BIOCHEM-LAB FINALS
EXPERIMENT #10 SALIVARY DIGESTION
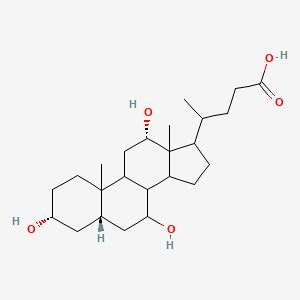
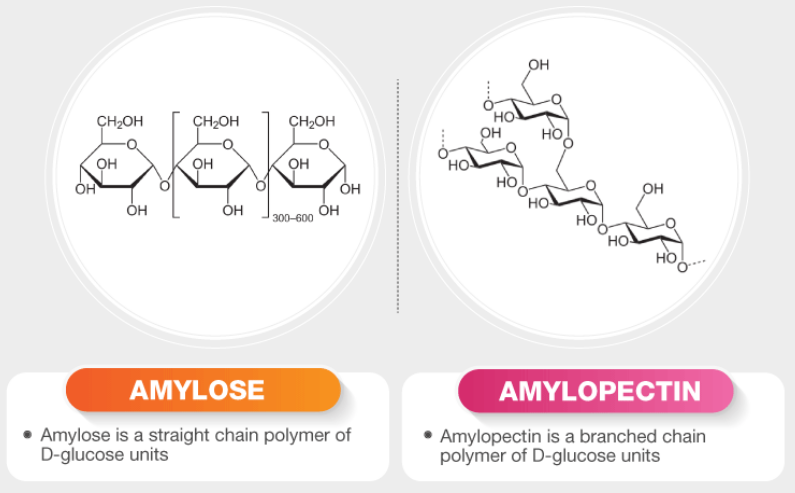
Alimentary Digestion
Ingested food materials are made assimilable
Assimilable— can be transported through intestinal mucosa and absorbed into the portal venous system.
Series of enzymatic hydrolyses:
Colloidal food molecules → Simple, non-colloidal solutes
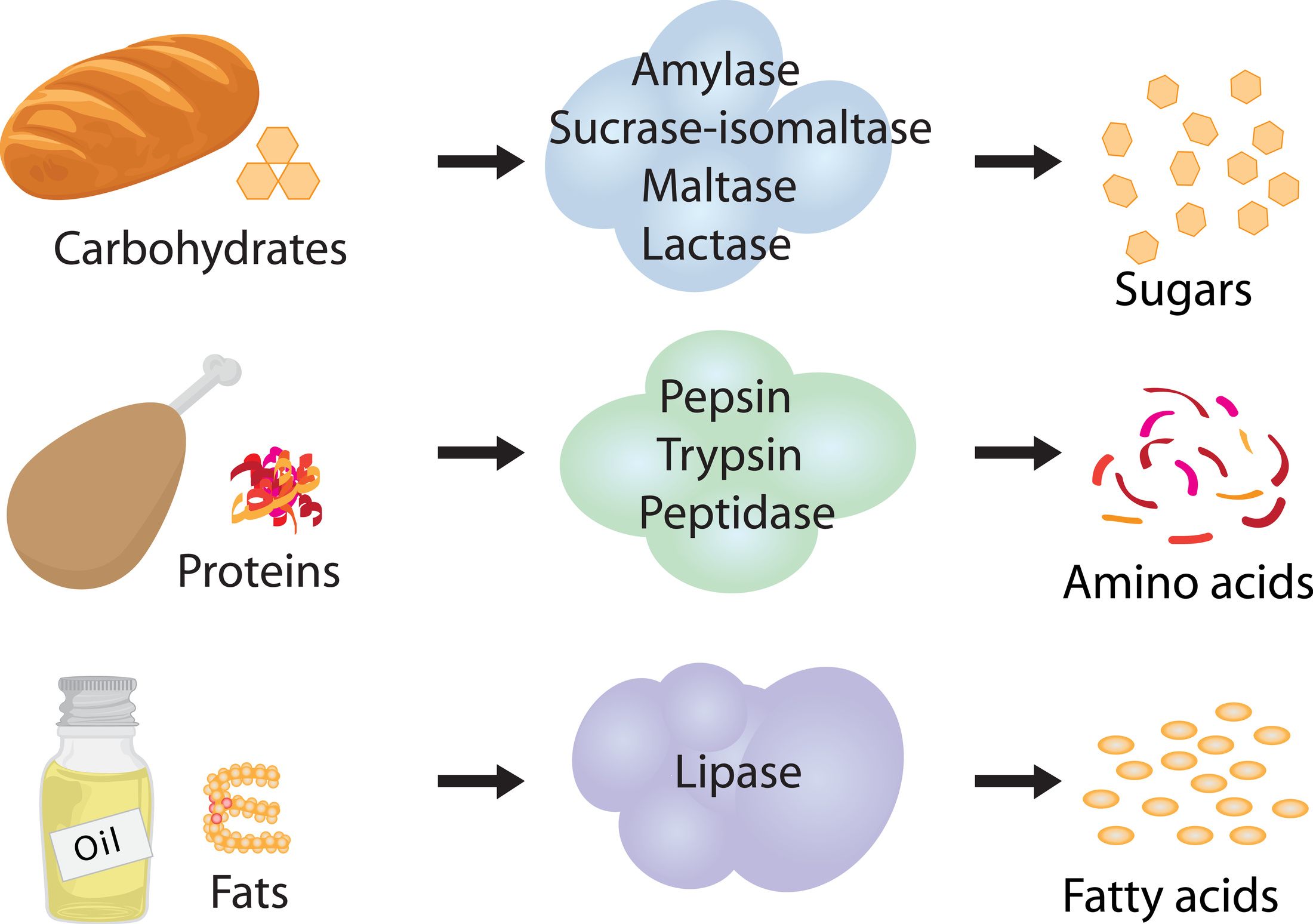
Hydrolytic enzymes
Involved in digestion
naturally occuring foodstuffs → assimilable forms
Catalyse hydrolysis of:
Proteins → amino acids
Starches → monosaccharides
Fats → acyl glycerol
Saliva
Watery secretion
Produced by:
3 pairs of large salivary glands
& many minute glands (buccal glands)
in mucusal lining of the mouth
speeds up chemical changes in carbohydrates
no chemical effects on:
proteins
fats
Components of Saliva
H20
~99% of salova
Salivary amylase
digestive enzyme which hydrolyses starch to maltose
mineral salts
eg. sodium carbonate
Purpose: maintain pH~ 6.5-7.5
Optimal for salivary amylase
mucin
sticky material (glycoprotein)
Purpose:
Binding of food particles
lubrication to assist swallowing
pH of Saliva
pH paper ~ 8.0
Actual pH: 6.5-7.5
Salivary amylase functions best
slightly alkaline but neutral due to sodium bicarbonate
