Topic 20- Digestion
Study Guide:







I. Introduction to Digestion
A. Heterotrophy
All animals are heterotrophs: must consume food for energy and nutrients.
Digestion pathway:
Mechanical digestion (e.g., chewing)
Chemical digestion (enzymatic hydrolysis)
Absorption into cells
Elimination of undigested material
B. Four Stages of Food Processing
Ingestion – Intake of food
Digestion – Breakdown of food
Mechanical: Larger pieces → smaller (more surface area)
Chemical: Enzymes break polymers into monomers
Absorption – Nutrient molecules enter cells (blood or lymph)
Elimination – Waste leaves via anus
C. Digestive Locations & Structures
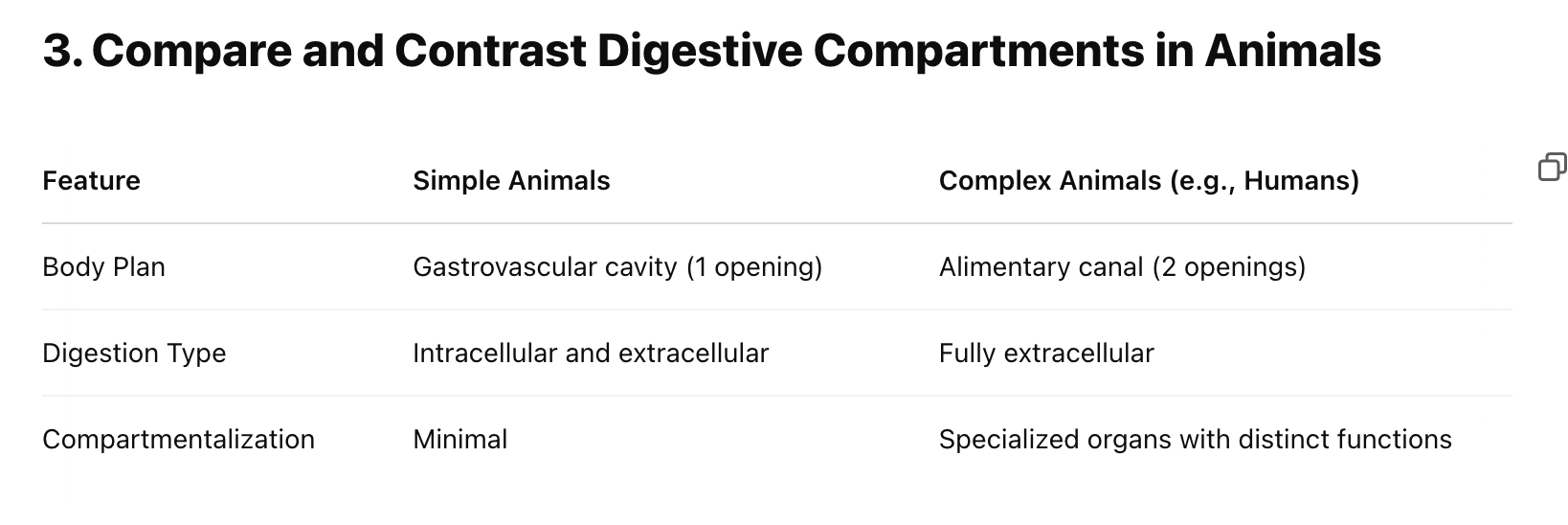
Single-celled organisms: Use vacuoles + lysosomes
Multicellular organisms:
Gastrovascular cavity: One opening (cnidarians, flatworms)
Alimentary canal: Two openings (mouth and anus)
Accessory glands: salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder
