Chapter 7: Production, Cost, and the Perfect Competition Model
7.1 The Production Function
Allocative efficiency: when marginal cost = marginal value
- Also known as efficiency in output
- Marginal cost: cost of producing one more unit
- Marginal value: value of one more unit
Technical efficiency: reached when economy’s factors of supply are used to maximize production
Also known as efficiency in production
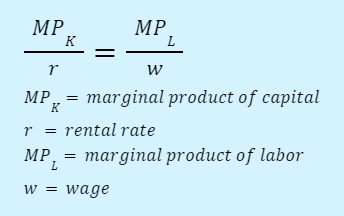
Marginal product: additional output produced per period when one more unit of an input is added
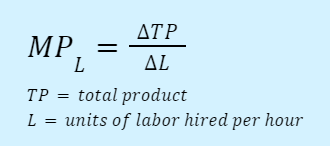
Law of diminishing marginal returns: as one amount of an input increases, marginal returns will eventually decrease
Average product:
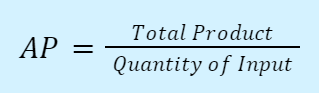
Total product curve: shows relationship between total amount of output produced vs. number of units of an input used
- Fixed costs: do not change when more output is produced
- Variable costs: do change when more output is produced
- Total Costs = Total Fixed Costs + Total Variable Costs
- TC = TFC + TVC
7.2 Short- and Long-Run Production Costs
Short run: time frame where at least one factor of production is constant
- Firms cannot enter/exist market
- Long-run: all factors of production are variable, no fixed costs
Economies of scale: exist over range of output where long-run average cost curve slopes down
- Cost per unit decreases
7.3 Types of Profit
- Profit: value remaining after paying all costs and financial obligations of a company
- Profit = TR - TC
- Gross profit: total sales - total cost of goods/services
- Operating profit: gross profit - operating expenses
- Net profit: amount left after deducting all other expenses
- Ex) After taxes, loan interests
7.4 Profit Maximization
- Profit: total revenue - total cost
- Break-even points: points on graph where total revenue = total cost
- Profit maximization: loss minimization
7.5 Perfect Competition
When is there perfect competition?
- Many sellers
- Products are standardized
- Firms accept market price → “price takers”
- Firms can enter/exit market freely
Economic profits: total revenue - total cost