
8
Chapter 8 Appendicular Skeleton
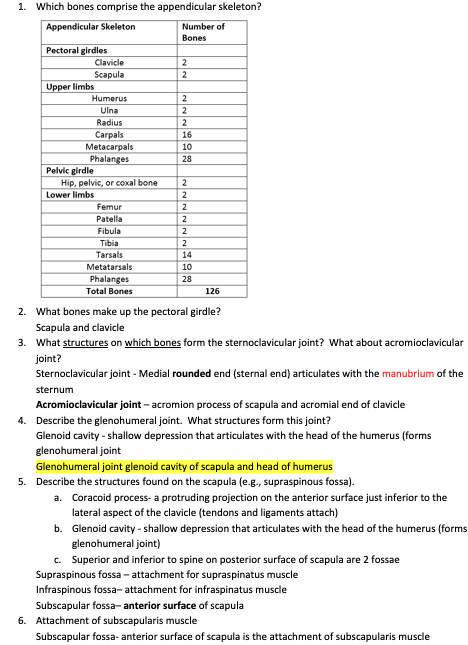
1. Which bones comprise the appendicular skeleton?
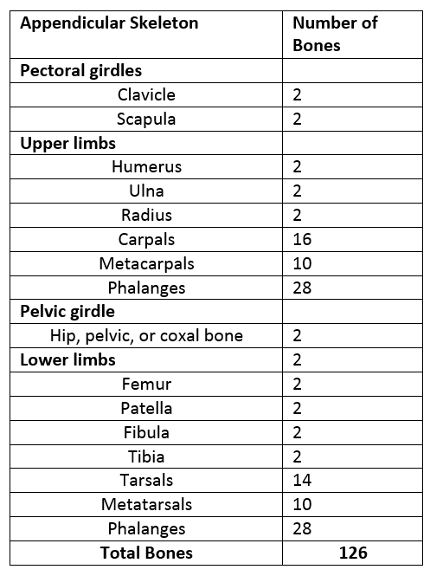
2. What bones make up the pectoral girdle?
Scapula and clavicle
3. What structures on which bones form the sternoclavicular joint? What about acromioclavicular joint?
Sternoclavicular joint - Medial rounded end (sternal end) articulates with the manubrium of the sternum
Acromioclavicular joint – acromion process of scapula and acromial end of clavicle
4. Describe the glenohumeral joint. What structures form this joint?
Glenoid cavity - shallow depression that articulates with the head of the humerus (forms glenohumeral joint
Glenohumeral joint glenoid cavity of scapula and head of humerus
5. Describe the structures found on the scapula (e.g., supraspinous fossa).
a. Coracoid process- a protruding projection on the anterior surface just inferior to the lateral aspect of the clavicle (tendons and ligaments attach)
b. Glenoid cavity - shallow depression that articulates with the head of the humerus (forms glenohumeral joint)
c. Superior and inferior to spine on posterior surface of scapula are 2 fossae
Supraspinous fossa – attachment for supraspinatus muscle
Infraspinous fossa– attachment for infraspinatus muscle
Subscapular fossa– anterior surface of scapula
6. Attachment of subscapularis muscle
Subscapular fossa- anterior surface of scapula is the attachment of subscapularis muscle
7. What structures form the elbow joint?
Olecranon process of ulna and olecranon fossa of humerus form bony elbow projection
8. Describe the humeroulnar and humeroradial joints. What structures form these joints?
Humeroradial joint– formed by the head of radius and capitulum of humerus (condyle)
* Notice no actual articulation between these structures
Humeroulnar joint – formed by the trochlea of humerus (condyle) and trochlear notch of ulna
9. Describe the structures found on the humerus.
· Surgical neck is constriction in humerus just distal (below) to tubercles where head tapers to shaft (body)
i. Below epiphyseal growth plate
· Coronoid fossa – anterior depression that receives coronoid process of ulna (flexion)
· Olecranon fossa– large posterior depression that receives olecranon of ulna
· Medial and lateral epicondyles – rough projections on either side of distal end of humerus (tendon attachment
