Unit 7: Air Pollution
{{7.1 and 7.2: Intro to Air Pollution and Photochemical Smog{{
^^The Atmosphere Consists of Several Layers^^
- Atmosphere: Thin layer of gasses around the earth
- Density: Number of gas molecules per unit of air volume. Decreases the higher up in the atmosphere we go.
- Atmospheric Pressure: Force per unit area of a column of air. Decreases with higher altitude.
^^Air Movement and Chemicals in the Troposphere Affect the Earth’s Weather and Climate^^
- Troposphere: Closest to the earth’s surface. 75 to 80% of earth’s air mass
- Composition of gases: 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen
- Rising and falling air currents and greenhouse gases play major roles in weather and climate
- Greenhouse gasses include: CO2, H2O, CH4, and N2O
^^The Stratosphere is Our Global Sunscreen^^
- Stratosphere: 17 to 48 kilometers above the earth’s surface. Lower volume of water vapor and higher concentration of ozone.
- Ozone Layer: Filters 95% of harmful UV radiation and allows life to exist on land.
^^Air Pollution Comes From Natural and Human Sources^^
- Air Pollution: chemicals in the atmosphere.
- Can be harmful to organisms, ecosystems, and human-made materials, or it can change the climate.
- Natural sources: Wind-blown dust, pollutants from wildfires or volcanic eruptions, volatile organics released by plants.
- Human sources: Mostly in industrialized and urban areas things such as motor vehicle exhaust or fossil fuels.
- Stationary Sources: Power plants and industrial facilities (places that stay in one place)
- Mobile Sources: Motor vehicles (moving pollution sources)
^^Major Outdoor Air Pollutants^^
- Industrial smog: Caused primarily by burning coal
- Photochemical smog: Caused by car exhaust, industrial facilities, and power plants.
- Carbon oxides: Carbon monoxide (CO2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Nitrogen Oxides and nitric acid: Acid decomposition plays a major role in photochemical smog
- Sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid: Reduce visibility and aggravate breathing problems
- Particulates or Particles: Made up of tiny pieces of solids or liquids that are in the air.
- Ozone: Can cause coughing and breathing problems
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Large groups of chemicals that are usually found in products that we use to clean our house (Methane, dry cleaning fluids, gasoline, plastic, cleaning supplies)
^^Air Pollution Comes from Natural Human Sources^^
- Primary Pollutants: Emitted directly into the air
- Secondary Pollutants: Formed from reactions of primary pollutants
^^Effects of Air Pollution^^
- Flows north which can create artic haze
- Arctic haze: when polluted air from populated areas flows north to the artic creating high rates of air pollution there.
- Since the 1970s air quality has improved in developed countries
- Particles can get inside our bodies specifically our lungs
- Can cause cancer, asthma, heart attack, and stroke
^^Nitrogen Oxides (NO, NO2)^^
- Human sources: Motor vehicle and fossil fuel combustion
- Natural Sources: Forest fires, lightning, soil microbes
- Effects: Respiratory irritant, acid rain, smog
^^Ground Level Ozone (O3)^^
- Sources: Secondary pollutants formed by sunlight and water reacting with VOCs, NOx, and O2
- Effects: Respiratory irritant, damages plant
- Stratosphere Ozone: Good (6-30 miles up)
- Troposphere Ozone: Bad (<6 miles)
^^Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)^^
- Human sources: From the combustion of coal and oil
- Natural sources: volcanoes or forest fires
^^Carbon Monoxide (CO)^^
- Formed during incomplete combustion of most matter
- Vehicle exhaust, other combustion
- Especially danger our indoors with poor ventilation--manure, charcoal, kerosene
^^Lead^^
- Sources: gasoline, paint in older buildings, pipes aka flint in them
- Toxic to the central nervous system of living organisms
^^Particulate Matter (PM)^^
- Human sources: Combustion of fossil fuels and biomass
- Diesel is much worse than gasoline
- Natural sources: Road dust, rock crushing, volcanoes, fires, dust storms
- It can block the sunlight and that can prevent the photosynthesis of plants which can lead them to die resulting in the food web being destroyed and it can harm the ecosystem.
