Chapter 11: Excretion
%%Catabolic activities%% are chemical processes which cause the breakdown of complex substances into simpler ones. For example, tissue respiration and deamination of proteins and amino acids to form urea.
%%Anabolic activities%% are chemical processes in which the simpler substances are built up into more complex substances. For example, the formation of new protoplasm from amino acids (proteins) and process of photosynthesis.
The sum of all chemical activities within the body is %%metabolism.%%
%%Excretion%% is the process by which metabolic waste products and toxic materials are removed from the body of an organism.
Excretory Products:
Carbon dioxide - lungs - gas is expired
Nitrogenous waste products - kidneys - urine
Excess Water
- kidneys - urine
- skin - sweat
- lungs - expired air
Bile pigments - liver - intestines
Mammalian Urinary System:
- Consists of a pair of kidneys, pair of ureter, a urinary bladder and urethra.
- ^^kidneys^^:
- Bean shaped.
- Attached to dorsal body wall.
- Lie above waistline.
- Renal artery & renal vein connected.
- Urine from each kidney passes through the ureter to the Urinary Bladder.
- Urinary bladder:
- elastic muscular bag.
- ventral to the rectum.
- stores urine.
- when the bladder is full the sphincter muscle relaxes to allow the urine flow into urethra and pass out of the body.
