Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
9.1 Cellular Respiration: An Overview
Chemical Energy and Food
Food gives living things the energy they need to grow
Autotrophs make their own food through photosynthesis
Heterotrophs must eat other living things for food. All living things,
Food molecules store chemical energy for all living things; that energy is released when they break those food molecules down
Energy in food can be measured in units called calories
A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius
Cells break down food molecules over time, getting a little bit of chemical energy at key steps
Overview of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
Cellular respiration gives off carbon dioxide, water, and energy and the process can be summarized like this:

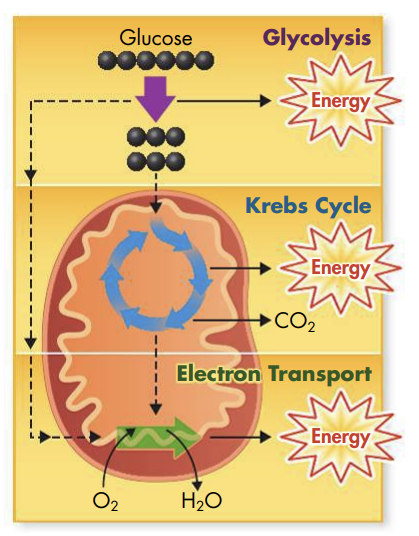
The first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis
Only a small amount of energy is used to make ATP during this stage; the rest is still locked in the bonds of a molecule called pyruvic acid
The second step of cellular respiration is the Krebs cycle
Pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle, where a little more energy is given off
The third step of cellular respiration is the electron transport chain
Most of the energy from cellular respiration comes from the electron transport chain; this stage uses oxygen and reactants from the other two stages to finish the job
Oxygen is used at the end of the electron transport chain; any time a cell needs more energy, it needs more oxygen, too
Chemical pathways that need oxygen are called aerobic
The Krebs cycle and electron transport chain are both aerobic
A chemical process that does not need oxygen is called anaerobic
Glycolysis is an anaerobic process
Mitochondria are the organelles most important in cellular respiration
The Krebs cycle and electric transport chain take place inside the mitochondria
Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration can be thought of as opposite processes, as the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration are the reverse of each other
Photosynthesis produces food molecules and removes carbon dioxide from the air, and cellular respiration puts it back
Photosynthesis gives off oxygen, and cellular respiration uses that oxygen to release energy from food
9.2 The Process of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration
During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid' ATP and NADH are also made
1 molecule of glucose, which has 6 carbon atoms, is changed into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, which each have 3 carbon atoms
One of the steps of glycolysis passes 4 electrons to an electron carrier called NAD+, or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Glycolysis does not need oxygen, meaning that glycolysis can quickly get chemical energy to cells when there is not any oxygen present
When oxygen is present, however, the pyruvic acid and NADH made during glycolysis become the materials needed for the other stages of cellular respiration
The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle takes place within the matrix - the innermost space of the mitochondrion
During the Krebs cycle, pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of steps that release chemical energy
Step 1: Pyruvic acid from glycolysis enters the mitochondrion’s matrix
Step 2: Enzymes split CO2 off from pyruvic acid, leaving a 2-carbon molecule, and NADH is produced from NAD
Step 3: The 2-carbon-atom molecule joins a 4-carbon-atom molecule to become citric acid
Step 4: More CO2 and NADH are made as citric acid becomes a 4-carbon-atom molecule
Step 5: More reactions make high-energy molecules of ATP, FADH2, and NADH
Step 6: The 4-carbon atom molecule can go through the cycle again
Because glycolysis makes 2 molecules of pyruvic acid from each glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle “turns” twice for each glucose molecule that enters glycolysis
Electron Transport and ATP Synthesis
Carriers from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle go into the last stage of cellular respiration, the electron transport chain
The NADH made during glycolysis can enter the mitochondrion to join the NADH and FADH2 made by the Krebs cycle
Electrons are then passed from all of those carriers to the electron transport chain, which uses them to change ADP into ATP
Together, glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain make about 36 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose
Those 36 ATP molecules represent about 36 percent of the total energy of glucose, meaning that the cell is actually better at using food than a car’s engine is at burning gasoline!
9.3 Fermentation
Fermentation
Fermentation is the process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen
Fermentation is an aerobic process and takes place in the cytoplasm
There are two different kinds—alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid from glycolysis is changed into alcohol and carbon dioxide
Yeasts and a few other microorganisms use alcoholic fermentation
A summary of alcoholic fermentation after glycolysis is as follows:

In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvic acid from glycolysis is changed into lactic acid
Most living things carry out fermentation by changing pyruvic acid into lactic acid
Unlike alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation does not give off carbon dioxide
Like alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation makes NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue
Lactic acid fermentation after glycolysis can be written as:
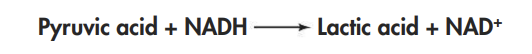
Energy and Exercise
You have three main sources of ATP: ATP already in muscles, ATP made by lactic acid fermentation, and ATP made by cellular respiration
At the beginning of a race, the body uses all three sources; however, stored ATP and lactic acid fermentation can give energy only for a short time
For quick bursts of energy, the body uses ATP already in muscles and ATP from lactic acid fermentation
For exercise longer than 90 seconds, the body uses cellular respiration
 Knowt
Knowt