- Particulate sizes
- PM2.5: Greatest health concern, can get stuck deep in the respiratory tract, more toxic
- PM10: Small and it can be hard to filter by the respiratory tract, health concern
- Anything larger than PM10 will be caught and filtered out
^^Other Major Pollutants:^^
- Bioaccumulates: Increase in contaminants in aquatic creatures.
- Hydrocarbons
- from building supplies and household products
- Examples: Benzene, toluene, formaldehyde
- Plants also release VOCs it’s natural though
- Mercury
- Coal and oil combustion: Concentrations have increased in fish--bioaccumulation
- Mercury Cycle:
- Mercury is emitted into the atmosphere
- It is deposited through rain, snow, gases, and particles
- Then it accumulates in lakes, reservoirs, and forests
- It is transported through watersheds and converted to methylmercury
- Methylmercury bioaccumulates in food webs
- How it enters our environment
- Deposition from atmosphere
- Soil contamination
- Urban sewage system
- Leakage in groundwater and water bodies
- Landfill
- Leakage into groundwater
- Coal powerplant
- Waste incineration and cremation
- Contaminated surface and water evaporation
- Cement plant
- Chlor-alkali plant
- Vinyl Chloride Monomer Plant
- Artisanal and small-scale gold mining
- Mercury is released into streams and water bodies
- Predatory fish eat smaller fish that are exposed to mercury and have a lot in it due to biomagnification
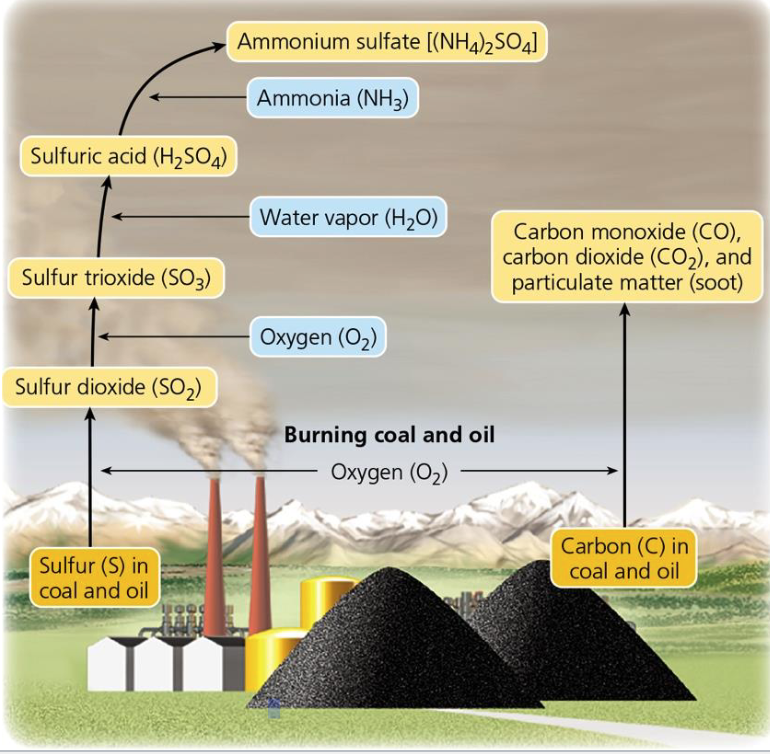
^^Burning Coal Produce Industrial Smog^^
Chemical composition of industrial smog
- Sulfur dioxide, sulfuric acid, and suspended solid particles
Combustion of coal and oil forms carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and soot
Common in industrialized urban areas
- Examples→ China, India, Ukraine
- Beijing's air quality is among the world’s worst
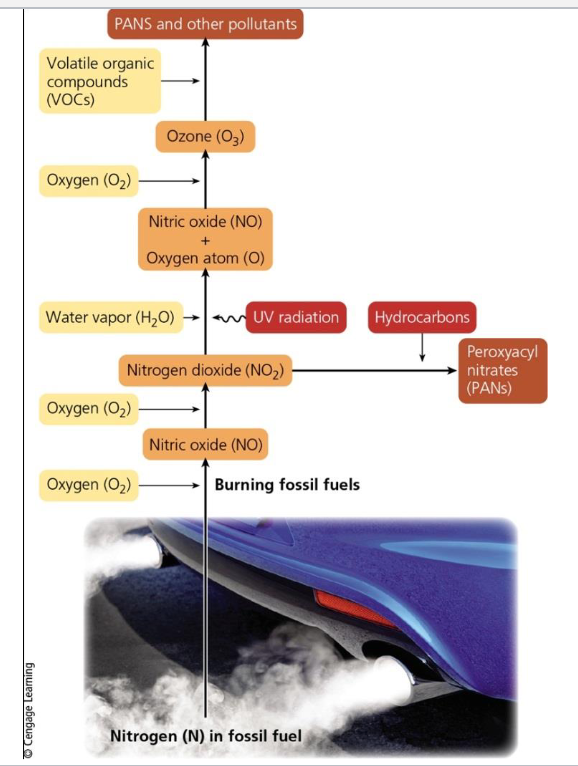
^^Sunlight Plus Cars Equal Photochemical Smog^^