Enzyme action
Mouth and elsewhere: enzyme action dependent on pH surroundings
Eg. pH optimum, salivary amylase: 6.5-7.5
Stomach: very acidic (pH 1.0-3.5)
Salivary amylase inactivated
no carb digestion in stomach
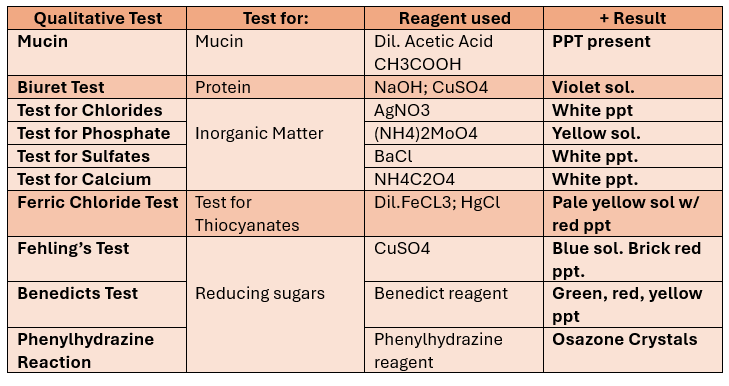
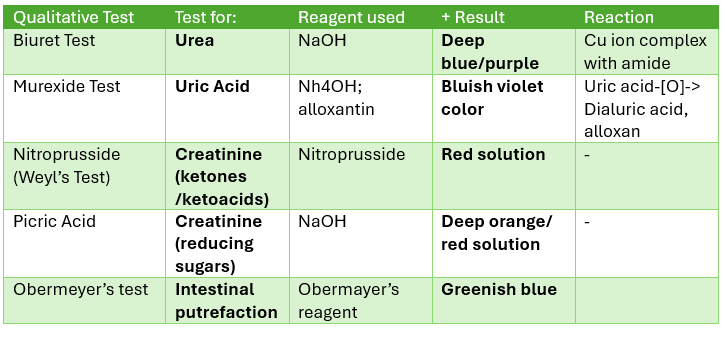
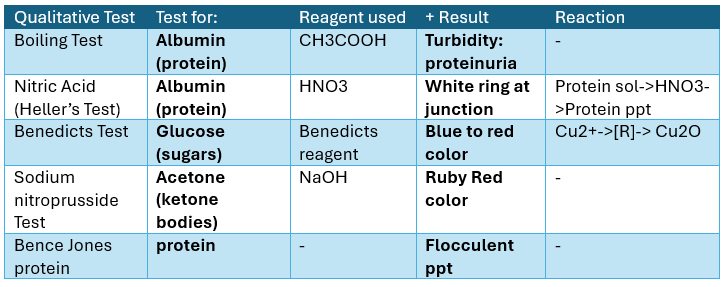
Qualitative Tests for SALIVA
Test for Mucin
Mucin
sticky
Highly glycosylated, extended, and hydrated protein
Extensive in salivary secretions
functions:
Increase viscosity of fluids in saliva
Binds and lubricates food particles
(+) result: ppt (mucin)
Test for proteins
Alias: Biuret test
(+) results: violet solution / purple product
Coordination complex
intensity of color is dependent on the number of peptide bonds

Test for Inorganic Matter
Test for Chlorides
(+) result: White ppt
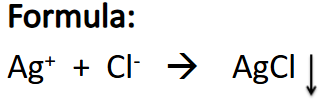
Test for Phosphates
(+) results: yellow ppt
(ammonium phosphomolybdate)
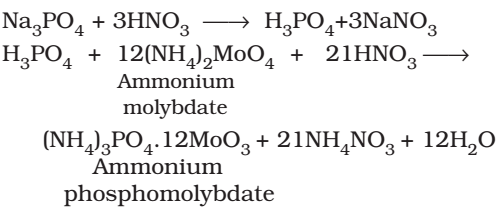
Test for Sulfates
(+) result: white ppt
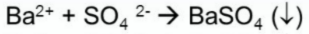
Test for Calcium
(+) result: white ppt
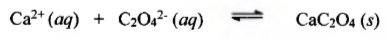
Importance:
Maintenance or stabilization of compact formation of a-amylase
Maintenance of enzymatically active conformation.
