AP Environmental Science 9.3: The Greenhouse Effect
Natural Global Processes
Location
Greenhouse Effect: in troposphere
Ozone Shield: in stratosphere
Details
Greenhouse Effect: a natural process that traps heat near the Earth’s surface.
- short wave radiation in (rays of sunlight)
- long wave radiation out (infrared radiation via heat)
- re-radiation downward by “greenhouse gases” in atmosphere (absorb heat, emitted as infrared radiation)
Natural gases involved:
- Greenhouse Gases: H2O, CO2 (holds heat for a longer time), CH4 (greater ability to hold in heat)
- Ozone Shield: O2, O3
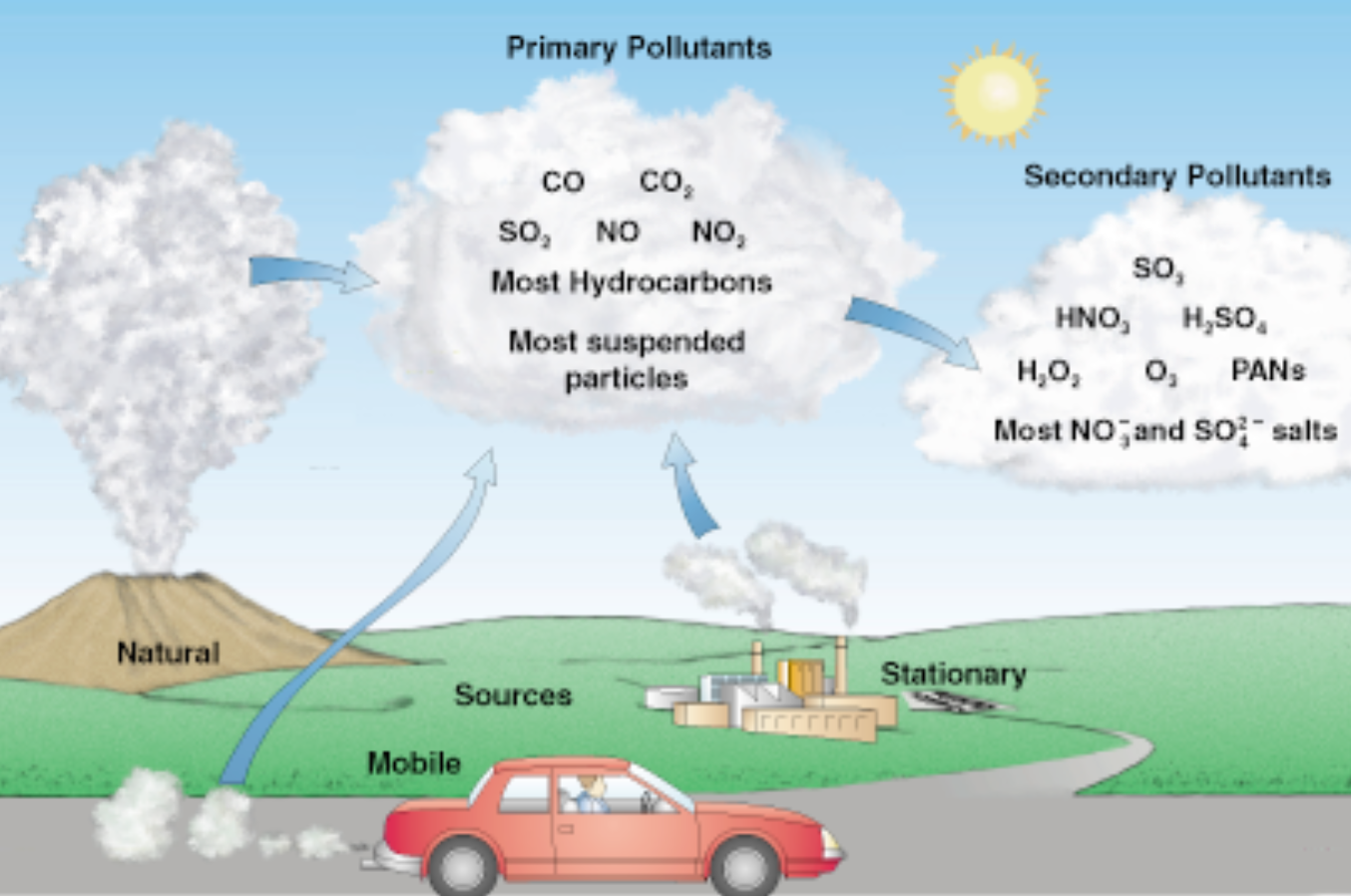
Greenhouse Gas Human Inputs:
- carbon dioxide (CO2)
- 75% developed countries
- 22% U.S.
