APSUH
UNIT ONE
Unit 1, Topic 2
Aztecs:
- Tenochtitlan
- Written language
- Huge population
Maya:
- Also developed large cities that utilized irrigation techniques
- Stone temples
- Yucatan
Incan:
- Andes mountains
- Today peru
- 16 million people
- Fertile mountains for growing crops
Common:
- All three cultivated maize
- Nutritious
- The crops allowed for settlement, irrigation, diversification, and money
- Cultivation spread north
Southwest
- Pueblo people
- Organized with separate shops for things
- Sedentary
Plains:
- Nomadic people who were hunter gatherers
- Yute people
Pacific Northwest:
- Lived by the sea
- Relied on elk and fishing
- Chinook People
- Chumash lived south on the coast
- Also hunter gatherers, but had permanent settlements
Mississippi River:
- Hopewell people
- Smaller towns that traded with other regions
- Cahokia people
- Chiefdoms centralizing the government and also trading
Northeast:
- Iroquois people who had a plethora of crops
- Maize, squash, and beans
Comprehension
There was a range of different native american tribes that were spread all across the US. They were all vastly different from each other, and this difference was greatly dependent on the region that the lived in. Tribes further inland focused more on trading with other groups near them, and all groups benefited greatly from growing crops, especially maize, which was something that allowed them to expand economically and technologically.
Unit 1, Topic 3: European Exploration
Reasons for Exploration
- European population was finally recovering from the plague
- Politics were becoming more unified, and monarchs were now in control
- Financial growth created a wealthy upper class, which caused rich people to want to spend money on luxury goods
- Created impulse for land expansion
- The land based trading routes to Asia were not in control of the Europeans, instead taken by Muslims, meaning they had to find another way to reach Asia, hence a water based route
Portugal
- Prince Henry the navigator was the first to attempt, trying to go around Africa
- Established a trading post all around African border
Spain
- Isabel and Ferdinand also wanted the financial benefits of the expansion, with an added goal, spreading christianity
- Christopher Columbus was sponsored by them, for his route to Asia, since they knew Portugal already had Africa
Columbus:
- Landed on San Salvador, thinking it was the indies, hence indians
- Set off the Columbian Exchange
- Columbus sailed back with the gold he had found off the natives, and brought back more spanish explorers with him
- Explored Caribbean and South America
Technology Used for Expansion:
- Caravels: Nimble, slimmer boats used specifically for travel, not war
- Used nautical tools such as maritime charts and astronomical tables for their routes
- Astrolabe and Stern-rudders to improve the boats
Comprehension:
Basically, there were a bunch of reasons for the Europeans to explore America, but the main one was that now that Europe wasn’t dying of the plague there was a solid upper class that had hella money they wanted to spend on fancy shit. The portuguese were first and they hijacked africa w trading routes and then spain got fomo so they were like okay christopher go get india but he was like actually stupid and totally ended up in the wrong place but his headass told everyone to come anyways. Also they invented cool shit to make sailing easier.
Unit 1, Topic 4: The Columbian Exchange
- Columbian Exchange: The transfer of food, minerals, animals, and diseases, between Africa, America, and Europe.
Disease:
- Aztec Empire had huge population
- Hernando Cortez was able to take down the entire empire with just 1000 people because of smallpox
- Africans, Europeans, and Asians had been around each other for years, allowing them to build immunity to the disease
- Americans had not been able to gain immunity, so disease wiped out huge native populations
- Populations decreased hugely after the start of the Columbian Exchange
Food
- The Americas gave maize, tomatoes, potatoes, cacao and tobacco to Europe
- Europe gave mainly grains as well as oranges and lemons
- Grains became a staple food item for the Americas
Animals
- Europeans brought over horses, pig, cattle, and chickens
- Pigs and cattle became a huge part of Native American diet
- Horses revolutionized warfare for the natives
Minerals
- The spanish were able to conquer the natives and take all of their gold and silver
- This made Spain insanely rich once brought back to their country
- This gave them even more reason to continue to come back to the Americas and drew more European attention
People
- Natives were enslaved and being brought back to Spain, although this number incomparable to the exchange of African American slaves
- African American slaves were picked up off the coast of Africa
- Crammed into boats
- Went through Middle Passage where many died of disease and starvation
- When arrived, they were sold into bondage
European Wealth
- Western Europe began experiencing huge economic growth, which changed the societal function
- Originally, Europe had been running on feudalism, where a peasant would work on the land of a noble in exchange for armed protection.