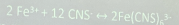
Test for Thiocyanate (FeCl3 Test)
(+) results: Pale yellow solution with red ppt
Confirmation: HgCl2

CNS
Metabolite of CN
End product of detoxification of CN- containing cpds
enzyme: rhodanase
CNS IN SALIVA:
Reasearch: present in saliva
Sources:
smoking
food containing cyanide
Digestion of starch paste
Starch→ (digestion by saliva)→ (smaller saccharide units)
Salivary digestion complete: Violet-colored product not formed
Achromatic point
Digestion of Starch will reach Achromatic point when:
↑in duration
↑ lightening of the color of violet-colored complex
Reaction mixture: no more color change with I2 solution
Complete breakdown of strach
Starch→ Dextrin →disaccharides→monosaccharides
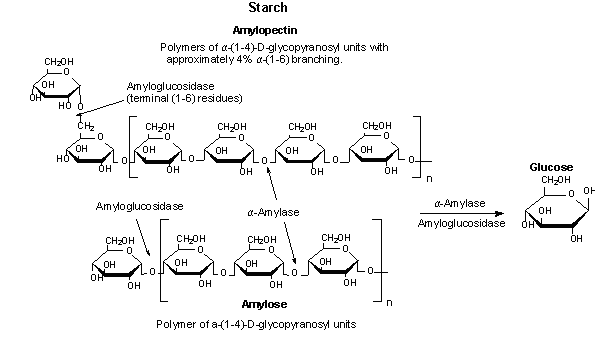
Salivary Amylase
Cleaves a-1-4 linkages starch
gives different colors in I2:
Amylodextrin: purple
Erythrodextrin: red
Achrodextrin: colorless
Maltose: colorless
Starch→ amylodextrin→Erythrodextrin→Achrodextrin→Maltose
Fehling’s Test
For reducing sugars
(+) Results: Blue Solution with Brick red ppt

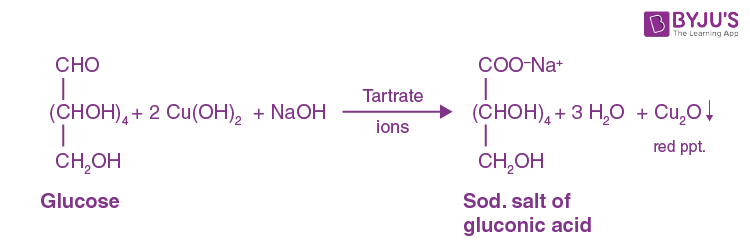
Benedicts Test
For reducing sugars
(+) result: green, red, or yellow ppt
All sugars except sucrose
Principle:
Aldehydes, ketone -[O] → OA : alkaline copper solution
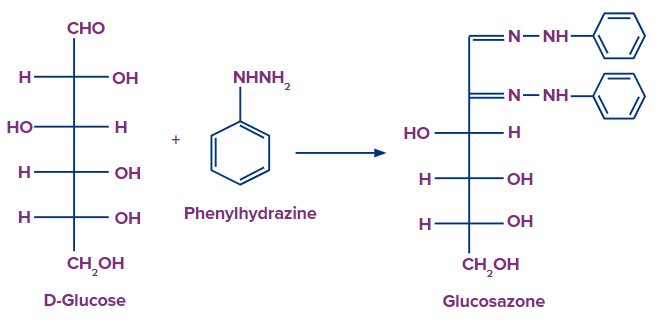
Phenylhydrazine Reaction
Salivary digestion of starch→ monosaccharides
Monosaccharides+ phenylhydrazine reagent → Osazone Crystals
Effect/ influence of free acid
Free acid: Hinders digestion of starch by salivary amylase
Same trend with dilute base.
Affect optimum pH
Inactivate the enzyme
