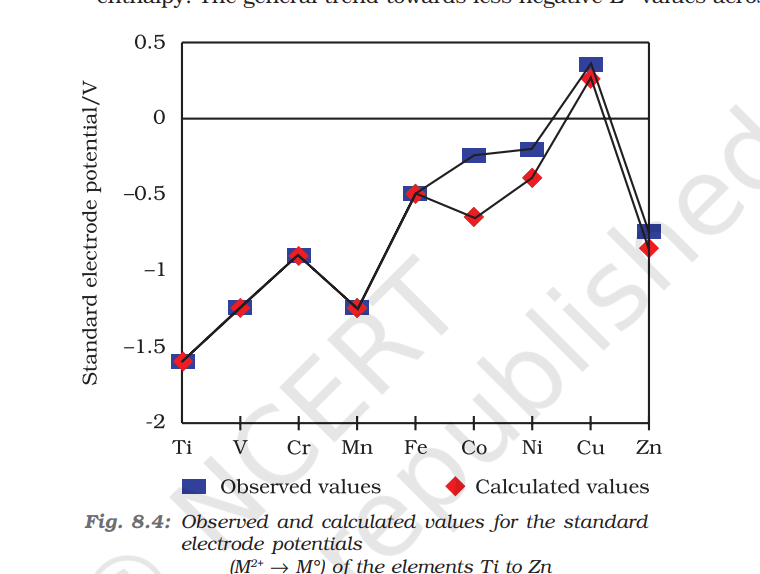
Table 8.4 contains the thermochemical parameters related to the transformation of the solid metal atoms to M2+ ions in solution and their standard electrode potentials. The observed values of E V and those calculated using the data of Table 8.4 are compared in Fig. 8.4. The unique behaviour of Cu, having a positive E V , accounts for its inability to liberate H2 from acids. Only oxidising acids (nitric and hot concentrated sulphuric) react with Cu, the acids being reduced. The high energy to transform Cu(s) to Cu2+(aq) is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy. The general trend towards less negative E V values across the series is related to the general increase in the sum of the first and second ionisation enthalpies. It is interesting to note that the value of E V for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected from the trend.
 Note
Note Studied by 1 person
Studied by 1 person Note
Note Studied by 14 people
Studied by 14 people Note
Note Studied by 18 people
Studied by 18 people Note
Note Studied by 32 people
Studied by 32 people Note
Note Studied by 27 people
Studied by 27 people Note
Note Studied by 5 people
Studied by 5 people Knowt
Knowt