Chapter 6 - Geometric and Physics Optics
Waves
- Wave: an oscillation that transfers energy from one place to another
- Transverse waves: particles in the wave move perpendicularly
- Ex: wiggling a string up and down
- Crest: top of the wave
- Trough: bottom of the wave
- Wavelength (λ): distance from crest to crest and from trough to trough
- Amplitude (A): distance from a peak to the horizontal axis or from a trough to the horizontal axis
- Frequency (f): Number of wavelengths that pass a given period in 1 second
- Period (T): Time necessary for one wavelength to pass a given point
- Wave equation: ==x = Acos(⍵t) = Acos(2πft)==
- Longitudinal waves: particles move parallel to the direction of the wave’s motion
- Interference
- Constructive interference: when the peaks of one wave align with the peaks of another
- Amplitudes add up
- Amplitudes return to normal after the waves pass one another
- Destructive interference: when the troughs of one wave align with the peaks of another
- Amplitudes subtract
- Amplitudes return to normal after the waves pass one another
- Electromagnetic waves
- Gamma Ray, X-Ray, UV Rays, Visible Light, Infrared, Microwave, Radiowaves
- These types of EM waves are from shorter wavelength to longer wavelength
- Higher frequency and energy to lower frequency and energy
- All EM waves travel at the same speed: 3 x 10^8 m/s (c) = the speed of light
- An oscillating electric field wave induces an oscillating magnetic field wave at a right angle to itself
- The EM wave is self-propagating and can travel through a vacuum at the speed of light
- EM waves are transverse
- Polarization of light
- Polarizing the E-field portion of the wave: move the charge back and forth in the horizontal direction
- Polarized light that is reflected off of flat surfaces (like the light that causes road glare) is polarized horizontally
- Longitudinal waves cannot be polarized
- Diffraction: the property of waves to hear sounds around corners
- Point-source model: each point on a wave is the starting spot for a new wave
- Waves don’t just travel forward - they travel outwards as well
- The smaller the wave is compared to the boundary, the less prominent the effects of diffraction will appear
- This is why we don’t see around corners - we only hear
Single and Double Slits
- When light is diffracted through 2 slits, a pattern of light and dark bands is created on the screen
- Bright areas are where constructive interference occurred
- Dark areas are where destructive interference occurred
- ==dsin(Θ) = mλ==
- d: distance between slits
- Θ: the angle an observer would have to look at the bright spot
- m: “order” of the bright/dark spot
- Bright spots: m = 1 (the bright spot immediately right/left of the central spot)
- Dark spots: m = 0.5 (the dark spot immediately right/left of the central spot)
- λ: wavelength
- Diffraction gratings
- Like the double-slit experiment but with multiple slits
- The bright spots produced are sharper dots - locations for bright and dark spots are the same as the double slit
- Single slit
- Produces interference patterns because light hits each side of the slit
- The central maximum is bright and wider than the double-slit experiments
- The other bright spots are spaced the same but are dim
Index of Refraction
- Index of refraction: the amount by which light slows down in a material
- ==n = c/v==
- n: index of refraction
- c: speed of light in a vacuum
- v: speed of light through the specific material
- Frequency doesn’t change when light speeds up or slows down
