1 Foundations of Biology
work in progress!
1.1 Studying biology: the practice of science
Biology - the study of living organisms
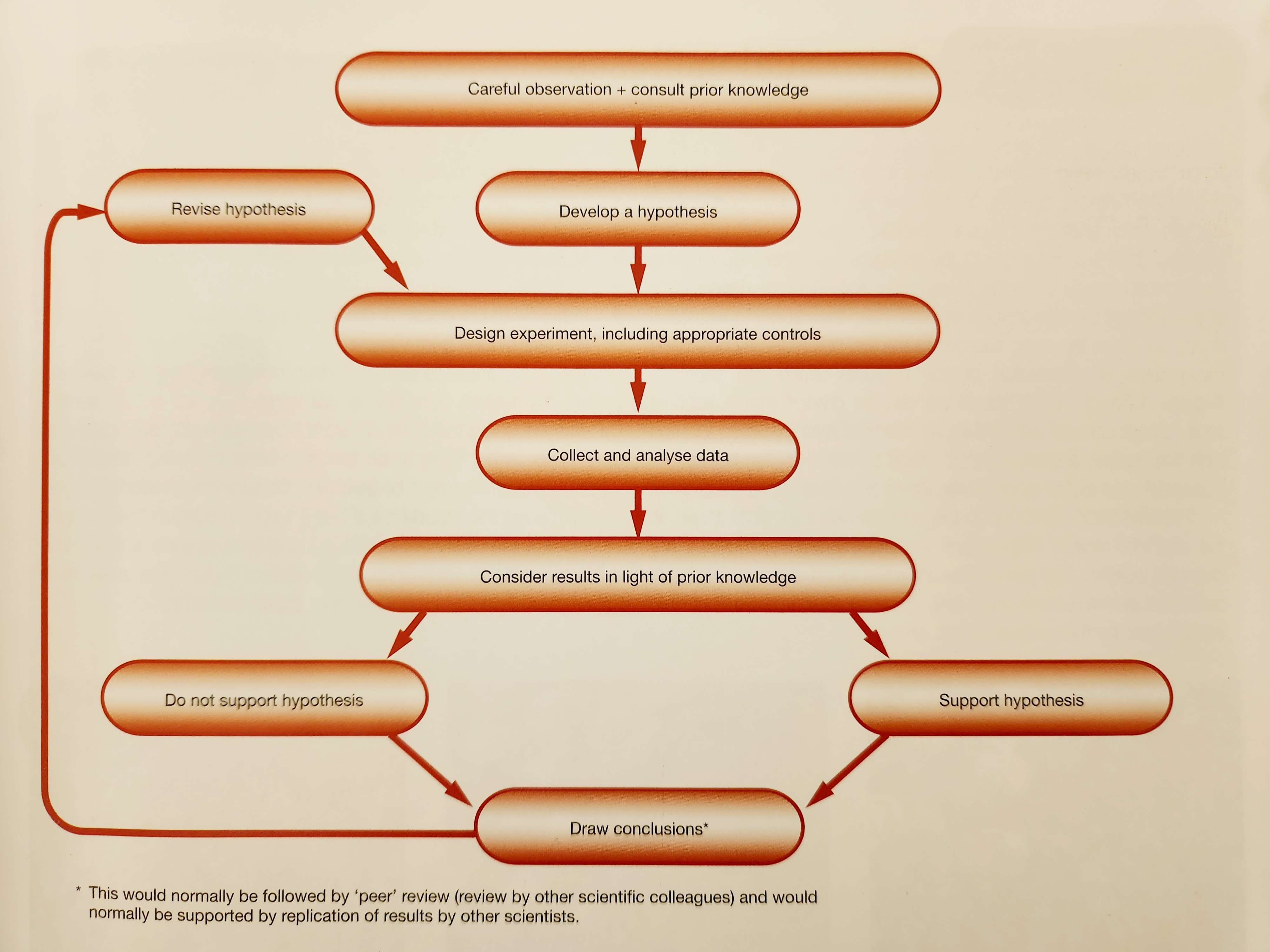
Scientific method is used to design and perform experimental investigations.
Well-designed investigations take into consideration current observations and previous results.
The importance of observation
Observations can reveal how organisms function and how they interact with others + the environment.
Observations take advantage of human senses and apparatus for more accurate results.
They can be interpreted differently based on what one already knows/has experienced.
