Driving Theory
Hierarchy of Road Users/Rules for Pedestrians
You MUST give way to pedestrians on a zebra crossing, parallel crossing, or at a light-controlled crossing when there is a green signal.
If there is no pavement, keep to the right-hand side of the road so that you can see oncoming traffic.
Types of Crossing
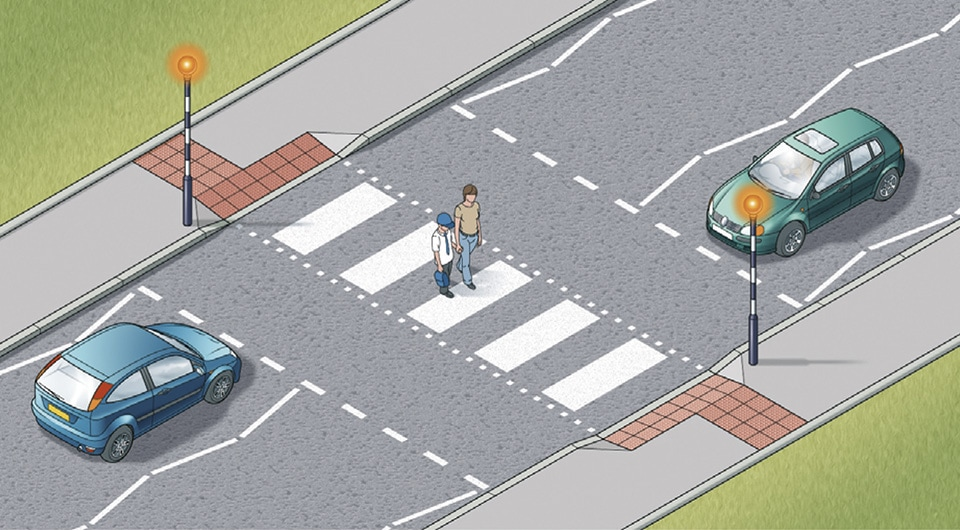
Zebra crossing
Traffic doesn’t have to stop until someone has moved onto the crossing.
Drivers MUST give way to pedestrians once they’re on a zebra crossing.

Traffic Lights
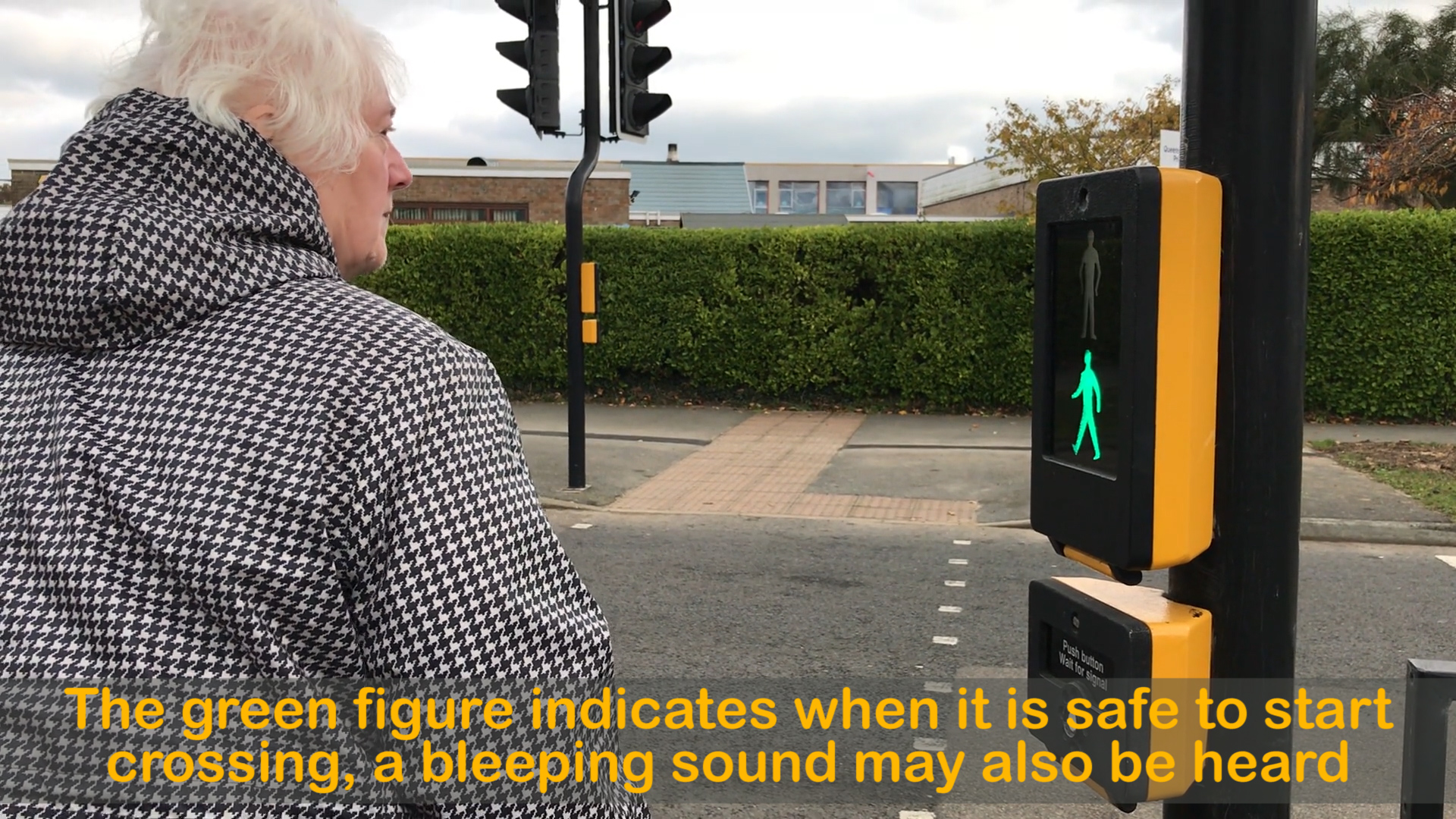
Start to cross the road when the green man shows
Pelican crossing
Signal-controlled crossings operated by pedestrians
When the green man begins to flash, you should not start to cross - if you have already started you should have time to finish crossing safely.

Puffin crossing
The red and green man are above the control box on your side of the road, and there is no flashing green man phase.
Press the button and wait for the green man to show.

Toucan crossing
Allows both pedestrians and cyclists to share the crossing space simultaneously.
Push-button operated
Cyclists may ride across
Never cross the road directly in front or behind a bus — wait until it has moved off and you can see clearly in both directions.
Tramways
May run through pedestrian areas
their paths will be marked out by shallow kerbs, changes in the paving, or other road surface, white lines, or yellow dots.
Rules for users of powered wheelchairs and powered mobility scooters
Powered wheelchairs and scooters MUST NOT travel faster than 4mph in pedestrian areas.
Class 3 vehicles (upper speed limit of 8mp are equipped to be used on the road as well as the pavement.