↑ concentration of dil. Na2CO3 → ↑Intensity of Blue color
SUMMARY OF QUALITATIVE TESTS
EXPERIMENT #11 URINE ANALYSIS
Physical properties of Urine
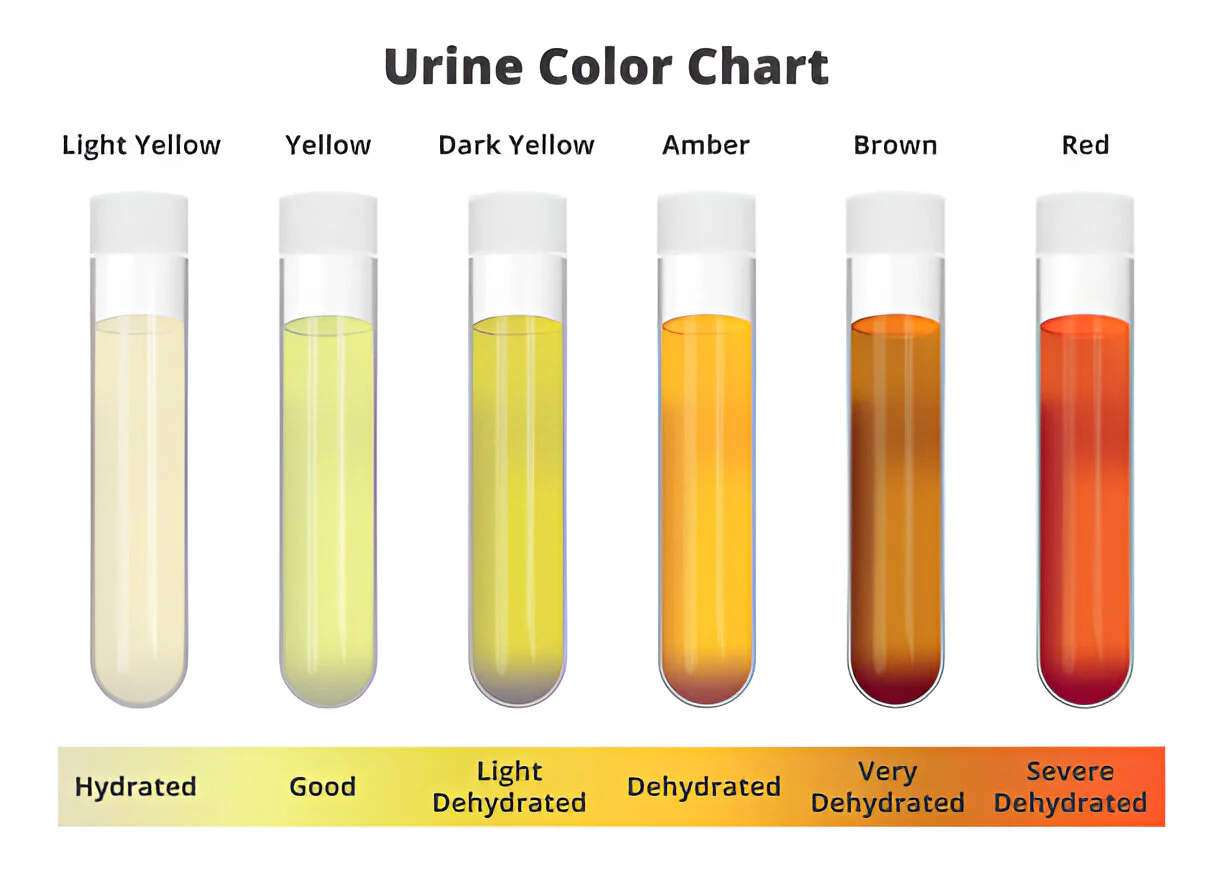
Color
Color of Normal urine:
Yellow to amber
Due to Urochrome:
Pigment
Urobilin and Peptide
Set aside undisturbed: will darken
Urubilin is released
Abnormal urine:
Varies; nearly colorless to black
depends on pathological condition
Milky urine:
possible:
WBC’S
Bacterias
Fats
Reddish-Amber
Urobilinogen
pigment
intestine: Bile or porphyrin-(bacteria)→urobilinogen
liver disease, Addison’s disease etc.
Brownish yellow or Green
Bile pigments
Red to smoky brown:
Blood and blood pigments
Appearance of abnormal urine
Cloudy:
Possible:
phosphates
urates
WBC
Bacteria
Epithelial cells
fat
Odor or normal and fresh urine
Slightly aromatic
set aside undisturbed: Ammonia (NH3) odor

Cause odor change in urine
drugs
food
pathological conditions
Specific gravity
within 24hours: 1.015-1.025
<1.015:
excess fluid intake
diabetes insipidus
chronic renal failure
>1.025
limited fluid intake/ dehydration
fever
kidney inflammation
Volume
V excreted / Day
0.5-1.5L
↑ : large amounts lipids
↓ : loss H2O (Perspiration)
pH
4.5-8.2
Factors
diet
drugs
pathological conditions
Organic Compounds
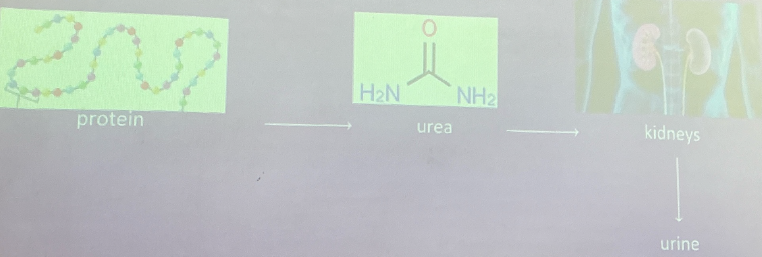
Urea
end product of protein metabolism (liver in humans)
Uric Acid
end product of purine metabolism (humans)
levels high in gout patients
amount produced in human urine: ~0.5-1.0g/h

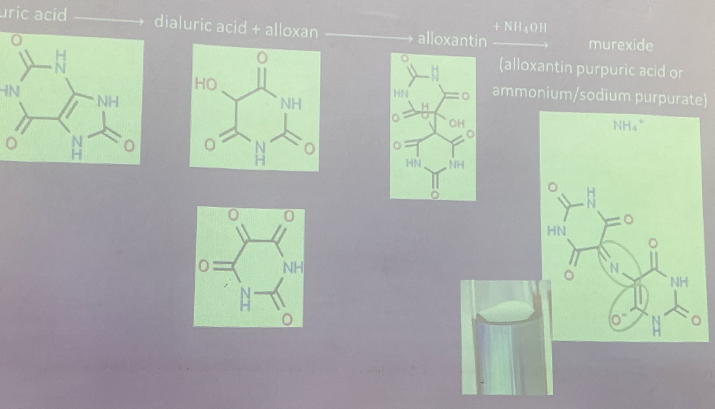
Creatinine
excreted by normal healthy adults: 1.2-1.7 g/h
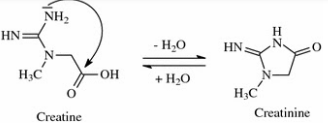
