Chapter 1
1.1-1.5
chemistry: the study of matter, its properties, the changes it goes through, and the energy that moves around
matter: anything that has mass and volume
composition: amounts of simpler substances that make up matter
properties: characteristics of substances
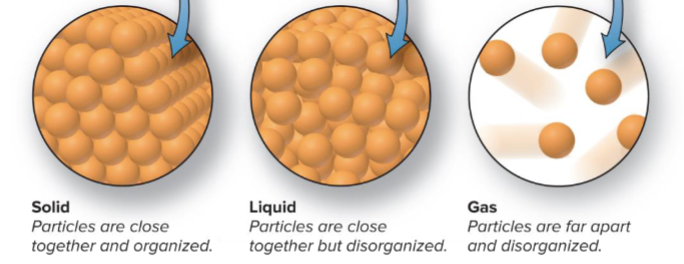
States of Matter:
Solid: fixed shape + volume
Liquid: moldable shape, conforms to shape of container, but has a fixed volume
- upper surface:
Gas: no fixed shape + no fixed volume, no surface
Properties:
Physical Properties: No interactions with another substance
- Color, melting point, boiling point, density.
Chemical Properties:
- Flammability, corrosiveness.
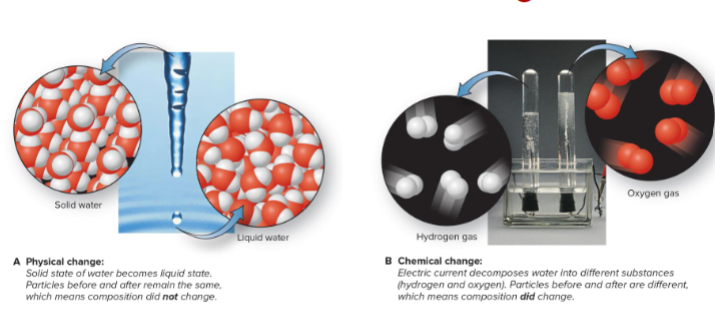
Temperature and Change of State:
Physical Change: reversible, physical form changes, composition does not.
- By changing temperature, reverse changes
Chemical Change: cannot be reversed by change in temp
Energy in Chemistry:
Energy: the ability to do work
Potential energy: energy due to the position of an object
Kinetic energy: energy due to the movement of an object
Total Energy= Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy
lower energy state=more stable
Temperature:
Temperature: measure of how hot/cold one object is relative to another
Heat: the energy that flows from object with higher temperature to object with lower temperature
Temperature Conversions:
T(K)=T(C)+273.15
T(C)=T(K)-273.15
T(F)=9/5 T(C)+32
T(C)= [T(F)-32] 5/9
K-Kelvin, C=Celsius, F=Fahrenheit
Sig Figs:
no decimal point= ending 0’s are not sig
zeros that end a number are sig if there is a decimal point
make sure the number has a decimal point
start at the left and move right until you reach non-zero
every digit to its right is sig (unless no decimal pt)
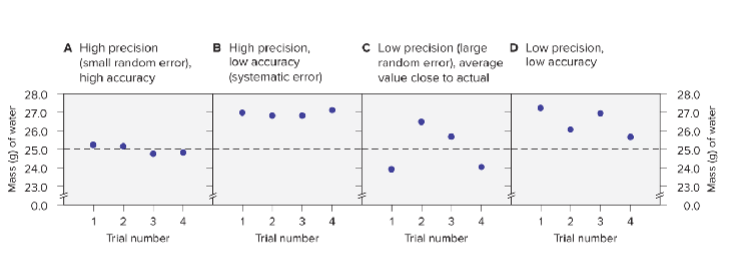
Precision, Accuracy, and Error:
Precision: refers to closeness of measurements in a series to each other.
Accuracy: how close each measurement is to the actual value.
Systematic error: produces values that are all higher or all lower than the actual value
- This error is part of the experimental system
Random error: produces values that are both higher and lower than the actual value (this always occurs)
Conversion Factors:
Conversion Factors: ration of equivalent quantities used to express a quantity
Dimensional Analysis: conversion factors as full ratios
Density:
density= mass/volume
Extensive/Intensive Properties:
Extensive Properties: dependent on amt of substance
Intensive Properties: independent of amt of substance