- Because of this new wealth, the feudalist society was quickly replaced instead by a more capitalist society, introducing the free and open exchange of good between property owners
Spanish Finance
- The Spanish was funded by the state
- Mercantilism: Depends on government intervention and direction
- Was the most popular method of finance in Europe
- Mercantilism was replaced by a new method of finance called Joint Stock Companies
Comprehension:
The Columbian Exchange had effects on all three societies in the triangle, America, Europe, and Africa. Through the exchange of food, disease, animals, minerals, and people society was altered greatly. In America, new food was added to the diet, huge amounts of Natives died due to a lack of immunity from disease, and gold and silver was taken from the natives. European financial and societal shifts occurred from the change in feudalism to capitalism, and from mercantilism to joint stock companies. Also slaves.
Unit 1, Topic 5: Labor
Slavery:
- Bondage changed completely with the introduction of Europeans
- Prior, it had been prisoners of war, which weren’t permanently enslaved, had rights, and was not an inherited bondage.
- Europeans had been establishing posts along the coast, trading goods like guns for enslaved people
- Africans that had been put up for sale were groups that had lost their power to stronger African groups
- The stronger groups were able to sell off their prisoners for guns, which gave them even more power, and increased the intensity of their fighting
- Europeans saw the Africans as completely foreign, almost alien.
- They knew that it was morally incorrect for them to label africans as humans then enslave, so they changed their thinking to prove that africans were inferior
- They said that africans were predisposed to be inferior and serve for their lives because of some bible lore
- Spanish brought the africans to the Americas to solve labor problems
Native Enslavement
- Encomienda System: Leading men, encomenderos, were given land. Any natives on that land became workers under the leading men
- System was introduced by Columbus
- Spanish monarchs wanted to spread christianity, so they released a document called Requerimiento
- The pope signed off saying monarchs could claim and and convert anyone they found in the americas
- They could send priests to america and if natives agreed to conversion, they were protected under the crown
- The system didn’t work because the natives kept dying due to disease
- Natives had more knowledge about the land as well, so they were able to escape from the Spanish
- This led to the importing of African slaves for labor
- To the spanish, this worked because they knew less about the land and were immune
- The Spanish imposed a caste system
- Created so that they could input a tax system, and so that they could distinguish who was at the bottom to be taxed the most
- Based on racial ancestry:
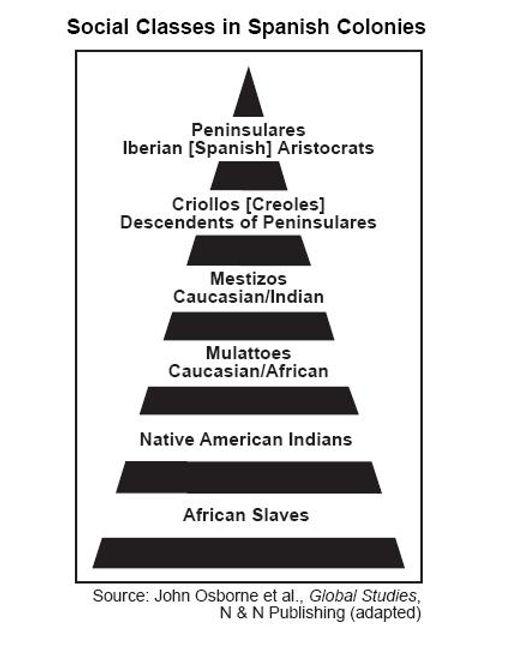
Spain Wealth
- Spain had transformed the Americas, which changed the homeland as well
- Wealth from America, especially silver, allowed for the upper class in Spain to become even wealthier
Comprehension:
Europeans created the slave industry, that was separate from what they loosely had in place before which was prisoners of war. They basically gaslit themselves into thinking that it wasn’t super morally incorrect to enslave people and used the Bible to justify it. They imported African American slaves, which they got in exchange for guns, and created a caste system including them, the Spanish, and the natives for tax. They had been using natives as slaves but they kept dying because of disease or running away, so the Africans were easier. They also kept making bank off of America and building their upper class. Also used encomienda to spread christianity and put the spanish in charge of labor.