- chlorofluorocarbons \n (CFCs)
- methane (CH4)
- nitrous oxide (N2O)
Ozone Shield Human Inputs
- chlorofluorocarbons \n (CFCs)
- other stable halogen–containing gases (halogens = chlorine, fluorine, & bromine)
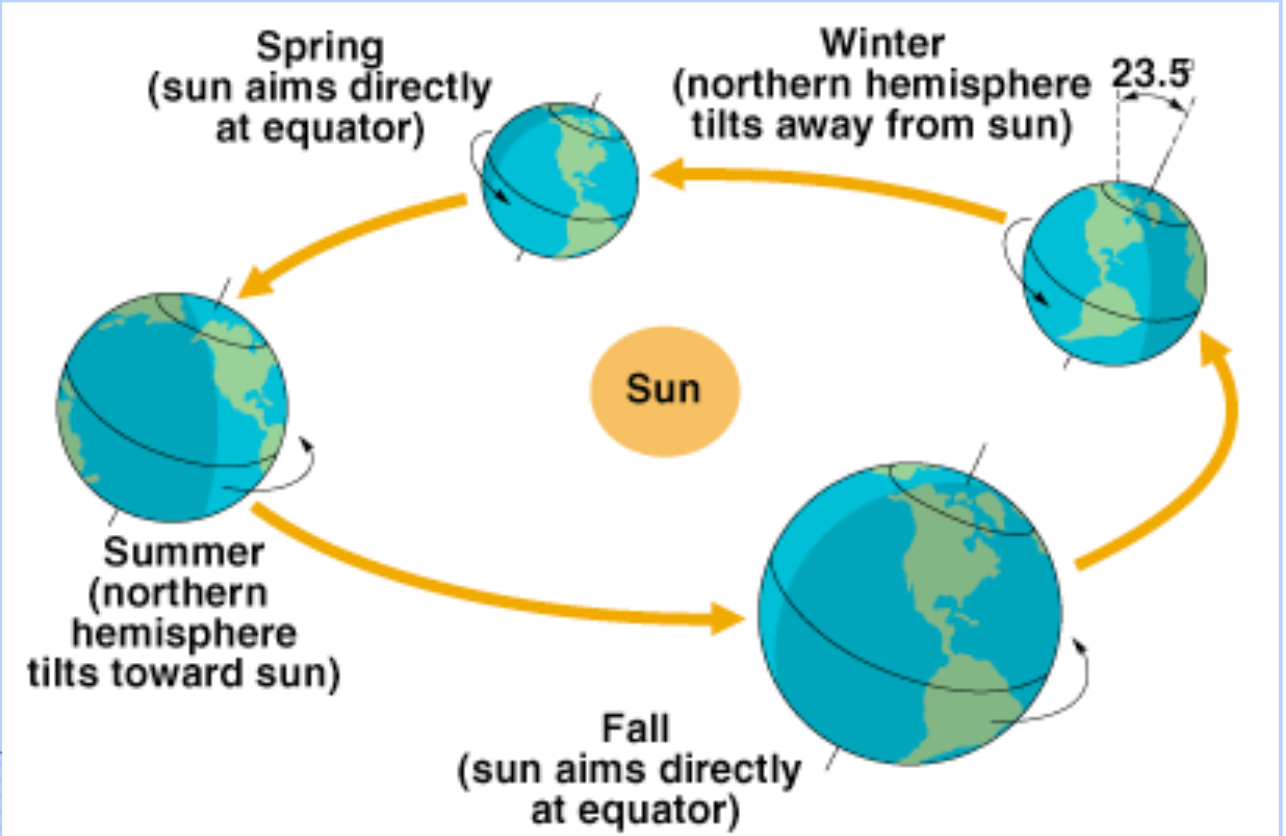
Geometry of Incoming Solar Radiation
Air Circulation Patterns

Ocean Currents

Gases Released through Human Activities