US Revolution
Contextualization
British vs American Army
British: Well-organized, 3x the population size, wealth, large army, ample supplies & weaponry, strongest navy
US Army: Relied on minutemen/militias (called minutemen because should be prepared to fight within a minute’s notice); Short of supplies, poorly equipped, rarely paid, not officially trained (volunteers)
Patriots (40%)
Mostly in New England and Chesapeake
African Americans- promised freedom if they fight in the war
Loyalists/Tories (25%)
Mostly upper class, wealthy, and Anglicans
Supplied redcoats with arms and food
Supported by Native Americans
Majority of colonists were neutral
Battles
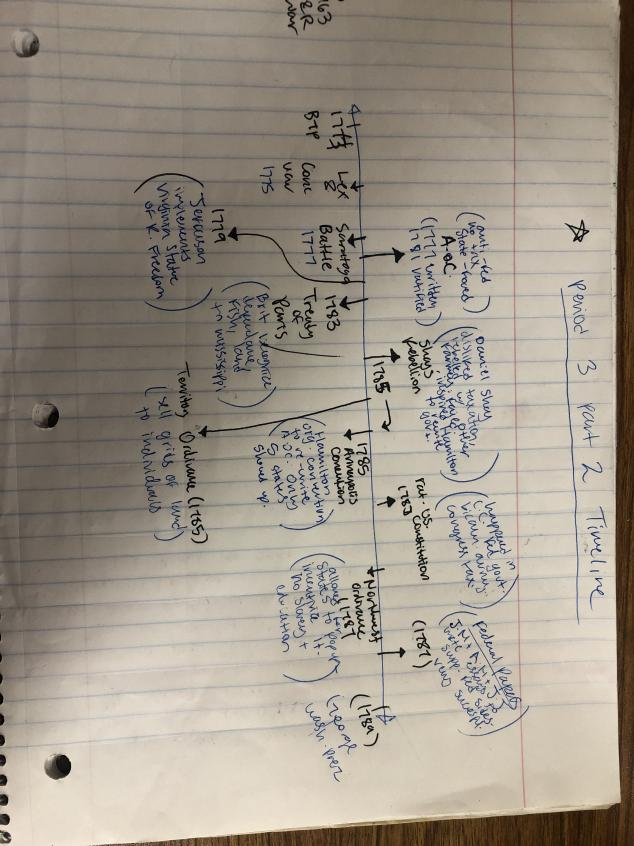
Lexington & Concord (1775)
British get word that there is a stockpile of colonial weapons in Lexington- try to seize
Paul Revere rides to warn Minutemen in Lexington
Near Concord, several Minutemen from small towns group together to defend against the British
Impact: Shot heard around the world—American Revolution begins; Americans win and inflict heavy casualties on British troops as British retreat to Boston
Battle of Bunker Hill (1775)
Americans inflicted heavy losses on the British
What was crucial turning point for American Revolution was the alliance of foreign nations
Winter at Valley Forge
Terrible winter with many dying but Washington kept his troops there and trained all winter long
Tough times created more unity amidst American army
Battle of Saratoga (1777)- Most important battle of the Revolution
Surprise victory of the revolution
Impact: Turning point—Gained French support contributed French Navy + supplies
Treaty of Paris (1782)
British must fully recognize the US as a nation
Established the western border of the US as the Mississippi River
Post War Society
Loyalists/tories
Most (over 80,000) fled to Canada or England
Lost property- immigration affected colonies
Religious Groups
Anglicans (Loyalists) & Quakers (non-violence many move away from Quaker Church to fight in the war) weakened
Roman Catholics strengthened (French)
Slavery
Slaves exposed to liberty
Revolutionary sentiment pushes for anti-slavery thought in the North
Southern plantation owners believe slavery necessary to their economy
Native Americans
Supported the British because promise of stopping expansion—now with new western border take away land largely settled by natives
Natives continue attacking western settlers with westward expansion
Women
Large contributors during war; Daughters of Liberty boycotts
Women take on roles tending to laundry, cooks, nurses, work in factories, helping in the war
Education- Republican Motherhood
Abigail Adams- “Remember the Ladies”
Economy
Self-sufficient economy—not government controlled
Traded finished American goods
State Governments- created during the war, most consisted of:
Limiting executive power
Republicanism- democracy in practice a form of government allowing citizens to directly vote or elect representatives
Citizen rights
Separation of Powers (Separate Legislature and Executive branch)
Voting (White males, held property)
Concept of equality—for white landowning males
Later on, the separation of church and state
Articles of Confederation
Adopted in 1777 ratified 1781-
Weak central government unable to perform necessary government functions
No executive power, Congress operates national government
Congressional Powers:
Conduct wars, foreign relations, territory
Non-Congressional Powers
Unable to draft an army or collect taxes and regulate trade
Had 913 states unanimous approval to amend the Articles and 9/13 states to pass new laws
Territory Ordinances