- ==λn = λ/n==
- λn: wavelength of light traveling through transparent medium
- λ: wavelength in a vacuum
- n: index of refraction
- Thin Films
- Thin films such as a thin layer of oil on a puddle results in some light reflecting off the film and some penetrating the film
- Constructive interference: 2t = mλ
- t: the thickness of the film
- m: how many extra wavelengths the light inside the film went
- λ: wavelength in the film
Mirrors
Plane (flat) mirrors
- The angle of incidence: angle from a ray hitting the mirror to a vertical axis
- Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
- Image produced by plane mirrors are upright (virtual image)
- The magnification is equal to 1 because the image and real object are the same size
Spherical mirrors
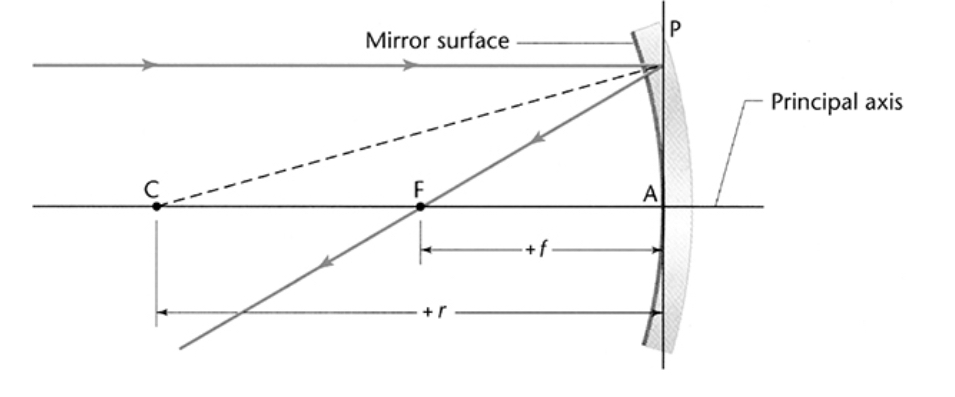
\
Principal axis: an imaginary horizontal axis running through the middle of the mirror
C: a point labeled C is the center of the sphere and is located a distance of r from the mirror
F: a point labeled F is the focal point of the mirror and is located a distance of f from the mirror
f = r/2
Rules for drawing rays:
Draw a ray that is parallel to the principal axis and reflects through the focal point
Draw a ray that foes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the principal axis
Any points that are on the same side of the mirror as the object are a positive distance from the mirror and any points on the opposite side of the mirror as the object are negative
==1/f = 1/so + 1/si==
- f: focal length
- so: distance from the object to the mirror
- si: distance from the image to the mirror
==|M| = |hi/ho| = |si/so|==
M < 1: image is reduced in size
M > 1: image is enlarged in size
Images that stand upright are virtual images
Images that are upside down are real images
Convex mirror - diverging mirrors
Cannot produce real images
If the object is to the left of the mirror, the mirror is shaped like a C
Concave mirror - converging mirrors
If the object is to the left of the mirror, the mirror is shaped like a backward C
Snell’s Law: ==nsinΘ== is constant
n: index of refraction
Θ: angle from the ray to a vertical axis
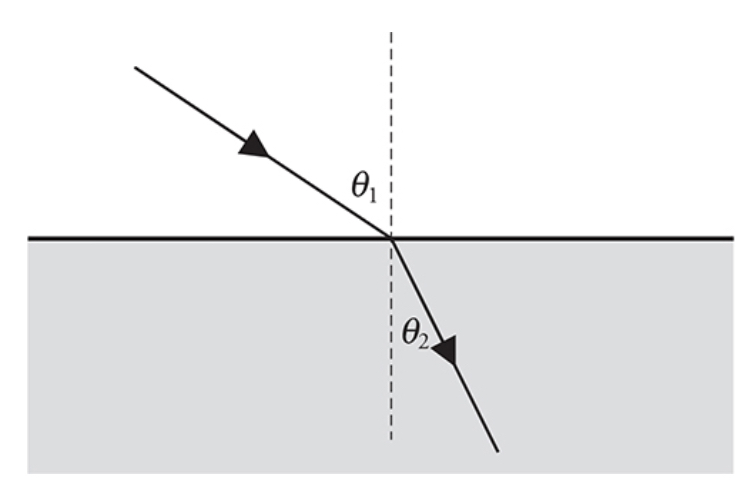
\
- Total internal reflection: when the light ray is directed at or beyond the critical angle
- Critical angle: angle past which rays can’t be transmitted to another material (reflects off of the boundary between materials
- ==sinΘ = n2/n1==
- Θ: critical angle
- n2: the second material’s index of refraction
- n1: the first material’s index of refraction
Lenses
- Convex lens: converging lens
- Shaped like a sideways eye
- Concave lens: diverging lens
- Shaped like a rectangle that caved in on both sides
- Rules for drawing rays for converging lens:
- Draw a ray that is parallel to the principal axis and reflects through the far focal point (the one on the other side of the lens)
- Draw an incident ray that goes through the near focal point and refracts parallel to the principal axis
- 1/f = 1/so + 1/si
- |M| = |hi/ho| = |si/so|
- Rules for drawing rays for diverging lens:
- Draw an incident ray parallel to the principal axis and refract it as if it came from the near focal point (dotted line from the focal point to the point where the parallel segment of the ray intersects the lens and a solid line following that same path)
- Draw an incident ray toward the far focal point that refracts parallel to the principal axis (a dotted line that continues the parallel line segment on the side of the object)
- 1/f = 1/so + 1/si
- |M| = |hi/ho| = |si/so|
\