Mitochondria & Golgi Body
Mitochondria
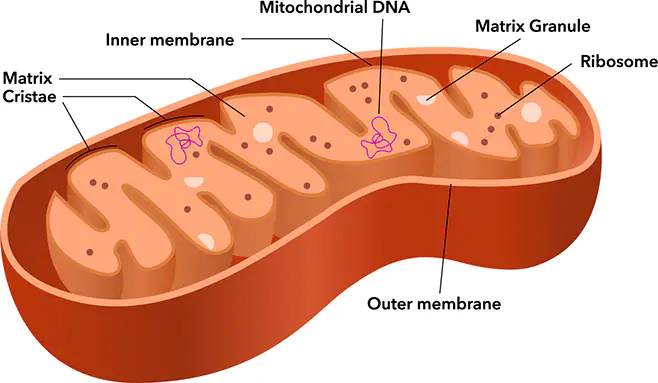
The mitochondria (singular – mitochondrion) are the powerhouse of the cell.
Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria, so the mitochondria convert the energy in our food to a form the cell can use. They take the energy stored in large molecules like glucose and convert them to ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is our cell’s preferred energy source. In other words, the mitochondria produce energy for organisms.
All eukaryotic cells have mitochondria, including plants. However, mitochondria will be more prevalent in cells that require a lot of energy.
- For example, our muscle cells have a lot of mitochondria because our muscles need lots of energy when we are exercising or moving around a lot to power our muscle contractions.
Cellular respiration is most efficient when our cells have an abundance of oxygen. We call this type of respiration, aerobic respiration.
- The root aerobic means “in the presence of oxygen.”
However, cellular respiration can work when our cells do not have a lot, or any, of oxygen, but it is less efficient. We call this type of cellular respiration anaerobic.
- The prefix means “without” so anaerobic means “without oxygen.”
- For example, when we are exercising, our cells will usually run out of oxygen before we run out of stored energy. So, during intense cardiovascular exercise, our body will often switch from aerobic respiration to anaerobic respiration.
In humans, this is called lactic acid fermentation because the end product is lactic acid and a small amount of ATP. Plants do not move much, so they don’t need a lot of ATP. They don’t need to do cellular respiration as much as organisms that move around, like humans.
Mitochondria are also an important organelle for another reason. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the only organelles that have their own DNA.
You get your mitochondrial DNA from your mother, not your father. So, your mitochondrial DNA will be identical to your mother’s mitochondrial DNA even though your cellular DNA is a mix of DNA from both parents. It is thought that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free-living single-celled organisms that developed a relationship with early cells and eventually became part of the cell (see “Endosymbiosis”).
Golgi Body
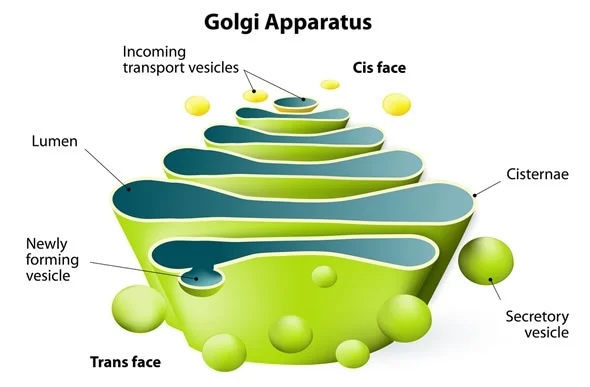
The Golgi body is also known as the Golgi complex or the Golgi apparatus.
This organelle was identified by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi, which is why it is named after him.
The Golgi body is usually located near the endoplasmic reticulum because it receives proteins from the ER, customizes them, and readies them for shipment to other parts of the cell or other cells. The cis face of the Golgi body faces the ER and is the receiving end of the Golgi body. The trans face of the Golgi body is where modified proteins leave the Golgi body. The Golgi body receives proteins at the cis face and then customizes the proteins, similar to a custom auto body shop, and, once they are ready, transfers them to the trans side where they are packaged and readied for shipment to other parts of the same cell or other cells.
 Edited: 05 October 2022
Edited: 05 October 2022