Class 2 users (upper speed limit of 4mph should always use the pavement when it is available. When there is no pavement, they should use the road with caution, always travelling in the direction of the traffic where possible.
These vehicles MUST NOT be used on motorways, unrestricted dual carriageways where the speed limit exceeds 50mph. If they are used on a dual carriageway, they must have a flashing amber beacon.
Rules about animals
All horse-drawn vehicles should have 2 red rear reflectors. If driving at night, a light showing white to the front and red to the rear MUST be fitted.
Children under 14 MUST wear a helmet when riding a horse - though this rules doesn’t apply to Sikhs wearing a turban.
If you are leading a horse at night, carry a light in your right hand, showing white to the front and red to the rear.
Never ride a horse without both a saddle and bridle.
Horses MUST NOT be taken onto a pavement or footpath or cycle track. Use a bridleway where possible.
Rules about cyclists
At night, you MUST have white front and red rear lights lit. A red rear reflector MUST also be fitted.
Cycle lanes are marked by a line white (which may be broken) along the carriageway.
You should not pass a horse on the left.
Most bus lanes may be used by cyclists indicated on signs.
Only pass to the left of large vehicles which are slow moving or stationary
On quiet roads + slower-moving traffic + at the approach to junctions —> ride in the centre of the lane.
On busy roads with fast-moving vehicles —> allow them to overtake whilst keeping at least 0.5m away from the curb edge.
Rules about motorcyclists
MUST wear a helmet + it is advisable to wear eye protectors.
You MUST NOT carry more than one pillion passenger.
You MUST be able to read a vehicle number plate in good daylight, from a distance of 20m.
