between sympathetic & parasympathetic stimulation is changed, sympathetic becomes dominant
■ Fear, stress, anger, danger, competition all evoke fight or flight response or alarm reaction
■ Prepares body for increased activity
 Knowt
Knowt