Learning by experimentation: the scientific method
Scientists observe what is already known, then ask questions (“why?”); an experimental approach to the study of science.
Hypothesis- a potential justification/explanation for things that are observed.
Can be used to predict events/behaviour.
Tested in experiments to determine accuracy; the hypothesis is rejected if inaccurate, supported if accurate.
Theory - if the hypothesis has been proven as correct under all the conditions that it has been tested in, it becomes this (AKA principle)
Asking the right questions: making hypotheses
Hypotheses have to be testable, but even if it can’t be tested, it doesn’t mean it’s not correct.
Gather information that is relevant to proving (or disproving) the hypothesis.
Choosing the right method
Methods have to be reliable; described in sufficient detail to allow for repetitions of the experiment.
If similar results cannot be obtained upon repetition, it is considered unreliable.
Avoid personal bias; be objective when collecting and analysing data.
Results should be clearly stated, separate from discussion of results.
Multiple trials should be conducted, to prove that results were not because of a one-time fluke.
Experiments and their results need to be able to replicated in order to be validated.
The need for experimental controls
Variables that can affect experiment outcomes:
Time of day
Temperature
Amount of light
Season
Level of noise
Independent variable - the variable that is being tested. (AKA experimental)
Dependent variable - the variable that is being measured when the independent variable changes.
Controlled variable - the variables that are kept constant between experiments
Control group - a secondary experiment that is identical to the first, bar the single experimental variable being tested.
As a controlled experiment, it means that one variable at a time can be tested and its effects can be analysed.
Used to eliminate the effects that random factors have on results.
Making valid conclusions
Valid conclusions depend on reliability of results and their interpretations.
Speculations - suggestions on what may be occurring based on results.
Conclusion - statement based on the observations and measurements.
Limitations of the scientific method
Can only be applied to hypotheses that are testable, and to questions that can be answered.
e.g it is impossible to conduct experiments around ‘life after death’
Cannot be used to test moral or ethical issues, but can predict environmental/biological impacts.
1.2 Important principles in biology
Biological principles - theories that are supported by immense amounts of evidence, that make it unlikely for it to be disproved in the future.
Relevant to the way that almost all living organisms function.
“Organisms are living things”
Organisms are made of cells
Cell theory - a theory which states that all organisms are made of cells, that all cells come from pre-existing cells, and that the cell is the smallest living organisational unit.
All cells have a cell membrane that encloses the interior fluid, cytoplasm.
All cells have DNA as genetic material.
Evolution explains diversity
Similarities, differences and geographic distribution of organisms → organisms have changed over time.
Phylogeny - study of evolutionary relationships between organisms.
Scientific classification - hierarchy of names based on phylogenetic relationships that encompasses all organisms.
Characteristics of organisms
Common to all organisms, no matter whether plant, animal, fungi, protist or bacteria.
Made of cells
Chemically complex and highly organised
Exchange energy and matter in their environment
Sense and respond to stimuli
Grow and reproduce
Evolve
Common requirements for life
All life requires a source of energy.
Amount of energy depends on organism type, stage of growth, activity level and reproductive state.
All life requires nutrients and water for growth, maintenance and repair.
Waste is produced as a result of the latter processes.
Simplicity of waste excretion depends on size of organism
All life is composed of water, organic compounds (proteins, carbs, lipids, vitamins) and minerals.
All life requires the ability to sense and respond to stimuli in their internal and external environments.
Organisms are adapted to their environment
Over time, species become adapted to their external environment
Natural selection - individuals with features most suited to their environment survive and pass those features down to their offspring.
Inherited behaviour and functions make organisms suited for survival in their environment.
1.3 The composition of organisms
92 types of naturally occurring elements on Earth (NB. this is approximate and may have changed from the years this textbook was published)
Organic compounds - complex compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen that are produced or found in living organisms.
Inorganic compounds - all other compounds that are not formed of carbon and hydrogen.
They are still important for living organisms (e.g water, oxygen)
Inorganic compounds
Water
Most organisms are 70-90% water.
Chemical reactions that occur in cells happen in a watery medium.
Water’s properties (such as pH and heat capacity) are very important in biological processes.
Water molecules are cohesive; strong tendency to stick together.
Surface tension - Bonds between surface of molecules.
Water’s surface tension allows small insects to walk across its surface without ‘breaking’ the molecule.
Heat capacity - The amount of heat needed to change the temperature of an amount of matter by 1°C.
Water’s heat capacity is very high.