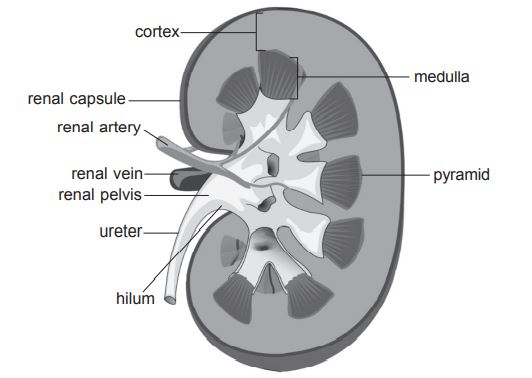
Longitudinal section of kidney:
Two regions:
- ^^Cortex^^
- outer region.
- ^^Medulla^^
- inner region.
- projects into a funnel shape space renal pelvis.
- nephrons.
- contains glomeruli; where blood is filtered and glucose, urea and salts are removed.
- contains tubule; where water and some mineral salts are reabsorbed (after filtration in glomerulus). This prevents loss of too much water. (urea is not reabsorbed leading to a high concentration in urine).
Formation of Urine:
- the glomerulus filters water and other substances from the bloodstream.
- the filtration membrane keeps blood cells and large proteins in the bloodstream.
- reabsorption moves nutrients and water back into the bloodstream.
- waste ions and hydrogen ions secreted from the blood complete the formation of urine.
Kidney as Osmoregulators:
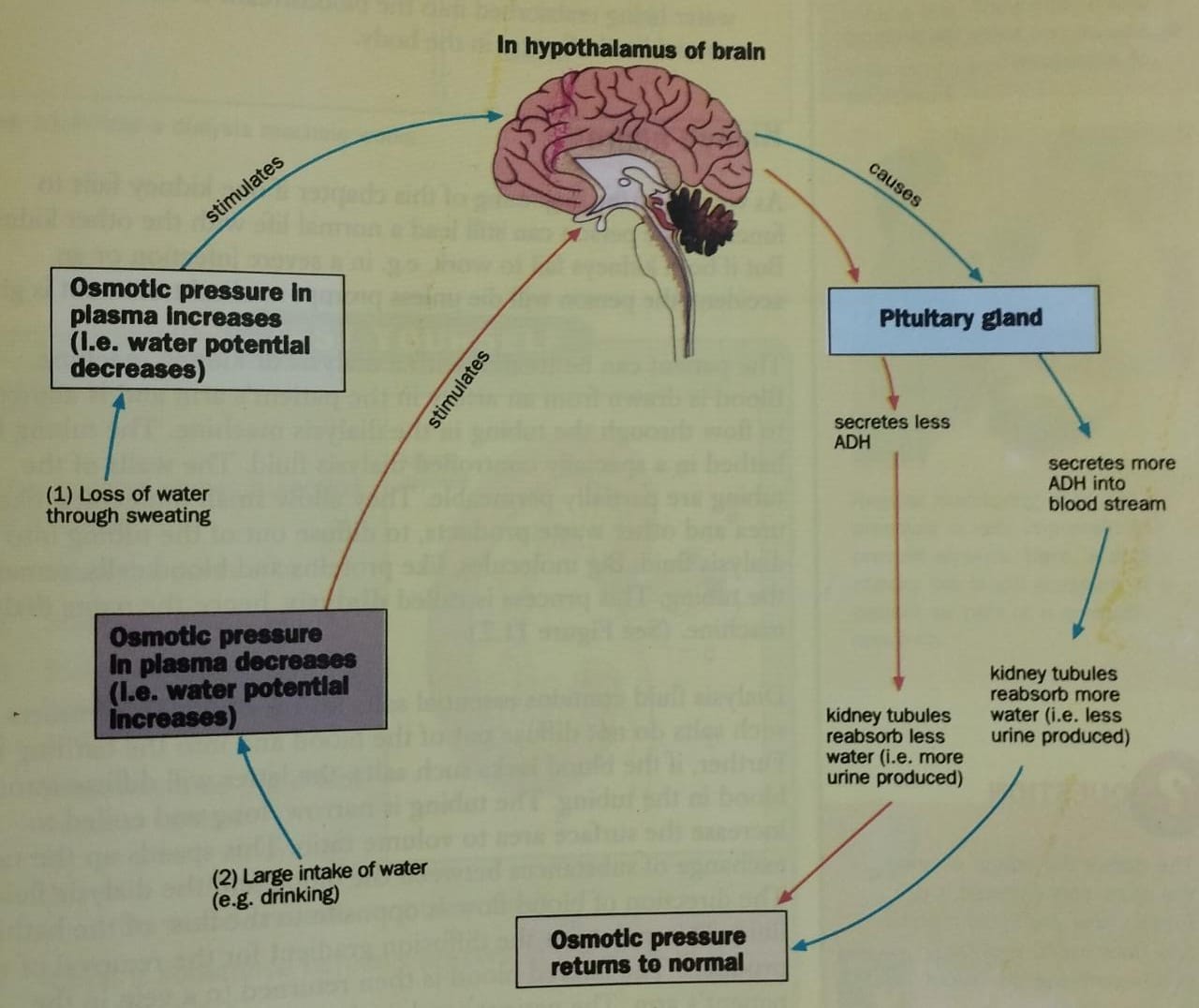
- %%Osmoregulation%% is the control of water and solute levels in the blood to maintain a constant water potential in the body.
Function of Kidneys:
- excretory organs.
- help regulate salt and water balance of the body fluid.
KIdney Failure:
two solutions:
- dialysis
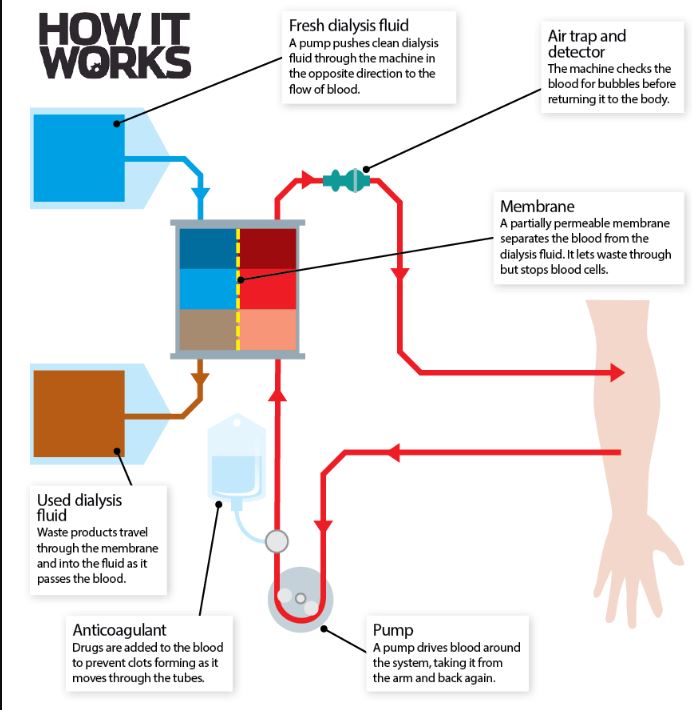
%%Dialysis fluid%% contains essential salts for the body - if the blood lacks essential salts dialysis fluid will diffuse its salts to it through membrane.