Unit 1, Topic 6: Culture
- Hegemony: Domination of one nation or group by another nation or group
- Spanish continued to expand north
- They changed from sending soldiers with guns to sending missionaries to convert people
- This method created the mission system
- Natives believed in a natural world filled with spirits
- Land was not meant to be bought and sold
- Large extended families
- Spanish believed in catholicism
- Land existed for the sake of private ownership
- Nuclear family
- Natives believed in a natural world filled with spirits
Similarities
- They did exchange some culture aspects
- Natives wanted access to metal tools, horse, and guns
- Spanish wanted access to the fur trade, and got this by marrying into native families
Differences
- The differences caused issues
- Conversion meant different things to the pueblos and to the priests
- Christinatiy is exclusive, with rejection of other gods
- Pueblos wanted to adopt all types of religion and integrate christianity into their religion
- Through this, pueblos could retain their religion
Pueblo Revolt - 1610
- Forced conversion and attack forced the pueblo to realize that the Spanish were the cause of their issues
- Pueblo rose together and killed colonizers, burning the churches
- The Spanish fled temporarily
- King Charles heard about the violence and organized priest and philosopher to discuss the conquering
- Some said that the natives were inferior, and education about the riches and religion was beneficial to them
- Others said that the dignity of the indians was being compromised
- Bartolome de las Casas argued for the natives, saying that if the Spanish continued this, their souls would be lost and Christianity would be hated
- He also fought against the encomienda
- He didn’t care as much about africans though, and replaced the natives with africans
UNIT TWO 1607-1754
Unit 2, Topic 2: Colonization
- Encomienda system gave way to slavery with African Americans
- Caste System was creating
- Missionaries tried to convert natives
French Colonial Effort: 1524
- Wanted to find a water route that passed through the Americas
- Slow to colonize because they were still recovering from the wars
- Dealing with the Huguenots
- Decided to stay in the Americas instead of trying to pass through
- Samuel De Champlain established the first french colony called Quebec
- French wanted to trade instead of conquer
- Especially wanted the fur trade
- Established trading settlements
- French traders would even marry native women for economic ties
- Interacted with Ojibwe indians and allied with them
-Cultural Exchange
- Indians got iron cookware and farming tools, manufactured cloth
- French got fur trade access and learned how to skin pelts, etc
Dutch Colonialism:
- Also wanted to find water-based passage
- Sent Henry Hudson
- Claimed the Hudson River portion of the continent for the Dutch, and created New Amsterdam
-Goals:
- Had mostly economic goals, and the creation of New Amsterdam attracted farmers and traders
-Comparison to Spanish
- Dutch did NOT want to convert natives
- Spanish DID
British:
- Reason for Colonization:
- Wanted to come to America for economy
- Had been fighting with everyone around them, and economy transformed after Columbian Exchange, so needed financial boost
- Economy was worsening for everyone, not just nobles
- Peasants were losing out because of the enclosure movement
- Enclosure Movement: took land from public and sold it to private parties
- Peasants also needed land, not just economy
- Others wanted to leave for religion
-Method:
- Unique in starting family establishments and homes
- No large empire around the area where they landed, so no group to take control over
- Agreed with Natives for a little, but soon ended in violence and tension.
-Comparison to Spanish
- Spanish subjugated natives, English expelled.
Comprehension:
English, Dutch, and French settlement showed that you didn’t have to be an asshole (Spain) to live in America. All three came with primarily economic motives, wanting to trade and expand. The French wanted to understand fur trading and created Quebec. The Dutch also wanted to trade and created New Amsterdam as their trading hub. English landed in Plymouth and uniquely wanted to settle down instead of just trade. None of them tried to convert native americans, but of the three, the British won the asshole award for kicking them out. These are D3 assholes. Spain is a D1 asshole.