As chemical reactions occur in the body produce heat, water present in the body can absorb said heat without heating the cells up significantly.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide
Cellular respiration - the process of releasing energy from food molecules using oxygen.
A constant supply of oxygen is needed to keep cells active.
Although oxygen can be easily obtained from the atmosphere, solely marine animals are usually small given that oxygen is not soluble in water.
Organisms that obtain oxygen from water are small, flat, inactive or have efficient ventilation systems (e.g gills)
Photosynthesis - the process of making the organic compound glucose with a by-product of oxygen, using carbon dioxide, sunlight and water by plants.
Carbon dioxide is converted into energy by plants in photosynthesis, and returned to the environment through organic material decay and as a result of cellular respiration.
The “carbon cycle” between organisms and the atmosphere is essential to survival.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen fixation- the process performed by bacteria of converting atmospheric nitrogen into compounds that plants can be used.
Nitrogen is a key component of all proteins and thus is needed in a relatively large amount.
Minerals
Biologically important minerals:
Phosphorous
Potassium
Calcium
Magnesium
Iron
Sodium
Iodine
Sulphur
Mineral ions (mineral salts) are retrieved from weathered rocks and absorbed into plant roots.
Also found in cell cytosol, structural components such as bone, and enzyme + mineral molecules.
Humans require more than 20 different minerals.
Organic molecules
Four main types:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acid
Can be converted from one form to others, in places like the liver.
Carbohydrates are converted to fats for storage when food is plentiful.
The reverse occurs when food is no longer plentiful.
Can be linked together into larger molecule chains.
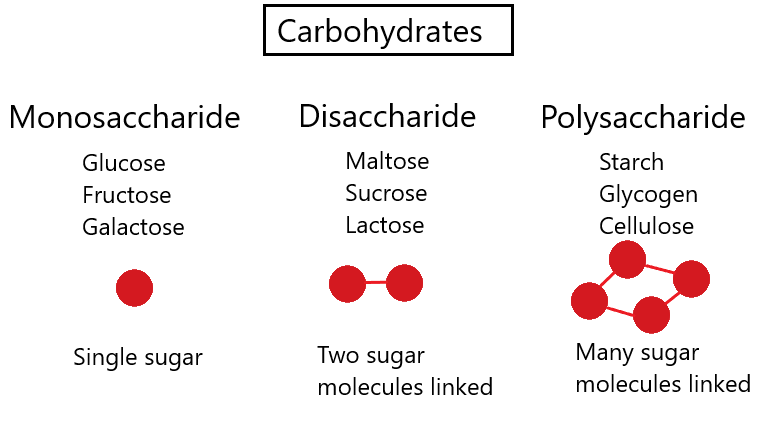
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates - compounds made out of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Most abundant organic compound.
Important source of energy for organisms.
Plants - the carbohydrate starch is used to store energy; the carbohydrate cellulose is used to support structure.
Animals; the carbohydrate glycogen stores energy.
Monosaccharides - subunits of carbohydrates; simple sugars.
Glucose is an example.
Monosaccharides have hydrogen/oxygen in the same proportions as water, meaning two hydrogens for every oxygen.
Disaccharides - two sugars joined together.
A molecule of water is removed.
Polysaccharides- many sugars joined together.
Lipids
Lipids - fat and oil molecules that store energy.
e.g phospholipids (cell membrane component) and steroids (hormones)
Composed of carbon, hydrogen and vitamins in different proportions to carbohydrates.
Smaller proportions of oxygen and can contain other elements (e.g nitrogen).
Proteins
Thousands of differing types of proteins; functions vary widely.
Each kind of organisms have own unique proteins.
e.g some are hormones, some are carrier molecules.
All are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
May also contain sulphur, phosphorus and other elements.
Composed in chains of units called amino acids.
Peptide bonds - the chemical links between amino acids in proteins.
Proteomics- the study of all proteins in an organism.
Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids- genetic material of all organisms.
Two types: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acids)
DNA contains instructions to assemble new proteins from amino acids.
RNA plays a role in protein manufacture.
Composed of subunits called nucleotides.
Vitamins
Vitamins - Organic materials used by animals in small amounts.
Used merely for normal functions.
Can be naturally synthesised, but other vitamins must be obtained in diet (e.g humans must obtain Vitamin C in our diet because we cannot ‘create’ them ourselves)
Vitamins can be used to make enzymes.
 Knowt
Knowt