10. The radius and ulna connect in 3 locations. What are these locations?
1. Interosseous membrane joins shafts (fibrous joint)
2. Head of radius articulates with ulna’s radial notch at proximal end (bony joints)
3. Head of ulna articulates with ulnar notch of radius distally (bony joints)
3. Describe proximal and distal radioulnar joints. What structures form these joints?
Proximal radioulnar joint - radial notch of ulna and head of radius
1. Uniaxial pivot joint (flexion and extension)
Distal radioulnar joint – ulnar notch of radius and ulnar head
4. What structure on the ulna stabilizes the wrist?
Styloid process
5. What are carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges?
6. Which 2 carpal bones articulate with the radius?
Scaphoid and lunate
7. What 8 bones make up the wrist/carpals?
Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
8. How many bones make up the phalanges per hand?
14 bones
9. Know the different parts on the upper limb (arm) and lower limb (leg)? Upper arms = Shoulder-> phalanges lower limb= hip to toes What bones comprise the upper arm and lower forearm? What structures can you find on each bone? What bones comprise the upper leg (thigh) and lower leg? What structures can you find on each bone?
Upper arm humerous
Lower forearm- radius and ulna
Upper leg(thigh) femur
Lower leg- tibia fibula
10. Which bones come together to form the pelvic girdle? Name the structures found on each bone. Think lab!
Ilium, pubic, ishium
11. What type of cartilage makes up the pubic symphysis?
Fibrocartilage
12. Describe the sacroiliac joint. What structures form this joint?
sacroiliac joint - Auricular surface of ilium articulates with iliac facet of sacrum
13. Describe the tibiofemoral joint. What structure form this joint?
Tibiofemoral joint – condyles of femur articulate with condyles of tibia (hinge joint; extension and flexion)
14. What type of bone is the patella?
Sesamoid bone
15. What types of movement is permitted at the hip?
Flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, external/ internal rotation
16. The proximal end of the femur articulates with what structure of the hip bone? acetabulum
What does the distal end of the femur articulate with? Tibia and patella
Proximal end (head) articulates with acetabulum of hip bone
Distal end articulates with tibia and patella
17. The proximal end of the tibia articulates with what structures? What about the distal end of the tibia?
Proximal End:
1. Lateral and medial condyles at the proximal end articulate with the femur to form tibiofemoral joints
2. Tibial tuberosity on anterior surface is point of attachment for patellar ligament
Distal End:
3. Distally medial malleolus articulate with the talus of the ankle and the fibula
18. What is the function of the fibula? Tibia?
Tibia- weight bearing bone of leg
FibuLA (Lateral) stabilize ankle joint
19. What bones articulate to form the ankle joint?
Medial malleolus of tibia
Lateral malleolus of fibula
Talus
20. What bones make up the tarsal bones? What are metatarsals and phalanges?
7TARSAL BONES - Talus and calcaneus (heel), Navicular and cuboid, Cuneiforms (1, 2, 3)
Metatarsals- 1st, 2nd, and 3rd cuneiform bones and with the cuboid
Phalanges- Each toe with the exception of the hallux (big toe) is composed of 3 phalanges
21. Describe the transverse, medial, and lateral arches of the foot.
· Medial part of arch originates at calcaneus, rises to talus and descends through navicular, 3 cuneiforms, and the heads of the 3 medial metatarsals
· Lateral part begins at calcaneus. It rises at cuboid and descends to the heads of the 2 lateral metatarsals
· Transverse arch Found between medial and lateral aspects of the foot formed by navicular, 3 cuneiforms, and the bases of 5 metatarsals
8
Chapter 8 Appendicular Skeleton
1. Which bones comprise the appendicular skeleton?

2. What bones make up the pectoral girdle?
Scapula and clavicle
3. What structures on which bones form the sternoclavicular joint? What about acromioclavicular joint?
Sternoclavicular joint - Medial rounded end (sternal end) articulates with the manubrium of the sternum
Acromioclavicular joint – acromion process of scapula and acromial end of clavicle
4. Describe the glenohumeral joint. What structures form this joint?
Glenoid cavity - shallow depression that articulates with the head of the humerus (forms glenohumeral joint
Glenohumeral joint glenoid cavity of scapula and head of humerus
5. Describe the structures found on the scapula (e.g., supraspinous fossa).
a. Coracoid process- a protruding projection on the anterior surface just inferior to the lateral aspect of the clavicle (tendons and ligaments attach)
b. Glenoid cavity - shallow depression that articulates with the head of the humerus (forms glenohumeral joint)
c. Superior and inferior to spine on posterior surface of scapula are 2 fossae
Supraspinous fossa – attachment for supraspinatus muscle
Infraspinous fossa– attachment for infraspinatus muscle
Subscapular fossa– anterior surface of scapula
6. Attachment of subscapularis muscle
Subscapular fossa- anterior surface of scapula is the attachment of subscapularis muscle