Photochemical smog forced under the influence of the sun’s UV radiation
VOCs + NOx + Heat + Sunlight
- Yields:
- Ground level 04 and other photochemical oxidants
- Aldehydes
- Other secondary pollutants
^^Consequences of Photochemical Smog^^
- Respiratory problems- asthma, bronchitis, emphysema
- Plant damage- crops, carbon cycle impacted
- Greenhouse gas- absorbs infrared radiation (heat energy) from Earth
^^Clean Air Act^^
- Clean air act: Designed to control air pollution on a national level
- EPA develops and enforces regulations to protect the general public from exposure to airborne contaminants that are known to be hazardous to human health
- Industrial production is a major greenhouse gas source
- Iron, steel, and oil production release a lot of fossil fuels
{{7.3: Thermal Inversion{{
^^Thermal Inversion^^
- A layer of warm air traps cool air under it
- This means pollutants can also get trapped
- Specifically in valleys
^^Causes^^:
- Warm fronts/high pressure
- Valleys
- Areas of oceanic upwelling
- Oceanic Upwelling: When cold deep water from the bottom of the ocean rises to the surface.
- When radiation from the earth exceeds radiation received from the sun (specifically during winter and at night)
- At poles during winter nearly always present (overland)
- Only on land in general as the ocean retains heat
^^How to mitigate the effects^^
- Drive less
- Take public transportation
- Be careful about what you burn
{{7.4: Natural Sources of CO2 and Particulates{{
- Oceanic atmosphere exchange- 40%
- Plant and Animal Respiration- 30%
- Soil Respiration and Decomposition- 30%
- Volcanic Eruptions- 0.03%
^^Particulate Matter^^
- Sea salt
- Dust (airborne soil)
- Secondary sulfate
- Pollen
- Black carbon from wildfires
- Volcanic ash
{{7.5: Indoor Air Pollution{{
- Health problems can be caused by indoor air pollutants such as mold, carbon monoxide, dust, rote, etc.