Unit 2, Topic 3: Regions of British Colonies
How and why did these British colonies develop into distinct societies?
Chesapeake:
- First north American colony established by the British was Jamestown in 1607
- Financed by Joint Stock Companies
- Spanish colonization was funded by the spanish crown, whereas joint stock companies were more of a private thing
- Investors would pool their money together to invest in a colonization attempt
- If the attempt failed, they would lose very little
- Shared the financial risk
- The purpose of the colony was to make money, looking for gold and silver, and building an army to protect resources
- Fell to famine and resorted to cannibalism
- Tobacco cultivation was discovered in 1612 by John Rolfe.
- Labor was done by indentured servants, who signed seven year labor contracts to work off their fees
- The farmers needed more land to plant tobacco, resulting in encroachment on native american land
- William Berkeley was governor
- Decided the cause was not worth the effort, leading to
- ’s Rebellion
- Decided the cause was not worth the effort, leading to
- Bacon’s Rebellion
- Started by Nathaniel Bacon, a farmer who was resentful
- Led indentured servants and farmers to attack the indians and the plantations owned by Berkely
- Elite planters saw the amount of servants working for them, and became fearful that servants would revolt against them because they were greatly outnumbered
- Began to seek new labor source, moving to african americans
New England Colonies
- Settled by pilgrims
- Influx of Puritan settlers against England
- Came to America primarily to find places to make a living
- Economic Reasons
- Unlike Jamestown, New England colonists migrated as families
- Intention to establish colonies
- Nearly half died off
British West Indies/Southern Atlantic
- Long growing seasons in these areas
- Cash crop became tobacco, until it was dethroned by sugarcane
- Sugarcane is labor intensive, and slaves from Africa were used for labor, increasing the black population
- Slave Codes were implemented, and slaves were considered property, also known as chattel
- South Carolina colonists replicated this type of working style
Middle Colonies:
- Situated by the sea
- Export economy based on cereal crops
- Elite class emerged, in order of wealth, with enslaved being on the bottom
- William Penn founded Pennsylvania
- Negotiated with the Indians for more land, contrasting the other colonies.
- Colonies all had somewhat democratic government models
- House of Burgesses in Virginia, Mayflower contract in New England, Middle and southern also had governing bodies headed by the elite.
Unit 2, Topic 4: Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade:
- Trade became global
- Triangular trade involves America, Africa, and Europe
- Merchants from europe would trade resources for slaves from Africa, which would then be traded into America
- Slaves were taken to america through the Middle Passage
- Many slaves died on the Middle Passage
- Slave Trade Act was passed in 1788, which lowered the amount of people that could be stuffed into one ship
- Mercantilism: The dominant economic system in Europe
- In mercantilism, it was assumed that there was only a fixed amount of wealth in the world, since it was based off gold and silver
- Goal of this economic method was to maintain a favorable balance of trade, balancing imports and exports
- Establishment of colonies allowed for access to raw materials, and an ability to create markets for their goods
- Navigation Acts forced merchants to only trade with England, and made sure that valuable trade items were going through British ports exclusively
- This guaranteed that the wealth would be centered around Britain
- Trading changed colonial societies drastically, for merchants and plantation owners
- Also turned America’s ports into trading hubs, leading to the rise of consumerism
- Consumer Revolution was when affluent families began to buy more goods and resources
- This made it so that the consumer lifestyle is what garnered someone’s societal status, and was based off of possessions, and less off of familial wealth
Unit 2, Topic 5: Interactions Between Natives and Europeans
- Spanish introduced the caste system based off of ancestry
- American indians were at the bottom of this caste system
- Santa Fe was the capital of New Mexico
- Spanish exploited brutal measures to convert the natives to Christianity
- This induced the Pueblo Revolt
- Purge the Spanish from the territory
- Spanish returned 12 years later to reclaim Santa Fe
- When British came to America, they settled in areas without large empires, leading to the lack of a workforce
- British colonists migrated as families, so didn’t want to intermarry with the Natives
- Groups borrowed from one another, with goods and techniques for farming
- New England population grew, needing new land
- This need for new land led to Metacom’s War, or King Philip’s War in 1675
- The chief of the Indians could see the British encroachment ruining the way of life for the Indians.