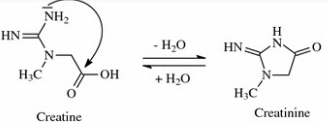
Factors:
diet
muscular development
higher in men tyhan in women and children
Nitroprusside
contraindicated in patients with renal failure

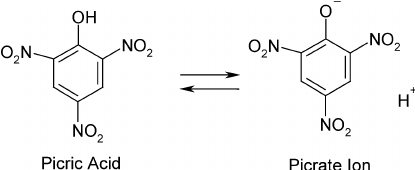
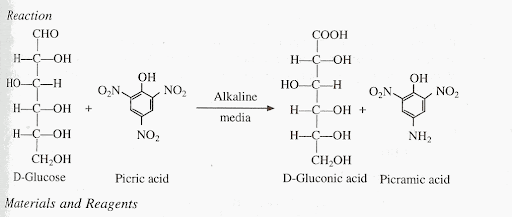
Picric acid
IUPAC NAME: 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP)
Yellow crystalline solid
one of the most acidic phenols
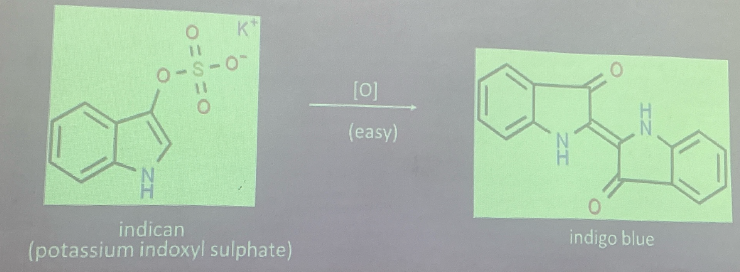
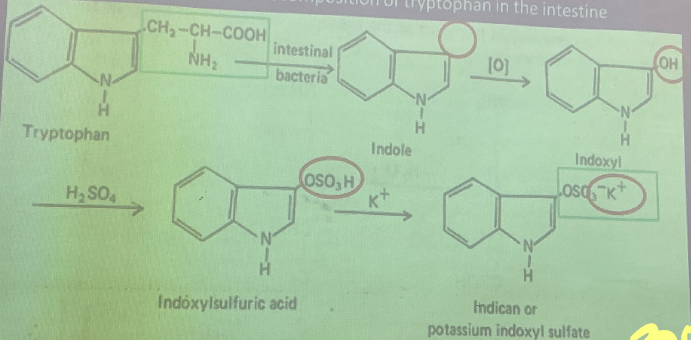
Indican
comes from the putrefactive decomposition of tryptophan in the intestine
Obermeyer’s Test
colorimetric method
For: Intestinal putrefaction
Pathological Components of Urine
Certain diseases:
Dysfunction of liver and kidneys
metabolic disorders
Main abnormal constituents
PROTEIN
ALBUMIN
Proteinuria
presence of protein in urine
Indicate: Kidney damage or nephritis
Albuminaria
presence of albumin in urine
Globulins
sometimes found in urine with albumin
larger molecules
indicate more extensive kidney damage
SUGAR
Glycosuria
(+) sugar in urine
Glucosoria
(+) glucose
Possible causes:
excessive carb intake
diabetes mellitus
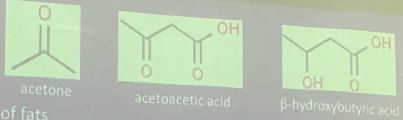
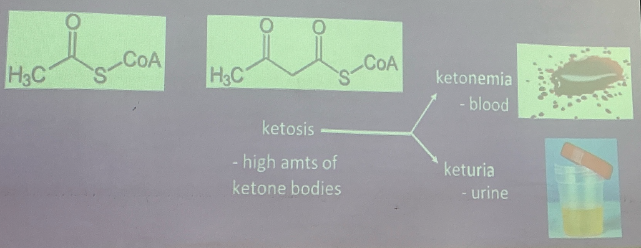
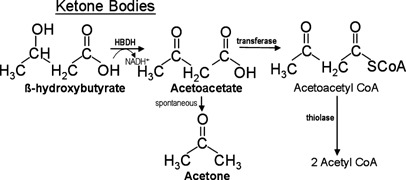
KETONE BODIES
From incomplete oxidation of fats
Results:
accumulation: Acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA
Indicates: Acidosis
abnormal amounts excreted
depletion of Na+ and K+
Conditions

BENCE-JONES PROTEIN
Monoclonal globulin
Location: blood or urine
precipitates at low temperature
Indicate:
multiple myeloma
another blood (plasma) disorder
Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinaemia (IgM)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (WBC’s)
Amyloidosis (protein amyloid)
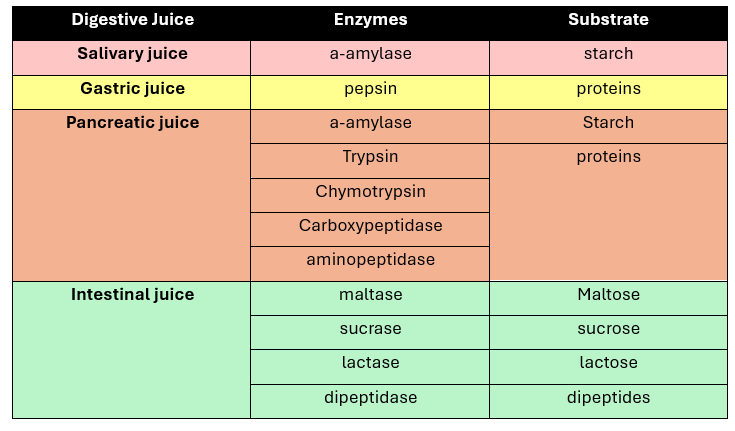
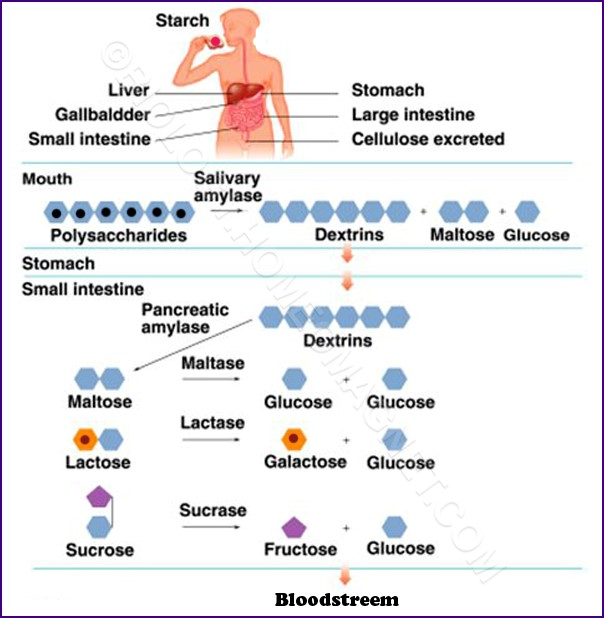
EXPERIMENT # 12 INTESTINAL DIGESTION
Small intestine
most important part: duodenum
3 juices enter the intestine (through duodenum)
pancreatic juice
bile
intestinal juice
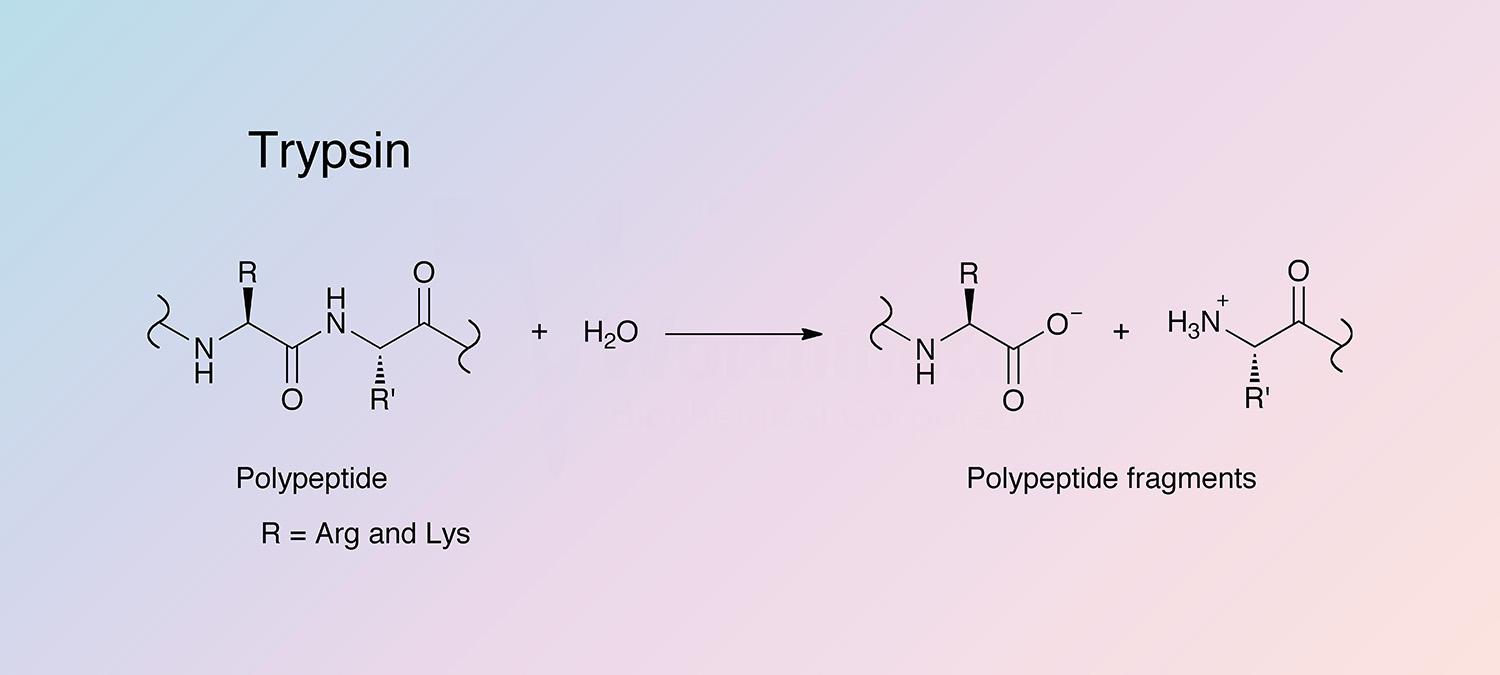
Trypsin (Enzyme)
hydrolyze peptide linkages involving Arginine and Lysine
Optimum pH: 7-9
Active form of trypsinogen
activated by enteropeptidase (enterokimase)
BAPNA (Substrate)
synthetic
Colorless→ yellow
Effects of Temperature on Trypsin
T optimum, trypsin: 40 C
↑ T: Trypsin denaturation
Result: Inactivation
other enzymes and proteins also denatures
↓ T: trypsin rigid and less active
cause decrease in mobility of atoms and molecules

Pancreatin
commercial mixture of enzymes (amylase,lipase and protease)
secreted also by normal human pancreas
extracted from pigs
For problems digesting fats starches and proteins
LIPASE
Family of enzymes for hydrolysis of fats
substrate:
Triglycerides
Cholesterol
Phospolipids
Lipid-soluble vitamins
etc
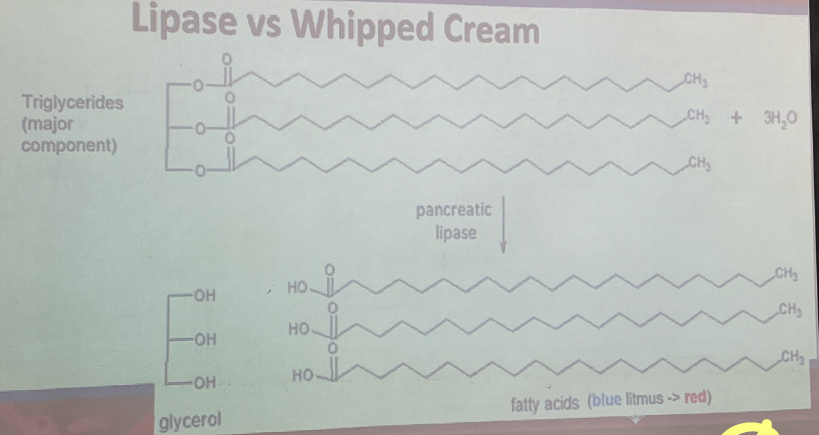
T optimum= 37 C
Same as trypsin
↑ T: Trypsin denaturation
↓ T: trypsin rigid and less active
Bile Salt
Emulsifying agents for lipids
↑ Surface area lipid
improve efficency of hydrolysis
↓ T: Activity of lipase
(+) : red solution - 37C
(-) : blue solution - 0 C
Practice Questions
Conceptual Questions (Q1–Q10)
What is the primary purpose of salivary amylase in the digestive process?
