6.1 - Intro To Trigonometry
Overview of Trigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics focused on the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. It is particularly useful for determining:
Lengths of missing sides
Sizes of missing angles
Areas of triangles
While trigonometry is often associated with right-angled triangles, it is commonly applied to all types of triangles in practical scenarios.
Key Concepts in Trigonometry
When approaching exam questions related to triangles, the primary challenge is often identifying the appropriate equations to use. The following flow diagram can help guide the decision-making process:
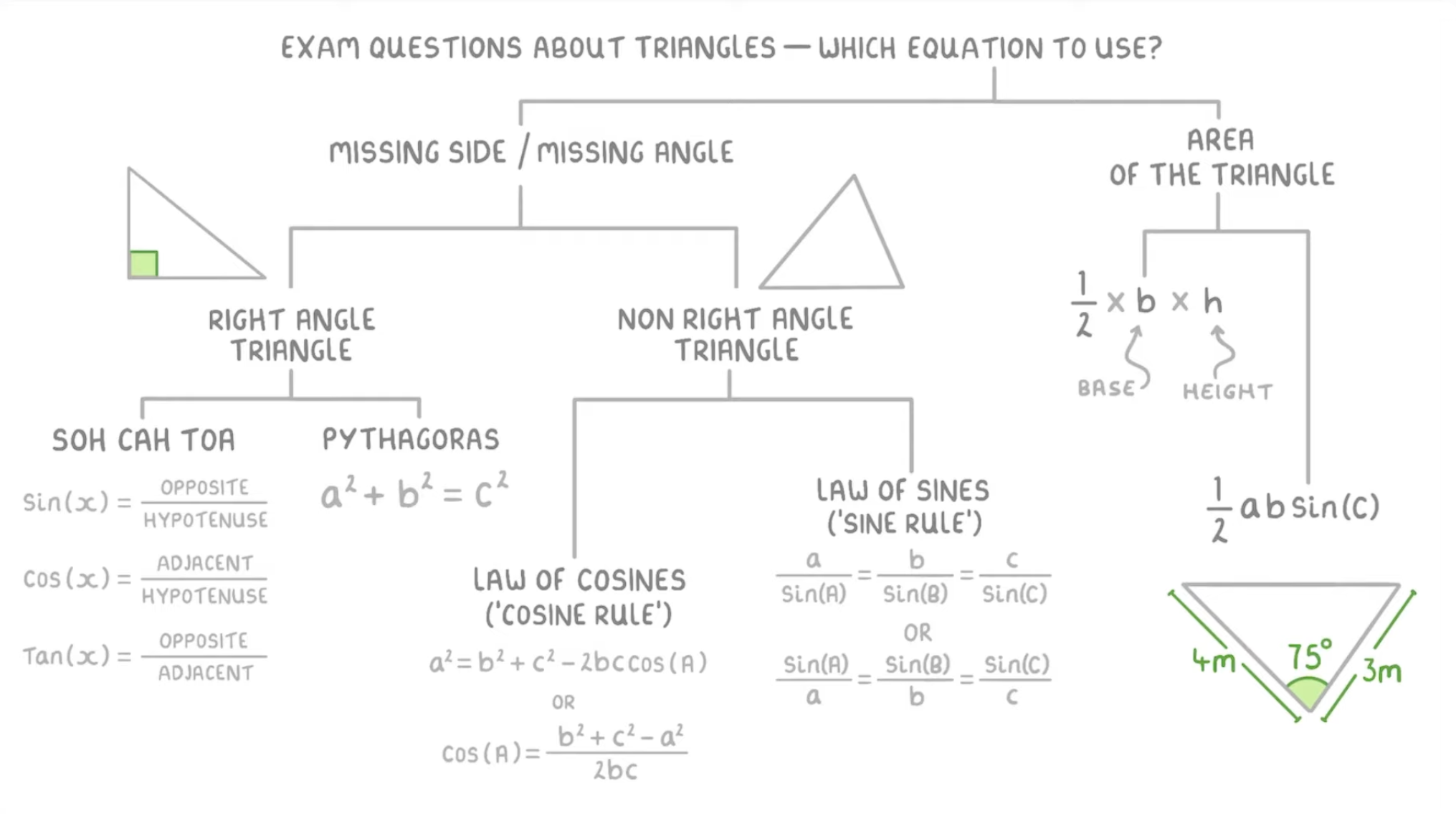
Identifying the Problem Type
Determine if you are looking for:
A missing side
A missing angle
The area of the triangle
Classify the triangle:
Right-angled triangle
Non-right-angled triangle (e.g., scalene triangle)
Equations for Right-Angled Triangles
If the triangle is a right-angled triangle, the following equations are typically used:
Pythagorean theorem
SOHCAHTOA (sine, cosine, tangent relationships)
Equations for Non-Right-Angled Triangles
For non-right-angled triangles, the following laws are applicable:
Law of Cosines (Cosine Rule)
Law of Sines (Sine Rule)
Finding the Area of a Triangle
To calculate the area of a triangle, you can use one of two equations based on the information available:
If the base and height are known, use the area formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height
If two sides and the included angle are known, use the formula: Area = 1/2 × a × b × sin(C)
Conclusion
This video serves as a brief overview of the main equations and concepts in trigonometry. Future videos will delve deeper into each equation, explaining their applications and how to use them effectively. If you found this introduction helpful, consider liking and subscribing for more content.