Peristalsis: Smooth muscle contractions push food
Sphincters: Muscular valves between compartments
II. Human Digestive System
A. Sequence of Digestion (8 Steps)
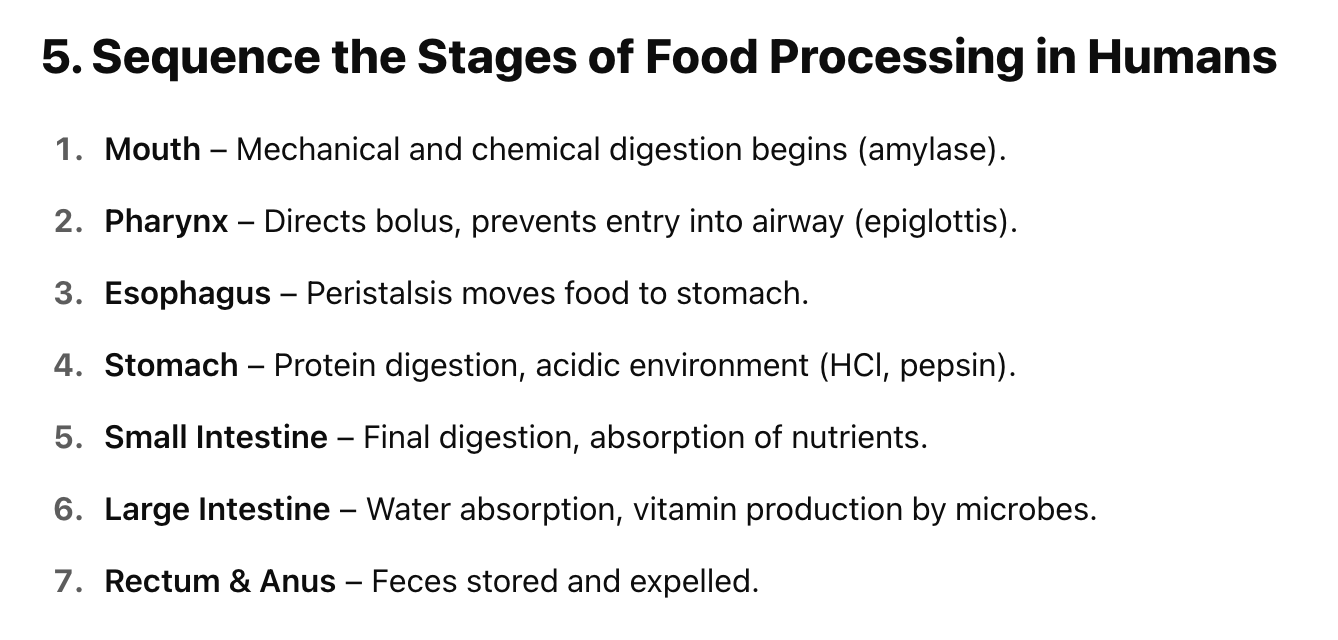
Oral Cavity (Mouth)
Teeth: Mechanical digestion
Tongue: Shapes food into a bolus
Saliva from salivary glands:
Amylase: breaks starch → maltose
Mucus (mucins): lubrication
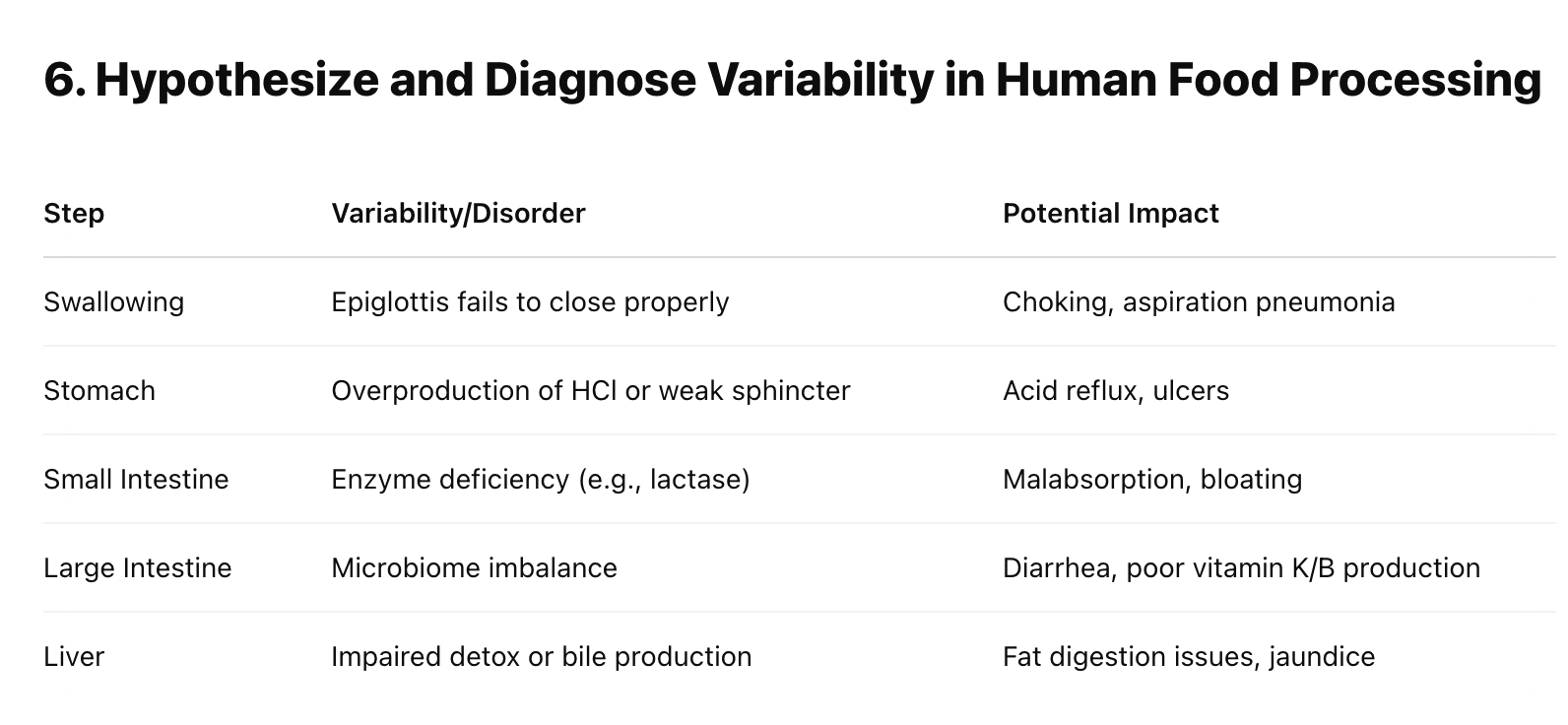
Voluntary swallowing begins digestion
Pharynx
Shared path for food/air
Epiglottis: Blocks trachea during swallowing
Esophagus
Muscular tube using peristalsis
Cardiac sphincter: entrance to stomach
Stomach
Elastic (can hold ~2L)
Gastric glands:
Mucus cells: Protect lining
Parietal cells: Pump H⁺ + diffuse Cl⁻ → HCl
Chief cells: Pepsinogen (inactive) → pepsin (active) via HCl
Pepsin: Digests proteins into polypeptides
Contents become chyme, exit via pyloric sphincter
