Chapter 3: Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport: Volume Ratio
Diffusion:
Is the ^^net movement of ions or molecules^^ from a region of ^^higher concentration to a region of low concentration^^ ^^down a concentration gradient.^^
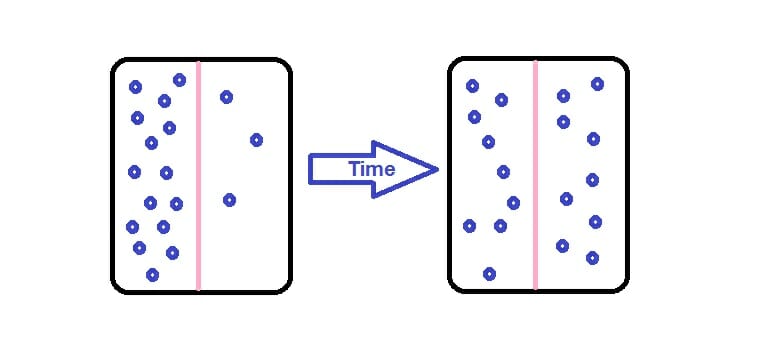
Factors Affecting Rate of Diffusion:
- ^^Surface Area:^^ larger the SA faster the rate of diffusion.
- ^^Temperature^^: higher the temp faster the rate of diffusion.
- ^^Diffusion Distance^^: the greater the distance the slower the rate of diffusion.
Example of Diffusion in human body:
Is exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in lungs.
Osmosis:
Is the ^^movement of water molecules^^ from a solution of ^^higher water potential to a solution of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane.^^
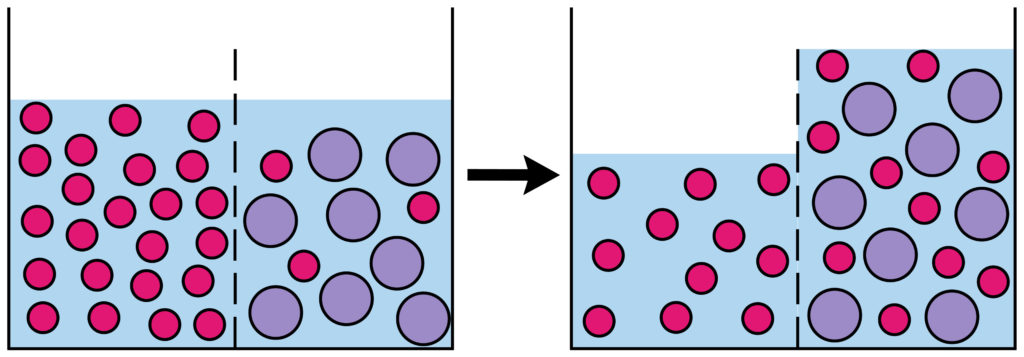
Terms to remember regarding Osmosis:
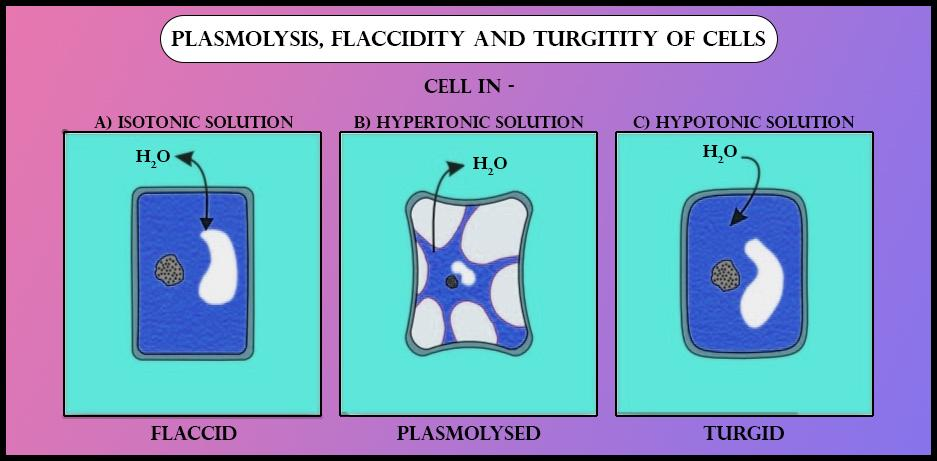
%%Turgid cells%% are described as turgid when they are swollen due to a high water content inside the cell and are causing turgor pressure. (occurs in hypotonic solution).
%%Turgor Pressure%% is the pressure on the cell wall from the cell membrane pushing upon it.
Cell becomes %%flaccid%% when water moves out of the cell via osmosis. The cell becomes shrink but the cell membrane does not peel away from the cell wall. (occurs in hypertonic solution).
%%Plasmolysis%% is shrinkage of cells when no or too little water is present inside.
In an Isotonic solution neither water enters or leaves due to no concentration difference.
Example of Osmosis in human body:
Exchange of substances in kidneys.
Active Transport:
Is the process in which ^^energy is used^^ to move the ^^particles of a substance against a concentration gradient^^ from a region where they are ^^in low concentration to a region where they are in high concentration^^.

Example of Active Transport in human body:
Absorption in villi.