Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
Three subatomic particles and their significance
Types of chemical bonds and interactions and how they form
Importance of Hydrogen bonding to the properties of water
Each unique property of water contributes to life on Earth
Interpret the pH scale
Changes in pH can alter biological systems
Importance of buffers in biological systems
The Chemical Contexts of Life
Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called “compounds”
Matter, anything that takes up space and has mass
Element, substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reaction
example: gold, cooper, carbon, and oxygen
Compound, substance consisting of two or MORE elements combined in a fixed ratio
example: water (H2O), table salt (NaCI)
C, H, O, N, 96% of living matters. 25/92 natural elements are known to be essential to life
C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, O = Oxygen, N = Nitrogen
An element’s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
Atoms, smallest units of an element that retain the property of the element. Unit of life.
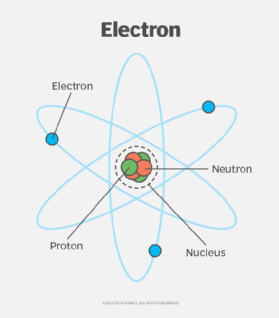
Made up of neutrons, protons, and electrons.
Building blocks of the physical world
Protons, positively charged particles found in the nucleus of the atom.
Positively charged (+) particle
Electrons, negatively charged particles found in electron shells around the nucleus. Determine the chemical properties and reactively of the element
negatively charged (–) particles
one of the three primary types of particles within the atom
Neutrons, particles with NO charge. Found in the nucleus. Their number can vary in a given element, resulting in isotopes.
uncharged particles
Some atoms have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus. These are called isotopes.
Isotopes, forms of an element with differing number of enutrons. Same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
example: 12C and 14 C are isotyopes of carbon. Both have 6 protons, but 12C has 6 neutrons, whereas 14C has 8 neutrons.
Radioactive isotopes, widely used in medicine for BOTH diagnostic and treatment. Radiometric data uses the rate of decay or half-life of certainisotopes to determine the ages of foissils and rock strata.
Atomic number, number of protons an element possesses. The number of protons in a nucleus.
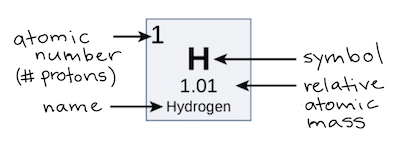
Mass number, an element is the sum of its protons and neutrons.