- He knew that they needed to be expelled from the land, so he burned their fields and killed their children and women
- British retaliated by asking the Mohawks to attack Metacom and kill him, thus squashing the rebellion
- Spanish subjugated indians, British forced them out
- French saw indians as trade partners and allies, even marrying into them
- Didn’t settle into their land, only created trade routes
- Europeans never had to worry about unified native rebellions because the groups of natives were all scattered
Unit 2, Topic 6: Slavery In British Colonies:
- Atlantic Slave Trade: Transported slaves
- Middle Passage: Packed slave transport boats
- All of the British colonies participated in and benefitted from the African Slave Trade
- Demand for enslaved workers is due to increased demand for colonial agricultural goods, and the shortage of indentured servants
- Bacon’s rebellion involved indentured servants working and enslaved African Americans to revolt against the governor
- Because of this, Europeans were scared the enslaved would outnumber them, and decided they didn’t want to use indentured servants anymore.
- New England:
- Smaller farms
- Less enslaved
- Enslaved mostly worked as household servants
- Chesapeake:
- More enslaved to be used for their plantation system
- British West Indies
- Most slaves
- The further south, the more slaves
- Chattel Slavery: Race based slavery
- Justified holding other people enslaved by thinking of them as property
- Slave Laws were established to
- Define africans as property
- Slavery was made to be passed from one generation to the next
- Laws became progressively harsher
- By the end of the 17th century, slave owners were allowed to kill defiant slaves
- Illegal for any black person to possess any weapons, or leave without permission
- Slave Laws made interracial relationships illegal
Resistance:
- Covertly:
- Practiced their cultural customs from their homeland
- Maintained their belief systems
- Spoke their native languages
- Kept their naming practices
- Slowed their pace of work by damaging crops and breaking tools
- Overtly:
- Scared the plantation owners because they were outnumbered by the slaves
- Stono Rebellion:
- Small group of enslaved men stole weapons from a store and killed the owner
- Joined by more enslaved men, and continued to kill farm owners and burned plantations
- Ended up being stopped by white militia when the rebellion reached 50 people
- Went against the self-gaslighting from the white people, who thought they were helping the enslaved.
Unit 2, Topic 7: Colonial Society and Structure:
Religion
- Enlightenment: Emphasized rational thinking over religious revelation and tradition
- Took root in the colonies through the transatlantic print culture which allowed the spread of British ideas to the colonies
- John Locke was one of the main ambassadors of this way of thinking
- Opened the colonists to the idea of Natural Rights
- Rights to life, liberty, and property, given to the people by God, not the government
- Social Contract
- Power to govern was in the hands of the people, some of which was given to the government so they could protect the people
- If the government abused this power, the people had every right to overthrow the government
- Colonists liked these ideas, but the authority of the Bible was undermined
- Scientific inquiry was valued more than just the Bible
- Because of the increase in enlightenment thinking, the confidence in the authority of biblical revelation went away
The Great Awakening:
- Preachers lamenting the loss of faith in Biblical authority were called New Light Clergy
- Some of the clergy were inspired by German pietism
- Valued spiritual matters from the heart over the head
- This new religious revival swept through the colonies, and re enthused the colonists in Christianity
- Jonothan Edawrds
- New england minister and scholar
- Preached enlightenment ideas AND religious fervor, which helped restore Biblical devotion
- Preached from his hometown, North Hampton
- George Whitfield
- Methodist Revival
- Took God’s salvation all across the country, and preached everywhere
- He was a talented preacher and people flocked to listen to him
Social Consequences:
- Lack of wealth did not equate to God’s favor
- Preachers gave colonists the initiative to go against the wealthy
- Colonies formed self-governing, elected structures
Overall Impact:
- Enlightenment thinkers gave colonists new ideas about liberty, rights, and democratic government
- The Great Awakening brought the colonists together, and allowed them to be more connected to democracy
- The colonists were exposed to Anglicanization, becoming more British-like in politics., they were also frustrated with the British, leading to resistance
Impressment:
- The practice of seizing men and forcing them to serve in the royal navy
- British thought this was reasonable and normal, but Americans did not agree
- British naval life was dangerous, due to disease
- King George’s War was being fought, and George ordered impressment of American men
- Colonists rioted, showing how colonists realize more and more violations of their natural rights, thanks to the goat John Locke.