Small Intestine (~6 m)
Duodenum: Most chemical digestion
Jejunum + Ileum: Absorption
Structures: villi & microvilli ↑ surface area
Pancreatic enzymes & bicarbonate neutralize stomach acid
Bile (from liver, stored in gallbladder): Emulsifies fats
Large Intestine (Colon)
Enters via ileocecal valve
Absorbs water, forms feces
Hosts beneficial bacteria (e.g., vitamin K producers)
Rectum & Anus
Feces: ~75% water, ~25% solids
Two anal sphincters (voluntary/involuntary)
III. Digestion of Macromolecules
A. Carbohydrates
Mouth: Salivary amylase → starch → maltose
SI:
Pancreatic amylase → maltose
Disaccharidases → monosaccharides
B. Proteins
Stomach: Pepsin → polypeptides
SI:
Pancreatic: Trypsin, chymotrypsin
SI enzymes:
Dipeptidase
Carboxypeptidase
Aminopeptidase
C. Nucleic Acids
Digested only in SI
Pancreatic nucleases
SI: Nucleosidases, phosphatases
D. Lipids
SI only
Bile salts: Emulsify fats
Pancreatic lipase: Breaks triglycerides → glycerol + fatty acids
IV. Absorption & Transport
A. Small Intestine Absorption
Via villi into:
Capillaries (blood) → sugars, amino acids
Lacteals (lymph) → fats
B. Transport Mechanisms
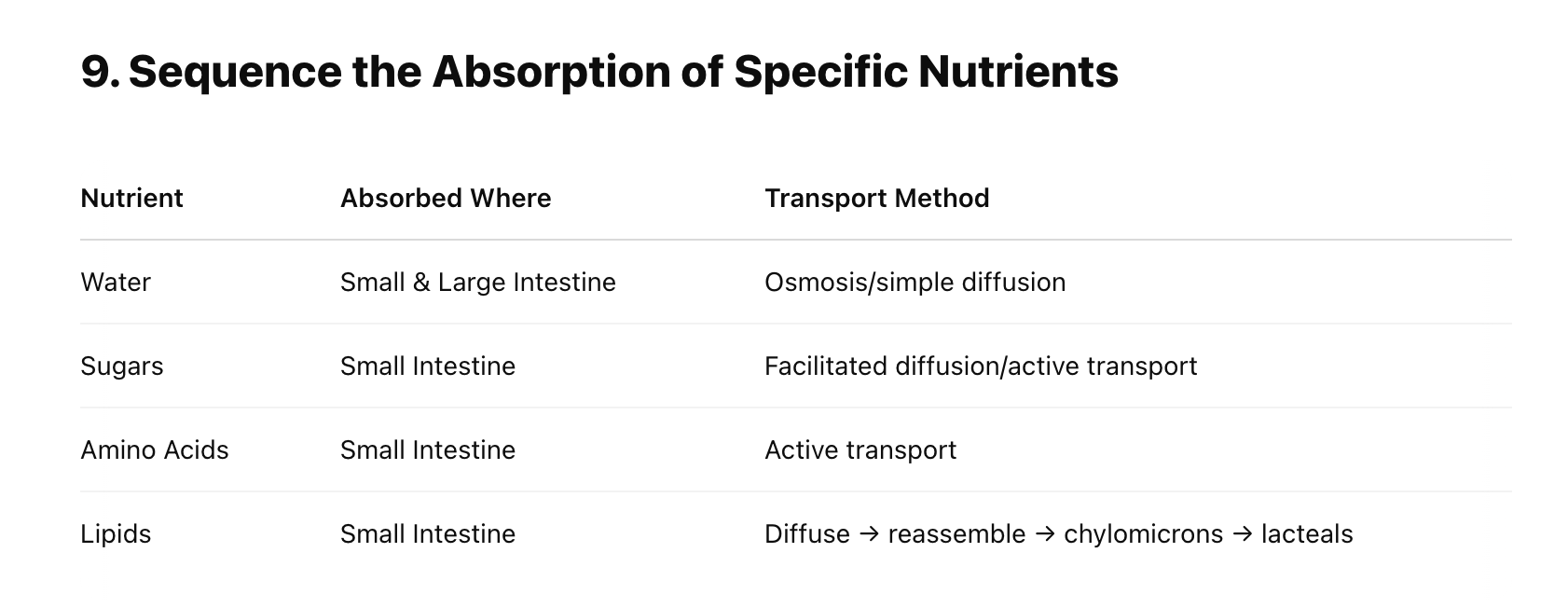
Simple diffusion: Water
Facilitated diffusion: Fructose
Active transport: Ions, glucose
C. Lipid Absorption
Lipids cross epithelium via diffusion
Reassembled into triglycerides
Packaged into chylomicrons
Enter lacteals → lymph → bloodstream
D. Functions of the Large Intestine
Water reabsorption
Houses gut microbiota:
Produce vitamins: K, B12, thiamine, riboflavin
Outcompete pathogens
Forms feces
E. Liver Functions
Bile production
Detoxifies substances (alcohol, drugs)
Stores glucose as glycogen (via insulin)
Blood from intestines enters liver via hepatic portal vein
Allows nutrient regulation before systemic circulation