a. Hydrolyzing proteins into amino acids
b. Hydrolyzing starch into maltose
c. Hydrolyzing fats into glycerol
d. Lubricating food particlesWhich pH range is optimal for salivary amylase activity?
a. 1.0–3.5
b. 6.5–7.5
c. 7.5–9.0
d. 4.0–6.0What is the function of mucin in saliva?
a. Hydrolyzing proteins
b. Binding and lubricating food particles
c. Maintaining salivary pH
d. Catalyzing starch breakdownWhich of the following is a qualitative test for mucin?
a. Precipitation test (ppt)
b. Biuret test
c. Fehling's test
d. Benedict’s testWhat is the result of Fehling’s test if reducing sugars are present?
a. Violet solution
b. Yellow crystals
c. Blue solution
d. Brick-red precipitateWhat is the achromatic point in starch digestion?
a. The point where starch turns blue with iodine
b. The point where no color change occurs with iodine
c. The point where starch digestion stops
d. The point where starch forms dextrinWhich enzyme activates trypsinogen into its active form, trypsin?
a. Lipase
b. Salivary amylase
c. Enteropeptidase
d. PancreatinWhat is the optimum temperature for trypsin activity?
a. 25°C
b. 37°C
c. 40°C
d. 50°CWhat condition is indicated by the presence of Bence-Jones protein in urine?
a. Diabetes insipidus
b. Multiple myeloma
c. Addison’s disease
d. GoutWhat does a yellow precipitate indicate in a phosphate test?
a. Presence of sulfates
b. Presence of phosphates
c. Presence of thiocyanates
d. Presence of chlorides
Analytical Problem Solving Questions (Q11–Q20)
You mix saliva with a starch solution and add iodine. Initially, the mixture is violet. Over time, the color fades. What does this indicate?
a. Starch is not digested
b. Salivary amylase is inactive
c. Starch is being digested into simpler sugars
d. The pH is too low for digestionIf urine appears reddish-amber, which condition is most likely the cause?
a. Gout
b. Kidney stones
c. Liver disease
d. DehydrationA sample shows a violet color in the Biuret test. What does this indicate?
a. Presence of reducing sugars
b. Presence of lipids
c. Presence of proteins
d. Presence of phosphatesWhy does salivary amylase become inactive in the stomach?
a. Lack of sodium bicarbonate
b. Presence of lipase
c. Low stomach pH
d. High stomach temperatureWhich condition increases the specific gravity of urine above 1.025?
a. Diabetes insipidus
b. Dehydration
c. Excess fluid intake
d. Chronic renal failureYou perform a Fehling’s test on a solution and observe a brick-red precipitate. Which carbohydrate is most likely present?
a. Glucose
b. Starch
c. Sucrose
d. CelluloseWhich of the following tests would confirm the presence of chlorides in saliva?
a. Biuret test
b. Benedict’s test
c. Precipitation test (white ppt)
d. Phenylhydrazine reactionWhat effect does a high concentration of sodium carbonate have on the digestion of starch?
a. Stops digestion
b. Changes starch to glycogen
c. Increases intensity of the blue color with iodine
d. Denatures salivary amylaseIn which qualitative test does ammonium phosphomolybdate form a yellow precipitate?
a. Chlorides test
b. Phosphates test
c. Sulfates test
d. Thiocyanate testWhat happens to trypsin activity when the temperature is increased beyond 40°C?
a. Activity increases indefinitely
b. Trypsin denatures and becomes inactive
c. Trypsin remains rigid and functional
d. The reaction slows down but does not stop
Identification and Chemical Structures (Q21–Q30)
Which of the following forms a pale yellow solution with a red precipitate in the presence of FeCl₃?
a. Thiocyanate
b. Chloride
c. Phosphate
d. SulfateWhat is the chemical formula of picric acid, used in some urine analysis tests?
a. C₆H₆O₃
b. C₆H₃N₃O₇
c. C₆H₅NO₂
d. C₆H₆N₆What color is associated with amylodextrin in iodine tests?
a. Purple
b. Red
c. Yellow
d. ColorlessWhich compound is the final product of starch digestion by salivary amylase?
a. Dextrin
b. Disaccharides
c. Maltose
d. PolysaccharidesWhat is indicated by the formation of osazone crystals in a phenylhydrazine reaction?
a. Presence of starch
b. Presence of amino acids
c. Presence of monosaccharides
d. Presence of fatty acidsWhich color change occurs when erythrodextrin reacts with iodine?
a. Purple
b. Red
c. Yellow
d. ColorlessWhat is the effect of bile salts on lipid digestion?
a. Emulsifies lipids to increase surface area
b. Breaks down lipids into amino acids
c. Converts lipids into sugars
d. Destroys lipid-soluble vitaminsWhat compound is a metabolite of cyanide and is often detected in saliva?