^^Natural^^
- Radon
- Mold (airborne spores)
- Dust
^^Radon^^
- Radon 222 (most stable isotope; half-life ~ 4 days)
- Naturally occurring radioactive gas
- Produced by the decay of uranium found in rocks and soils
- Moves up through the soil and enters the home via the basement or crack in the walls or foundation
- Dissolves in groundwater that enters homes through a well
- Unit of measurement: pCi/L = Picocuries/liter
- Recommended
- World Health Organization: 2.7 Level
- EPA: 4.0 (equivalent to 100 chest X-rays)
- #1 environmental cause for cancer
- #2 cause of lung cancer deaths
- Attach to dust or smoke, enters through the respiratory system and decays internally, emitting alpha, beta, and gamma rays
- Alpha radiation damages lung tissue
- Prevention:
- Stop smoking
- Use fans to circulate air indoors
- Seal cracks in floors and walls
^^Anthropogenic^^
- Insulation
- Lead from paint
- VOCs (like formaldehyde from building materials, furniture, upholstery, and carpeting)
- Kitchen Cabinet Manufacturers Association
^^Combustion^^
- Carbon monoxide
- NOx
- SO2
- Particulate matter
- Tobacco smoke
^^Developing Countries^^
- Indoor burning of wood, charcoal, dung, crop residues, coal
- Poor suffer the greatest risk
^^Countries?^^
- Indoor air pollution is a bigger problem than outdoor air pollution
- 11 of the common air pollutants are higher inside than outside
- Greater in vehicles than outside
- Health risks magnified: people spend 90% of their life indoors
^^Sick Building Syndrome^^
- Describes poor air quality in a building
- Causes illnesses to anyone inside the building, especially in places such as office buildings or schools because you spend an extended period of time there
- Headache, cough, fever, skin rash, muscle ache, sore throat
{{7.6: Reduction of Air Pollutants{{
^^Methods to Reduce Air Pollutants^^
- Regulatory Practices
- Conservation Practices
- Alternative Fuels
^^Vapor Recovery Nozzle^^
- Vapor Recovery Nozzle: Prevents fumes from escaping into the atmosphere when fueling a motor vehicle
- Regulatory practice
^^Catalytic Converters (1975)^^
- Catalytic Converter: Devices for internal combustion engines that convert pollutants in the exhaust into less harmful molecules
- Input: Carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, hydroxides
- Output: Carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen
^^Scrubbers^^
- Industrial
- Scrubbers: Remove particulates and gases from industrial exhaust streams.
- Wet Scrubber: Introduces the dirty gas stream with a scrubbing liquid -- typical water
- Particulate gases are collected in the scrubbing liquid
- Generally the most appropriate for collecting both particulate and gas in a single system
- Dry Scrubber: Is sprayed into an exhaust system
- Pollutants are neutralized
- React and turn into a different substance
- That substance then falls out of the gas stream or is caught in a particle screen
^^Coal Burning Power Plant^^
- Electrostatic Precipitator: Dirt particles gain a negative charge from one wire or plate before being attracted to a second wire or plate with a positive electric charge for collection and disposal.
- They can be expensive so they are not used so much
^^Desulfurization^^
- Reduce SO2 (sulfur dioxide) emissions
- Burn coal near CaCO3 (calcium carbonate)---produces CaSO4 (sheetrock-- drywall)
^^Additional Solutions^^
- Energy-efficient power generation and buildings
- Improve waste management
- Greener and more compact cities
- Reduce agricultural burning
- Access to clean, affordable fuels
- Safe and affordable public transit
^^Laws and Regulations^^
- United States: Clean air acts: 1970, 1977, and 1990 created regulations enforced by states and cities
- EPA
- Established air quality standards for 6 outdoor pollutants
- Carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, suspended particulate matter, ozone, and lead
- EPA’s national emission standards for 188 hazardous air pollutants (HAPs)
- Toxic Release Inventory (TRI)
- New U.S. regulations
- Limit CO2 emissions from coal-fired power plants
- New air quality standards in China
- Ban on high sulfur, high ask content coal in major cities
- Levels of key air pollutants in the US dropped between 1980-2015, despite the increases in other factors
^^Using the Marketplace to Reduce Outdoor Air Pollution^^
- Buy and sell air pollution allotments in the marketplace
- 1990 Clean air act authorized emission trading or cop-and-trade program success depends on
- How low initial cap is set
- How often it is lowered
- Cop-and-Trade: Everyone has a set limit of pollution emissions and if a company does not use it entirely they can save it or they can sell it to another company.