Vehicles towing and loading
You should distribute the weight in your caravan/trailer evenly with heavy items over the axle(s) and ensure a downward load on the tow ball.
You MUST secure your load and it MUST NOT stick out dangerously.
If your vehicle is narrower than your trailer/load, or if the load obstructs your rearward view, then towing mirrors MUST be used.
The trailer MUST be fitted with a secondary coupling device e.g. a safety chain
Max speed limit of 60mph on motorways and dual carriageways
Seat belts and child restraints
You MUST wear a seat belt in cars, vans, and other goods vehicles if one is fitted.
People aged 14+ MUST wear a seat belt when seated in minibuses, buses, and coaches.
Passengers over the age of 14+ are responsible for wearing a seat belt.
The driver MUST ensure that all children under 14 wear seat belts or sit in an approved child restraint where required.
If a child is under 1.35m tall, a booster seat/baby seat MUST be used.
A rear-facing baby seat MUST NOT be fitted into a seat protected by an active frontal airbag - as it can cause injury in the event of a crash.
For children under 3, if the correct child restraint isn’t available, they may travel unrestrained.
Signals
Signals warn and inform other road users (including pedestrians)
Use an arm signal to emphasize/reinforce your signal if necessary.
Police stopping procedures
If the police want to stop your vehicle, they will by…
flashing blue lights, headlights, or sounding their siren or horn, usually from behind
directing you to pull over by pointing and/or using their left indicator
You MUST then pull over and stop as soon as it is safe to do so. Then switch off your engine.
Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency officers (flash amber lights) - can stop you on all roads.
Traffic Officers (flash amber lights) - can stop you on most motorways and some ‘A’ class roads.
Flashing headlights and use of the horn should ONLY be used to warn other road users of your presence/let them know you are there.
Lighting requirements
You MUST ensure all sidelights and rear registration plate lights are lit in daylight hours
Use headlights at night, except on a road which has lit street lighting (generally restricted to 30mph).
Use headlights when visibility is seriously reduced.
Use front or rear fog lights unless visibility is seriously reduced. You MUST switch them off when visibility improves to avoid dazzling other road users.
In stationary queues, drivers should apply the parking brake and take their foot off the footbrake to deactivate the vehicle brake lights. This will minimize glare to road users behind until the traffic moves again.
Use dipped headlights at night in built-up areas and in dull daytime weather, to ensure that you can be seen.
Keep your headlights dipped when overtaking until you are level with the other vehicle and then change to main beam if necessary, unless this would dazzle other road users.
Night is defined as the period between half an hour after sunset and half an hour before sunrise.
Hazard warning lights: Used when your vehicle is stationary, to warn that it is temporarily obstructing traffic. You MUST NOT use them while driving unless you are on a motorway or unrestricted dual carriageway and need to warn drivers behind you of a hazard ahead.
Skids
Caused by the driver braking, accelerating, or steering too harshly, or driving too fast for the road conditions.
If skidding occurs, remove the cause by releasing the brake pedal fully or easing off the accelerator. Turn the steering wheel in the direction of the skid.
Brakes affected by water (e.g. deep puddle)
Test them at the first safe opportunity by pushing gently on the brake pedal to make sure that they work.
If they are not fully effective, gently apply light pressure while driving slowly — this will help dry them out.
Stopping distances
Allow at least a 2-second gap between you and the vehicle in front on high-speed roads and in tunnels where visibility is reduced.
The gap should be at least doubled on wet roads and up to ten times greater on icy roads.
If driving a large vehicle in a tunnel, you should allow a 4-second gap between you and the vehicle in front.
Lines and lane markings on the road
Broken white line: Marks the centre of the road. Do not cross it unless you can see the road is clear and wish to overtake or turn off.
Double white lines where the line nearest to you is broken: You may cross the lines to overtake if it is safe. White direction arrows on the road indicate that you need to get back onto your side of the road.
Double white lines where the line nearest you is solid: DO NOT cross or straddle the line unless you need to enter adjoining premises/a side road. You must cross the line to pass a stationary vehicle, or overtake a cyclist, horse, or road maintenance vehicle.
Areas of white diagonal stripes: To separate traffic lanes or to protect traffic that is turning right.
Lane dividers: Short, broken white lines which are used on wide carriageways to divide them into lanes. Keep between them.
