Cancer- Neoplasia
neoplasia: abnormal mass of tissue growth
}}Hallmarks of Cancer:}}
- self-sufficiency in growth signals
- insensitivity to anti-growth signals ( because they don’t have receptors)
- evading apoptosis( telomeres)
- sustained angiogenesis
- limitless replicative potential
- invasion and metastasis
- escaping immune surveillance (checkpoint inhibitors)
- variation in population of cells
- heritable: Mutations in DNA, chromosomes, methylation pattern
^^Terminology^^
tissue types
- carcinoma → epithelial cells
- sarcoma → connective tissue
- leukemia → circulatory or lymphatic
cell types
- adenomatous cells → ductal or glandular cells
- squamous cells → flat cells
- myeloid → blood cells
- Lymphoid → lymphocytes or macrophages
begin vs malignant
benign tumors → suffix “- oma”
except carcinomas + sarcomas + lymphomas
malignant → all other tumors
carcinoma in situ (CIS) → epithelial malignant tumors that have not broken through or invade the surrounding stroma (can be cut out cleanly)
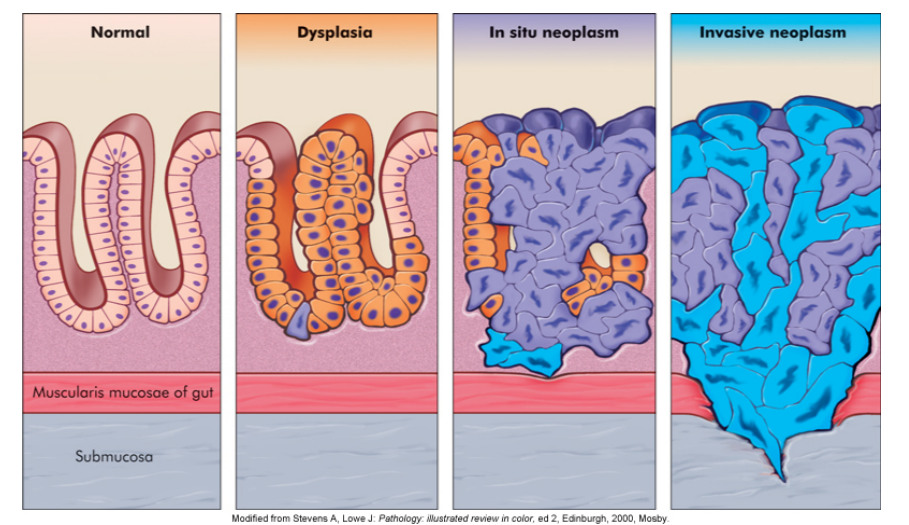
Cancer Progression
stages of malignant cancers:
- stage 1: confined to the organ of origin
- stage 2: locally invasive
- stage 3: spread to lymph nodes
- stage 4: spread to distant sites
Tumor staging by TNM System
- Tumor
- Nodes
- Metastasis
How does cancer progress in the body( from embryo to death)?
- fertilized egg → toti potent stem cell → proliferation(copy-paste) → differentiation (specialization) → ♾ → advantageous driver mutant → clonal expansion → saturation the point where tumor is its bigger because there is no more food/ energy/ space) → new advantageous mutant( even more aggressive) → new colonial expansion wave
- remember:
- limitless replicated potential ( due to enzymes that elongate the telomeres→ telomerase p53 CANCER! )
- what is the paradox
- fast growing tumors are easiest to treat
Tumor Markers
- → biological markers that are produced by cancer cells
- enzymes
- genes
- Antigens ( PSA -prostate-specific antigens are associated with prostate cancer)
- antibodies
Bengin vs. Malignant cancer
| <<Benign<< | <<Maligant<< |
|---|---|
| grow slowly | Grow rapidly |
| Well defined capsule | Not encapsulated |
| Not invasive | Invasive |
| well differentiated | poorly differentiated |
| low mitotic index | High mitotic index |
| Do not metastasize | Can spread distantly(metastasis) |
- \
Viral Infection → Cancer
- PAP smear- cervical l screaming via a swab, the smear is histologically analyzed and checks if to dysplasia
- ==red stained cells== are dysplasia or cancer
- could also show cells is mitosis and multiple nuclei
- blub that starts to grow → lesion
- HPV causes cancer in basal cells( because they proliferate the most)
- due to the alteration of genome of the host develops cancer
- HVP produced proteins that block p53( hallmark in cancer) if the p53 build-ups and it does not function the cell does not go into apoptosis
- ^^blue + purple^^ stained cells are normal
- Other viruses can cause tumors because the disturb normal cell development
- hepatitis B → liver
- EBV → kissing disease ( mononucleosis) + Burkitt lymphoma
- Can bacteria cause cancer?
- yes → Helicobacter pylori → stomach cancer