National government must organize territory—overcrowding in Eastern coast of the US
Decide to sell off territory (in the Ohio River Valley)
Land Ordinance of 1785
Ohio territory was surveyed, sold, and marked into grids called townships
Always reserved land for public schools
Northwest Ordinance 1787
Ways to become a state
60,000 apply for statehood must abide by the Constitution
Freedom of religion, trial by jury, prohibit slavery
Northwest ordinance opposed by Southern states—giving power to Northern states in Congress
Shay’s Rebellion 1786
Large debt due to the war
Articles of Confederation has no power to tax, thus states increase taxes
Federalism division of power between Federal Govt and States
Daniel Shay organizes rebellion in Mass
Daniel Shay was owed money for fighting in war but did not receive any—states had debt thus raised taxes
Rebellion made of ex-soldiers and debtors
Increase paper money, tax relief, suspend debts
Attempt to seize arsenal
State militias put down rebellion
Importance
Showed the lack of power of the Confederation and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation
Creating a new government
Hamilton pushes for a national convention —> Anapolis Convention 1786 only 5 state representatives present
Thought of how to get all 13 states at the convention
Agree to meet in Philadelphia next year
Constitutional Convention 1787
Virginia Plan (Bigger State)
3 branches
Legislature 2 houses (upper and lower determined by state population)
New Jersey Plan (smaller states)
1 house legislature (Continental Congress) equal representation from every state
Expand powers to tax and regulate commerce
Great Compromise/Connecticut Plan
3 branches of government
Bicameral legislature with two houses (upper house (senate) 2 representatives each; lower house (house of representatives) based on population)
3/5 compromise- Lower house based on pop. since Southern states have larger populations due to slaves; Each slave counted as 3/5 for population
Potential Problems
Government interferes with the Southern economy
Agreed for slave trade to stop in 20 years—law ends up getting vetoed
No individual rights yet
Federalists
Supporters of the Constitution and a strong central government
Need to convince people to support (Federalist Papers- 85 essays written by John Jay, Hamilton,)
Else would lead to anarchy
Anti-Federalists
True defenders of the principles from Revolution
Problems with the Constitution—lack of a bill of rights
State Convention
Need 9 states to ratify
Constitution gets ratified by 1789
Whiskey Rebellion (1794)
Farmers refused to pay excise tax and terrorized tax collectors
Govt knows citizens enjoy drinking whiskey so taxes whiskey distillers often from western Pennsylvania
Militia assembled and were supported by the Continental Army intimidated rebels so they stopped tax evasion
Comparable to Shay’s Rebellion
Neutrality with Foreign Nations
French Revolution
Debate over whether US should support, not support, or stay neutral; Thomas Jefferson supports, and George Washington neutrality, believe we should focus on America before assisting France
French minister “citizen” Genet broke all rules of diplomacy by appealing DIRECTLY to American citizens to support the French cause—Washington asked French to remove him and Genet eventually becomes a citizen in the US due to his party being overthrown
Jay’s Treaty (1794)
Finish out the Treaty of Paris 1783
British army would impress (raid and capture) American seamen (sailors) into the British Navy (British and French war after French Revolution)
US drive away British influence in Northwest
US neutral in British-French conflicts
 Knowt
Knowt