Lab Practical 1 – Key Concepts (Ch 1-8)
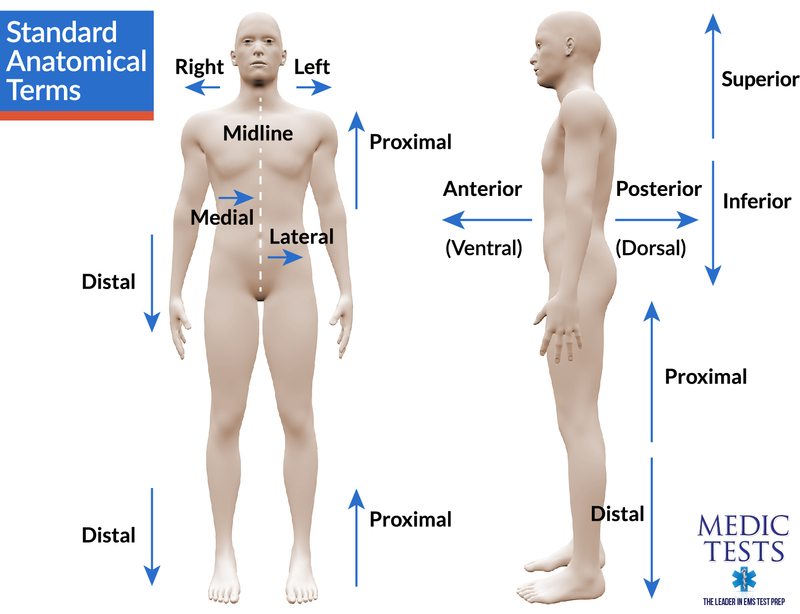
Anatomical Position and Directional Terms
Anatomical position: describe and demonstrate standard posture.
Directional terms (with simple synonyms):
Superior (cranial/cephalic)
Inferior (caudal)
Medial
Lateral
Proximal
Distal
Anterior (ventral)
Posterior (dorsal)
Superficial (external)
Deep (internal)
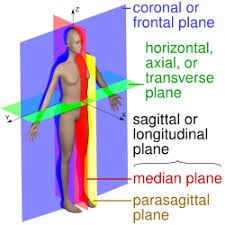
Body Planes and Regions
Planes and sections:
Sagittal plane
Frontal (coronal) plane
Midsagittal plane
Transverse (horizontal) plane
Parasagittal plane
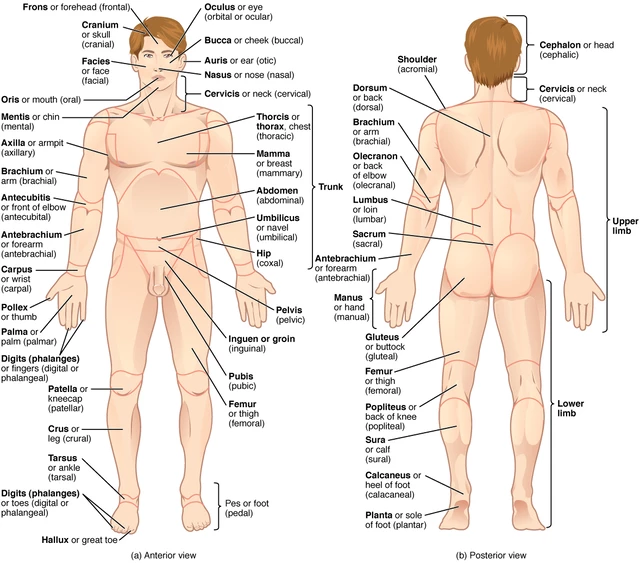
Regional terms (sample list):
Anterior View, Abdominal, Crural, Palmar, Antebrachial, Digital, Patellar, Antecubital, Femoral, Pedal, Axillary, Frontal, Pelvic, Brachial, Inguinal, Pubic, Buccal, Nasal, Sternal, Carpal, Oral, Tarsal, Cervical, Orbital, Posterior View, Calcaneal, Lumbar, Vertebral, Cephalic, Occipital, Gluteal, Plantar
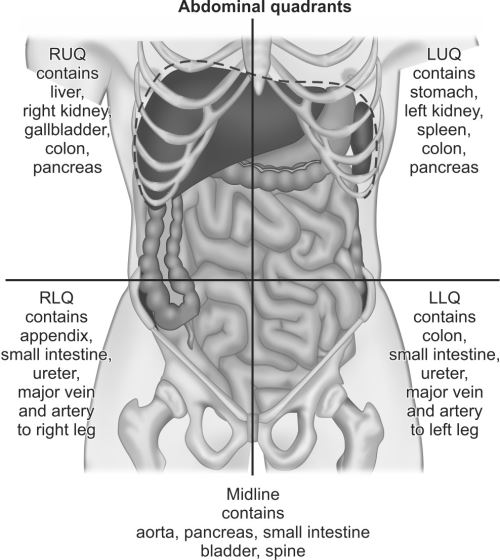
Body Cavities and Quadrants
Body cavities:
Dorsal body cavity: Cranial cavity, Vertebral (spinal) cavity
Ventral body cavity: Thoracic cavity (includes pleural, pericardial, mediastinum), Abdominopelvic cavity (abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity)

Lab reference: identify one organ in each abdominopelvic quadrant:
Right upper quadrant (RUQ): liver
Left upper quadrant (LUQ): stomach
Right lower quadrant (RLQ): appendix
Left lower quadrant (LLQ): sigmoid colon
Organ Systems (Reference)
Integumentary system: skin
Endocrine system: thyroid gland
Digestive system: esophagus, stomach
Skeletal system: bones
Cardiovascular system: heart
Urinary system: kidneys
Muscular system: skeletal muscles
Lymphatic system: lymph nodes, spleen
Reproductive system: testes, ovaries
Nervous system: brain, spinal cord
Respiratory system: lungs
Use of the Microscope
Parts and functions:
Ocular lens (eyepiece)
Iris diaphragm
Fine adjustment knob
Objective lenses
Condenser
Mechanical stage knobs
Revolving nose piece
Base
Power switch
Stage
Arm
Illuminator (light source)
Magnification:
Total magnification = \text{Ocular magnification} \times \text{Objective magnification}
Levels: Scanning, Low power, High power, Oil immersion
Other: proper transport, cleaning, and storage of the microscope
Cells
Parts of a cell (major organelles):
Cell/plasma membrane
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pore
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Cytoplasm (cytosol)
Cytoskeleton
Ribosome
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
Lysosome
Peroxisome
Centrioles
Chromosome
Diffusion and temperature:
Diffusion: movement from high to low concentration; rate increases with higher temperature
Osmosis:
Hypotonic solution vs hypertonic solution effects on Elodea cells
Cell cycle phases (models):
Interphase
Mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Cytokinesis
Histology/Tissues
Epithelial tissues:
Simple squamous
Simple columnar
Stratified squamous
Simple cuboidal
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Transitional
Connective tissues:
Loose (areolar) CT
Dense regular CT
Elastic cartilage
Adipose CT
Hyaline cartilage
Bone
Integumentary System
General functions of the integumentary system
Skin layers: epidermis and dermis; hypodermis is not part of skin