Reflective Road Studs
Mark the lanes of the middle of the road
Red studs mark the left edge of the road
Amber studs mark the central reservation of a dual carriageway or motorway
Green studs mark the edge of the main carriageway at lay-bys and slip roads
Green/yellow studs indicate temporary adjustments to lane layouts e.g. where roadworks are taking place
Dual carriageway
A road which has a central reservation
On a 2-lane dual carriageway, you should stay in the left-hand lane and use the right-hand lane for overtaking or turning right.
On a dual carriageway with 3+ lanes, you may use the middle lane or the right-hand lane to overtake but should return to the left-hand lane when safe to do so.
Climbing and crawler lanes
Provides on some hills. Used by slow-moving vehicles or if there are vehicles behind you wishing to overtake.
Safety rules inside the car
In England and Wales, the driver MUST NOT smoke or allow anyone to smoke in an enclosed private vehicle carrying someone under 18.
You MUST NOT pick up and use a hand-held phone while stationary in traffic.
Overtaking
Leave at least 1.5 meters when overtaking cyclists at speeds of up to 30mph, and give them more space when overtaking at higher speeds.
Pass horse riders at speeds under 10mph and allow at least 2 meters of space.
Allow at least 2 meters of space and keep to a low speed when passing a pedestrian who is walking in the road.
When overtaking large vehicles, you should DROP BACK — this will increase your ability to see ahead and should allow the driver of the large vehicle to see you in their mirrors.
If a driver is trying to overtake you, maintain a steady course and speed, slowing down if necessary to let the vehicle pass.
Box junctions
These have yellow crisscross lines painted on the road
You MUST NOT enter the box until your exit road is clear
You may enter the box and wait when you want to turn right, and are only stopped from doing so by oncoming traffic, or by other vehicles waiting to turn right.
At signaled roundabouts, you MUST NOT enter the box unless you can cross over it completely without stopping.
Mini-roundabouts
All vehicles MUST pass around the central marking except large vehicles which ar ephysicallyy incapable of doing so.
Avoid making a U-turn at mini-roundabouts
Reversing
Don’t reverse from side road into a main road — when using a driveway, reserve in and drive out if you can.
Get someone to guide you if you cannot see clearly
You MUST NOT reverse your vehicle further than necessary.
You may have your seatbelt undone while reversing.
Driving in adverse weather conditions
You MUST use headlights when visibility is seriously reduced, generally when you cannot see for more than 100m. You may also use front or rear fog lights but MUST switch them off when visibility improves.
In wet weather, stopping distances will be at least double those required for dry roads. If the steering becomes unresponsive, ease off the accelerator and slow down gradually.
DO NOT drive in icy/snowy conditions unless your journey is essential. Before you set off, you MUST be able to see out the windows, ensure that lights are clean and number plates are visible/legible, remove all the snow that might fall off into the path of other road users.
When the roads are icy, drive at a slow speed in as high a gear as possible; accelerate and brake very gently.
Waiting and Parking
You MUST NOT wait or park on yellow lines during the times of operation shown on nearby time plates.
Double yellow lines indicate a prohibition of waiting at any time even if there is no sign.
Use off-street parking areas or bats marked out with white lines on the road as parking spaces, wherever possible.
Parking at Night
You MUST NOT park on a road at night facing against the direction of the traffic flow unless you’re parked in a recognized parking space.
All vehicles MUST display parking lights when parked on a road with a speed limit greater than 30mph.
Parking on Hills
Turn your steering wheel away from the curb when facing uphill
Turn your steering wheel towards the curb when facing downhill
Hard Shoulder
You MUST NOT use a hard shoulder except in an emergency or if directed to do so by the police or a traffic sign.
It is used as an extra lane on some motorways during periods of congestion.
A red ‘X’ or a blank sign above the hard shoulder means that you MUST NOT use it except in an emergency.
Breakdowns
If your vehicle breaks down…
Keep your sidelights on if it is dark or visibility is poor.
Put a warning triangle on the road at least 45m behind your broken-down vehicle on the same side of the road, or use other permitted warning devices if you have them.
Do not stand between your vehicle and oncoming traffic.
Get your vehicle off the road if possible.
Warn other traffic by using your hazard warning lights if your vehicle is causing an obstruction.
Incidents — documentation
If you are involved in a collision which causes damage or injury to any other person, vehicle, animal, or property, you MUST…
Stop (in a place of safety)
Give your own and the vehicle owner’s name and address, and the registration number of the vehicle, to anyone having reasonable ground for requiring them.