a. Thiocyanate
b. Chloride
c. Urea
d. IndicanWhich enzyme in the intestine hydrolyzes peptide bonds involving arginine and lysine?
a. Lipase
b. Pancreatin
c. Trypsin
d. AmylaseWhat is the appearance of a positive result in the test for sulfates?
a. Yellow precipitate
b. Blue solution
c. White precipitate
d. Red precipitate
Conceptual Questions (Q31–Q40)
What is the role of sodium carbonate in maintaining salivary pH?
a. Acts as a digestive enzyme
b. Neutralizes acids in saliva
c. Maintains the pH at 6.5–7.5
d. Activates salivary amylaseWhich of the following substances contributes to the yellow color of urine?
a. Urochrome
b. Indican
c. Creatinine
d. Uric acidWhat does the Biuret test specifically detect in a sample?
a. Reducing sugars
b. Salts
c. Peptide bonds in proteins
d. GlycoproteinsWhich of these components is essential for emulsifying fats during digestion?
a. Pancreatic amylase
b. Bile salts
c. Mucin
d. Sodium bicarbonateWhat happens to starch when digested by salivary amylase?
a. It forms peptides
b. It forms monosaccharides directly
c. It is broken down into maltose and dextrins
d. It is converted into celluloseWhich physical property of urine is typically measured with a hydrometer?
a. Color
b. Odor
c. Specific gravity
d. pHWhat type of bonds does trypsin hydrolyze in proteins?
a. Disulfide bonds
b. Peptide bonds involving arginine and lysine
c. Hydrogen bonds
d. Glycosidic bondsWhich pH range supports optimal lipase activity?
a. 7.0–9.0
b. 5.5–6.5
c. 1.0–3.0
d. 8.5–10.5Which of the following is a pathological component in urine?
a. Creatinine
b. Albumin
c. Urobilin
d. SodiumWhat does a green precipitate in Benedict’s test indicate?
a. Absence of reducing sugars
b. Low concentration of reducing sugars
c. High concentration of reducing sugars
d. Presence of proteins
Analytical Problem Solving and Identification Questions (Q41–Q50)
You add iodine to a reaction mixture and observe a purple color. What is present in the mixture?
a. Glucose
b. Maltose
c. Amylodextrin
d. AchrodextrinA urine sample is tested and found to contain high levels of uric acid. What condition does this most likely indicate?
a. Gout
b. Diabetes insipidus
c. Chronic renal failure
d. Liver diseaseIn a phenylhydrazine test, what kind of crystals are formed when monosaccharides are present?
a. Maltose
b. Osazone crystals
c. Glycoside crystals
d. PolysaccharidesWhat happens when thiocyanate reacts with FeCl₃?
a. A violet solution forms
b. A yellow precipitate forms
c. A pale yellow solution with a red precipitate forms
d. No visible reaction occursWhat is the effect of increasing the temperature above 40°C on lipase?
a. Lipase denatures and loses activity
b. Lipase activity remains constant
c. Lipase becomes rigid and more active
d. Lipase breaks down into smaller enzymesWhat does a white precipitate indicate in a test for sulfates?
a. Presence of sulfate ions
b. Absence of sulfates
c. Presence of thiocyanates
d. Presence of proteinsWhy is pancreatin extracted from pigs used in commercial enzyme preparations?
a. It is a source of bile salts
b. It mimics human amylase
c. It contains enzymes for digesting fats, proteins, and starches
d. It activates trypsinWhat abnormal urine characteristic might result from the presence of WBCs or bacteria?
a. Milky appearance
b. Reddish-amber color
c. Cloudy appearance
d. Dark brown colorWhat test confirms the presence of indican in urine?
a. Biuret test
b. Benedict’s test
c. Phenylhydrazine reaction
d. Obermeyer’s testWhat does a colorless solution indicate in the iodine test for starch digestion?
a. Starch digestion is complete
b. Starch digestion has not started
c. Amylodextrin is present
d. Erythrodextrin is present
Questions on Indicators (Q51–Q60)
What disease is commonly indicated by the presence of albumin in urine (albuminuria)?
a. Gout
b. Diabetes insipidus
c. Kidney damage or nephritis
d. Liver failureHigh levels of ketone bodies in urine suggest which condition?
a. Acidosis
b. Hypoglycemia
c. Chronic renal failure
d. Excess fluid intakeThe presence of Bence-Jones protein in urine is most often associated with which disease?
a. Multiple myeloma
b. Diabetes mellitus
c. Addison’s disease
d. GoutWhat abnormality is indicated by the reddish-amber appearance of urine?
a. Presence of lipids
b. Dehydration
c. Liver disease (e.g., urobilinogen presence)
d. Chronic renal failureThe presence of uric acid in excess quantities in urine is most commonly associated with which condition?
a. Liver failure
b. Kidney stones
c. Hypernatremia
d. GoutCloudy urine may indicate which of the following conditions?
a. Diabetes insipidus
b. Presence of WBCs, bacteria, or epithelial cells
c. Liver failure
d. DehydrationWhich condition is suggested by the presence of glycosuria (glucose in urine)?
a. Diabetes mellitus
b. Liver disease
c. Protein deficiency
d. HyperlipidemiaA positive test for indican in urine can indicate what underlying issue?
a. Intestinal putrefaction (tryptophan metabolism)
b. Diabetes mellitus
c. Kidney inflammation
d. HypertensionWhat does a high concentration of creatinine in urine suggest?
a. Diabetes insipidus
b. Hypothyroidism
c. High muscular activity or protein intake
d. Liver dysfunctionA green or brownish-yellow color in urine is often an indicator of what condition?
a. Kidney damage
b. Diabetes mellitus
c. Presence of bile pigments due to liver disease
d. Dehydration
 Knowt
Knowt