digestion (march 11)
change of insoluble (non dissolvable) large molecules to soluble small molecules
large insoluble small soluble
carbohydrate ————→ simple sugar
proteins ——————→ amino acid
lipids ———————→ fatty acid
nucleic acid ————-→ nucleotide
the digestive system: group of organs work together to change large insoluble to small soluble.
there are 2 types of digestion:
mechanical (changing the size) : cutting smashing grinding chewing crushing.
chemical: breaking down food into smaller molecules using enzymes and acids, allowing nutrients to be absorbed into the bloodstream. (enzymes can be changed by temperature and ph)
digestive systems:
main organs (the organs which the food go through): mouth, oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine
accessory organs (the organs which the food dong go through but still effect it): salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancrease
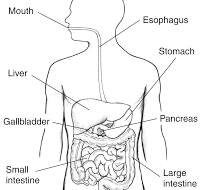
mouth:
has 2 types of digestion mechanical (chewing) and chemical (saliva)
mouth has a ph of 6.5-7
food + saliva = bolus
the mouth produces amylase
oesophagus:
connects the mouth and stomach
has a flap like thing called epiglottis preventing the food (bolus) from going down the windpipe.
stomach:
breaks down protein to amino acid
acid→gastric juice→ hydrocloric acid (HCL) kills bacteria
chyme → partially digested food.
small intestine:
length of 7m
blood capillaries absorb nutrients from the digested food, which are then transported to the liver for processing.
thinnest blood vessel
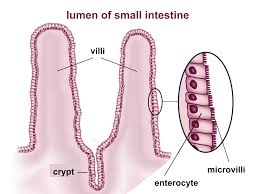
villi: tiny, finger-like projections that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients.
microvilli: even smaller projections on the surface of villi that further enhance nutrient absorption by providing an extensive surface area.
large intestine:
absorption ← excess food into solid waaste
microbes = useful
E.coli ← useful bacteria
accessor organs:
pancreas→ insulin→ control the blood sugar level
diabetic:
pancreas stop produsing insulin
body stop responding to insulin
Enzyme:
slaiva (6.8-7 ph)
sliva is water mucus and digestive enzymes
salivary amylase : An enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars, initiating the digestive process in the mouth.
lingual lipase : An enzyme secreted by the salivary glands that begins the digestion of fats in the mouth, although its activity is more pronounced in the stomach.
lysozyme: An enzyme that helps to break down bacterial cell walls, providing an antibacterial function in the oral cavity.
carbohydrate → carbohydrase
protien → protase
lipid→ lipase
nucleic Acid →nuclease
stomach (1.5-3.5)
gactric juice is HCL and pepsin
pepsin changes protien into amino acid by breaking the polypeptide bond
pancreas
amylase: strach → Monosacharid
lipase: lipid → fatty acids and glycerol.
trypsin: protein → amino acids.
nuclease: nucleic acids → nucleotides.