Epidermal strata (from superficial to deep):
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
Accessory structures:
Dermal papillae
Sebaceous gland
Nail
Hair shaft
Merocrine (eccrine) sweat gland
Nail plate
Hair root
Free nerve ending
Meissner’s corpuscle
Lunula
Arrector pili muscle
Pacinian corpuscle
Pore
Eponychium
Nail folds
Hair follicle
Skeletal Terms, Bone Histology, and Microanatomy
Bone shapes by location:
Long bone
Flat bone
Sesamoid bone
Short bone
Irregular bone
Bones by location (example list): Carpals, Humerus, Scapula, Femur, Phalanges, Sphenoid, Frontal, Sacrum, Vertebrae
Long bone structures:
Compact bone
Proximal epiphysis
Epiphyseal line
Spongy bone
Distal epiphysis
Diaphysis
Marrow (medullary) cavity
Compact vs. spongy bone:
Osteon, Lamellae, Central (Haversian) canal
Lacunae, Osteocyte
Perforating (Volkmann’s) canals, Trabeculae
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
Distinguish between axial and appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton bones example list (from the references): skull bones, vertebral column components, sternum, ribs
Notable skull bones and features:
Frontal bone, Parietal bones, Temporal bones
External acoustic meatus, Styloid process, Mastoid process, Mandibular fossa
Occipital bone, Foramen magnum, Occipital condyle
Sphenoid bone, Sella turcica, Optic canal
Ethmoid bone, Crista galli, Cribriform plate, Perpendicular plate
Maxillae, Palatine bones, Zygomatic bones, Lacrimal bones, Nasal bones, Vomer, Mandible
Suture lines:
Sagittal, Coronal, Squamous, Lambdoid
Skull features:
Hard palate
Fontanels (fetal skull): anterior, posterior
Hyoid bone
Bones of the Vertebral Column and Thoracic Cage
Vertebral column segments: Cervical ($C1$ to $C7$), Thoracic ($T1$ to $T{12}$), Lumbar ($L1$ to $L5$), Sacrum, Coccyx
Atlas and Axis:
Atlas ($C_1$)
Axis ($C_2$) with odontoid process (dens)
General vertebral features:
Vertebral body, Vertebral canal, Transverse process, Spinous process, Intervertebral discs
Bony thorax (thoracic cage):
Sternum: Manubrium, Body, Xiphoid process
Ribs: True (7 pairs), False (3 pairs), Floating (2 pairs)
Pectoral and Pelvic Girdles; Limbs
Pectoral girdle and upper limb:
Clavicles, Scapulae (Acromion, Coracoid process, Glenoid cavity)
Humerus (head, greater/lesser tubercles, epicondyles, trochlea, capitulum, fossae)
Radius (radial head, tuberosity, styloid process)
Ulna (olecranon, trochlear notch, coronoid process, radial notch, styloid)
Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
Pelvic girdle and lower limb:
Os coxae: Ilium (iliac crest, greater sciatic notch), Ischium (ischial tuberosity), Pubis (pubic symphysis, pubic arch)
Acetabulum, Obturator foramen
Femur (head, neck, greater/lesser trochanters, epicondyles, condyles)
Patella
Tibia (medial/lateral condyles, tibial tuberosity, anterior crest), Fibula (head)
Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges
Notes on Bones by Region
Appendicular skeleton bones and markings (overview):
Pectoral girdle and upper limb bones, Pelvic girdle and lower limb bones
Important bone markings include heads, processes, fossae, epicondyles, condyles, tubercles, acetabulum, olecranon, trochlear notch, etc.
Visible Body Resource
Useful for study: Visible Body interactive tool (CCBC Library) via Library databases