If you don’t give your name and address at the time of the collision, report it to the poice as soon as possible, definitely within 24 hours.
Flashing red lights: you must stop
Signs with red circles: mostly prohibitive (e.g. no overtaking)
Signs with blue circles but no red border: mostly give positive instruction (e.g. keep left)
Triangular signs: warnings (e.g. road narrows on both sides)
Rectangular blue signs: gives directions - found on motorways
Rectangular green signs: gives directions - found on primary routes
Rectangular white signs with black borders: gives directions - found on non-primary and local routes
Signs with black symbol and yellow background: shows emergency diversion route for motorway and other main road traffic
Information signs - all rectangular
Road markings
Across the carriageway
Thin solid white line: stop line at signals or police control
Thick solid white line: stop line at ‘stop’ sign
Thin broken white line: stop line for pedestrians at a level crossings
Double thin white broken line: give way to traffic on a major road (can also be used at mini roundabouts)
Thin broken white line with large spaces: give way from the right at a roundabout
Thick broken white line: give way to traffic from the right at a mini-roundabout
Motor vehicle documentation
Driving licence
you MUST have a valid driving licence for the category of motor vehicle you are driving
you MUST inform the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA) if you change your name/address
Holders on non-European Community licences who are now a UK resident may only drive for a maximum of 12 months before needing to obtain a British provisional licence and passing a driving test.
MOT
Cars and motorcycles MUST normally pass an MOT test 3 years from the date of the first registration and every year after that.
You MUST NOT drive a motor vehicle without an MOT certificate when it should have one. However, you may drive to a pre-arranged test appointed or to a garage for repairs required for the test.
Driving an unroadworthy motor vehicle may invalidate your insurance.
From 2018, cars, vans, motorcycles et,. manufactured or first registered over 40 years ago will be exempt from the MOT test, unless the vehicle has been substantially changed within the last 30 years.
Insurance
You MUST have a valid insurance policy to use a motor vehicle on the road.
This MUST cover you for injury or damage to a third party while using that motor vehicle.
Uninsured drivers can now be automatically detected by roadside cameras.
Third-party insurance: the cheapest form of insurance, and is the minimum cover required by law. It covers anyone you might injure or whose property you might damage. It doesn’t cover damage to your own vehicle or injury to yourself.
Comprehensive insurance: the most expensive but the best insurance. Apart from covering other persons and property against injury and damage, it also covers damage to your own motor vehicle, up to the market value of that vehicle, and personal injury to yourself.
Registration certificate
Issued for all motor vehicles used on the road, describing them (make, model, etc.) and giving details of the registered keeper.
Vehicle tax
MUST be paid on all motor vehicles used or kept on public roads.
Statutory Off-Road Notification (SORN)
A notification to the DVLA that a motor vehicle is not being used on the road
If you are the vehicle keeper and want to keep a motor vehicle untaxed and off the road, you MUST declare SORN.
The vehicle will remain SORN until you sell, tax, or scrap it.
Learner drivers
MUST hold a valid provisional licence
MUST be supervised by someone at least 21 years old who holds a full EC/EEA licence for that type of car, and has held one for at least 3 years.
The vehicle being driven MUST display a red L plate which is visible to drivers.
Penalty points and disqualification
The penalty point system is intended to deter drivers and motorcyclists from following unsafe motoring practices.
A driver or motorcyclist who accumulates 12 or more penalty points within a 3-year period MUST be disqualified. This will be for a minimum period of 6 months (or longer if the driver has been previously disqualified).
In the case of serious offences, e.g. dangerous driving and drink-driving, the court MUST order disqualification. The minimum period is 12 months.
Tyre pressures
Check weekly. Do this before your journey, when tyres are cold.
Warm or hot tyres may give a misleading reading.
Your braking and steering will be adversely affected by under-inflated or over-inflated tyres.
Excessive or uneven tyre wear may be caused by faults in the braking or suspension systems, or wheels which are out of alignment.
Fluid levels
Check the fluid levels in your vehicle at least weekly
Low brake fluid may result in brake failure and a crash
Overheated engines or fire
Most engines are water-cooled.
If your engine naturally overheats, you should wait until it has cooled naturally. Only then remove the coolant filler cap and add water.
Petrol stations
Any spilled fuel should be immediately reported to the petrol station attendant.