7. What structures form the elbow joint?
Olecranon process of ulna and olecranon fossa of humerus form bony elbow projection
8. Describe the humeroulnar and humeroradial joints. What structures form these joints?
Humeroradial joint– formed by the head of radius and capitulum of humerus (condyle)
* Notice no actual articulation between these structures
Humeroulnar joint – formed by the trochlea of humerus (condyle) and trochlear notch of ulna
9. Describe the structures found on the humerus.
· Surgical neck is constriction in humerus just distal (below) to tubercles where head tapers to shaft (body)
i. Below epiphyseal growth plate
· Coronoid fossa – anterior depression that receives coronoid process of ulna (flexion)
· Olecranon fossa– large posterior depression that receives olecranon of ulna
· Medial and lateral epicondyles – rough projections on either side of distal end of humerus (tendon attachment
10. The radius and ulna connect in 3 locations. What are these locations?
1. Interosseous membrane joins shafts (fibrous joint)
2. Head of radius articulates with ulna’s radial notch at proximal end (bony joints)
3. Head of ulna articulates with ulnar notch of radius distally (bony joints)
3. Describe proximal and distal radioulnar joints. What structures form these joints?
Proximal radioulnar joint - radial notch of ulna and head of radius
1. Uniaxial pivot joint (flexion and extension)
Distal radioulnar joint – ulnar notch of radius and ulnar head
4. What structure on the ulna stabilizes the wrist?
Styloid process
5. What are carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges?
6. Which 2 carpal bones articulate with the radius?
Scaphoid and lunate
7. What 8 bones make up the wrist/carpals?
Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
8. How many bones make up the phalanges per hand?
14 bones
9. Know the different parts on the upper limb (arm) and lower limb (leg)? Upper arms = Shoulder-> phalanges lower limb= hip to toes What bones comprise the upper arm and lower forearm? What structures can you find on each bone? What bones comprise the upper leg (thigh) and lower leg? What structures can you find on each bone?
Upper arm humerous
Lower forearm- radius and ulna
Upper leg(thigh) femur
Lower leg- tibia fibula
10. Which bones come together to form the pelvic girdle? Name the structures found on each bone. Think lab!
Ilium, pubic, ishium
11. What type of cartilage makes up the pubic symphysis?
Fibrocartilage
12. Describe the sacroiliac joint. What structures form this joint?
sacroiliac joint - Auricular surface of ilium articulates with iliac facet of sacrum
13. Describe the tibiofemoral joint. What structure form this joint?
Tibiofemoral joint – condyles of femur articulate with condyles of tibia (hinge joint; extension and flexion)
14. What type of bone is the patella?
Sesamoid bone
15. What types of movement is permitted at the hip?
Flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, external/ internal rotation
16. The proximal end of the femur articulates with what structure of the hip bone? acetabulum
What does the distal end of the femur articulate with? Tibia and patella
Proximal end (head) articulates with acetabulum of hip bone
Distal end articulates with tibia and patella
17. The proximal end of the tibia articulates with what structures? What about the distal end of the tibia?
Proximal End:
1. Lateral and medial condyles at the proximal end articulate with the femur to form tibiofemoral joints
2. Tibial tuberosity on anterior surface is point of attachment for patellar ligament
Distal End:
3. Distally medial malleolus articulate with the talus of the ankle and the fibula
18. What is the function of the fibula? Tibia?
Tibia- weight bearing bone of leg
FibuLA (Lateral) stabilize ankle joint
19. What bones articulate to form the ankle joint?
Medial malleolus of tibia
Lateral malleolus of fibula
Talus
20. What bones make up the tarsal bones? What are metatarsals and phalanges?
7TARSAL BONES - Talus and calcaneus (heel), Navicular and cuboid, Cuneiforms (1, 2, 3)
Metatarsals- 1st, 2nd, and 3rd cuneiform bones and with the cuboid
Phalanges- Each toe with the exception of the hallux (big toe) is composed of 3 phalanges
21. Describe the transverse, medial, and lateral arches of the foot.
· Medial part of arch originates at calcaneus, rises to talus and descends through navicular, 3 cuneiforms, and the heads of the 3 medial metatarsals
· Lateral part begins at calcaneus. It rises at cuboid and descends to the heads of the 2 lateral metatarsals
· Transverse arch Found between medial and lateral aspects of the foot formed by navicular, 3 cuneiforms, and the bases of 5 metatarsals

 Knowt
Knowt