Thermal Expansion
%%Thermal Expansion Examples%%
- When trying to unscrew a jar heating the top can help in making it easier to remove
- The liquid inside the thermometer rises with an increase in temperature
- Bridges have spacing between them because during the summer the bridge expands
- Electrical wiring is tighter during the winter and loser during the summer
%%Temperature and Heat%%
- Temperature is the measure of the warmth or coldness of a substance
- Heat is the thermal energy
- Particles have kinetic energy and so are constantly moving the higher the temperature the higher the kinetic energy.
- If two substances have the same temperature but a different mass the substance with the larger mass will have the higher thermal energy
Energy will flow from a substance with higher temperature to one with a lower temperature -
Particles in the warmer object LOSE kinetic energy
Particles in the colder object GAIN kinetic energy
This is will happen until both substances reach the same temperature -
- Thermal Equilibrium
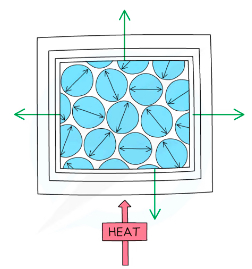
%%Thermal Expansion%%
- When a substance gains thermal energy its particles start to move more
- In the solid The vibrations take up more space and expansion occurs in all directions
- When the temperature falls the material will contract
- Liquids expand more than solids and gases expand more than liquids
When designing a rooftop made of concrete which other material is the most efficient and why?
- Steel because its coefficient of expansion is the closest to concrete this decreases the difference in contraction and expansion. Prevents breaking and spaces between the two materials.
You are provided with a glass thermometer without any readings. How can you convert it into a useful thermometer?
- You can place the thermometer in an area with a set temperature and mark the readings accordingly
- Put it in a substance in its boiling and then melting point and mark the readings
ex. A cup of ice or boiling water
- Now you have two readings 0 and 100 divide them equally be able to find the rest of the readings
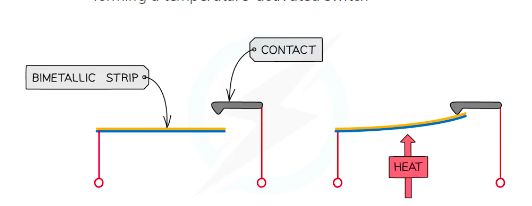
%%Bimetallic Strip%%
When heated a bimetallic strip will bend
Low expansion metal is bonded to aa high expansion metal
As is it is heated the high expansion metal expands more than the low expansion metal
This causes the strip to bend
Can be used in thermostats
Why does ice float in water?
Due to the anomalous behaviour of water
%%Anomalous behaviour of water%%
- The abnormal property of water where it expands instead of contracting when the temperature goes from 4C to 0 C, and it becomes less dense.
The density is maximum at 4 degree centigrade and decreases below that temperature.
The density becomes less and less as it freezes because molecules of water normally form open crystal structures when in solid form.
%%Examples of Thermal Expansion%%
Bimetallic strips
The strip works as a bridge in an electrical circuit connected to the heating system. Normally the 'bridge' is down
The strip c-arries electricity through the circuit, and the heating is on.
When the strip gets hot, one of the metals expands more than the other so the whole strip bends very slightly. Eventually, it bends so much that it breaks open the circuit.
The "bridge is up", the electricity instantly switches off, the heating cuts out, and the room starts to cool.
As the room cools, the strip cools too and bends back to its original shape.
Later , it snaps back into the circuit and makes the electricity flow again, so the heating switches back on
Expansion Joints
Large bridges have expansion joints
When heat causes the bridge to expand during the sunlight hours of a hot day, the two sides of the expansion joint move toward one another
Once the bridge cools they begin to contract
If not there would be no room for expansion pr contraction
The comb shape staggers the gap between the two sides of the joint ; minimizing the bump drivers experience.