^^Motor Vehicle Air Pollution Solutions^^
Prevention
- Walk or bike or use mass transit
- Improve fuel efficiency
- Get older and polluting cars off the road
Reduction
- Require emission control devices
- Inspect car exhaust systems twice a year
- Set strict emission standards
^^Indoor Air Pollution Solutions^^
- Prevention
- Ban indoor smoking
- Set stricter formaldehyde emissions standards for carpet, furniture, and building materials
- Prevent radon infiltration
- Use naturally based cleaning agents, paints, and other products
- Reduction/Dilution
- Use adjustable fresh air vents for workspaces
- Circulates air more frequently
- Circulate a building’s air through rooftop greenhouses
- Use solar cookers and efficient, vented woodburning stoves
- What can you do?
- Test for radon and formaldehyde inside your home and take corrective measures as needed
- Do not buy furniture and other products containing formaldehyde
- Smoke outside or in a closed room with ventilation going outdoors
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in sleeping areas
- Use fans to circulate indoor air
- Grow more houseplants
- Do not store gasoline, solvents, or chemicals inside a home or attached garage
- Remove shoes before entering the house to reduce dust, lead, particulate matter, and pesticides
7.7: Acid Deposition
^^What is it? Why is it a problem?^^
- Caused mainly by coal-burning power plants and motor vehicles emissions
- Threatens human health, aquatic life, ecosystems, forests, and human-built
- Human-generated NOx and SOx in the atmosphere
- Wet deposition: Acidic rain, snow, fog, or cloud vapor
- Dry deposition: Acidic particles
- Substances remain in the atmosphere for 2-14 days
^^Sources^^
| Nitrogen Oxides (NO, N2O, NO2) | Sulfur Oxides (SO2, SO) | |
|---|---|---|
| Natural | lightning, microbes | Volcanoes |
| Anthropogenic | Motor vehicles and coal-burning power plants | Coal-burning power plants |
^^Harmful effects^^
- Contributes to respiratory disorders
- Releases toxic metals from soils and rocks
- Bioaccumulation in fish
- Lower pH in aquatic ecosystems
- Leaches soil nutrients
- Damages forests (Biodiversity + ecosystem service)
- Damages statues and buildings
- Large risk to downwind communities
- Property values are affected
- Entire communities leave and/or are negatively affected
- Regional differences in soils and bedrock affect the degree of a harmful impact
- Limestone bedrock (CaCO3) can neutralize acid rain (buffering ability)
^^Solutions^^
- Prevention
- Reduce coal use and burn only low-sulfur coal
- Use natural gas and renewable energy resources in place of coal
- Remove SO2 and NOx from smokestack gases and remove NOx from motor vehicular exhaust
- Tax SOx emissions
- Cleanup
- Add lime to neutralize acidified lakes
- Add phosphate fertilizers to neutralize acidified lakes
- Add lime to neutralize acidified soils
{{7.8: Noise Pollution{{
^^What is it?^^
- Sound at levels high enough to cause physiological stress and hearing loss
^^Sources^^
- Transportation
- Construction
- Industrial and domestic activities
^^Harmful Effects on Other Organisms^^
- Stress
- Masking of sounds used to communicate or hunt
- Damaged hearing
- Changes to migratory routes
- Mostly happen in aquatic environments
^^Air^^
- Birds can adjust pitch and frequency for others to hear
- Some birds might sing at night
- Birds and bats cannot hear their prey
- Noise Sources
- Transportation
- Airports
- Gas wells
^^Land^^
- Frogs can only hear each other for 14 meters instead of 800 miles
- Prairie dogs are unable to hear their prey, communication, or predators
^^Ocean^^
- Hearing loss for dolphins, porpoises, and whales
- Animal’s solar and navigation systems are disturbed
- Octopuses and squids will lose balance and hunting ability
- Ecyostsms are disrupted when areas are too noisy because animals will move
- Sources
- Ships
- Oil & gas exploration
- Sonar
- Marine mammals are especially affected
- Use of sonar
- Sound carriers father through the water
- There is no downtime because the sonar is always working