UNIT THREE 1754-1800
Unit 3, Topic 2: The French and Indian War
- Two sides of the war: Conflict between British and French n Indians
- French allied with the Indains
Causes:
- Seven Years War
- Worldwide conflict of which the French and Indian was a small part
- American British were encroaching on the land the French had claimed
- Washington was a Lieutenant Colonel of Virginia militia, and was sent west to warn French against encroaching on British holding in Ohio Valley
- Fort Duquesne
- French took control of it originally from Americans
- Washington claimed it
- French took it back
- Land conflicts in the Ohio River Valley between the French and British was the main cause of the French and Indian War
- Before Washington was defeated at the fort, the Albany Congress was formed
- discuss how to organize British colonial defense, trade, and westward expansion
- Colonists met
- The Iroquois Confederacy was also invited in hopes of wanting to ally with them
- They were not involved in the conversation
- The only reason the Indians wanted to ally with the Europeans was because they saw opportunity to maintain control of their land as long as two of the European nations were fighting
- Ben Franklin introduced the Albany Plan of Union, where they would have a council of reps to decide on those three matters
- Plan was rejected because of high taxation required for it to exist
- This however laid the foundation for the revolutionary congress
- British ended up implementing policies that were unpopular with the Americans
- Impressment: Forcing Americans to join the British Navy
- Troop Quartering, where resistance led to threats of violence
- King George didn’t like how expensive the war was, and opened to peace negotiation with French
- War ended in 1763 with the signing of the Treaty of Paris
- Spain ceded florida to the British
- French were kicked out of North America, and their land was given to Spanish
- Land east of mississippi was given to the British
Effects:
- Because Ohio River Valley was given to British, American colonists were hungry for more land and wanted to go west
- This intensified conflict with native americans
- When word of this got back to the natives, the leader of an Ottawa tribe, Pontiac, waged raids against the colonists in detroit, virginia, and Pennsylvania
- British created Proclamation Line of 1763, which stopped the colonist from going past Appalachian Mountains west
- Colonist went anyway because the war was fought on their soil with their blood, and they should get the spoils of the war
- Added to american resentment against british
- War was also expensive, causing the british to raise taxes on products bought by colonists
Unit 3, Topic 3: Taxation Without Representation
- Effects of the French and Indian War are what led to the American Revolution
- The French and Indian War was extremely expensive, so the British decided to tax the Americans
- British thought this was fine because the Americans were technically under British Rule
- Salutary Neglect: Led the colonists to think that they were more independent than the British thought they were
- Technically, the British could tax the Americans because the colonists were under British Rule.
- However, the British were all the way across the world, meaning the day-to-day law enforcement was left up to the colonists themselves
- Parliament passed Navigation Acts:
- Restricted trade to going through only British ships and merchants
- It was more of a suggestion than a law however, which led to the smuggling and trade with other nations
- Now that British were in debt, they wanted control again over salutary neglect, so they could get money back
- George Grenville (PM of Britain) made a three pronged plan
- Stricter enforcement of current laws, like Navigation Acts, to prevent smuggling
- Extended wartime provisions into peacetime
- Led to the Quartering act of 1765, where the British soldiers were stationed in the colonies, and colonists were the ones having to take care of their food and housing
Taxes:
- Quartering Act
- Sugar Act:
- Tax of coffee, wine, luxury items, and existing taxes on molasses
- Stamp Act
- Taxes on all paper items in the colonies like newspapers and cards
- Currency Act
- Prohibited the printing of paper currency
- At the same time the British were demanding money from colonists, the supply of money was going down and being restricted
- As salutary neglect was fading, the colonists were feeling suffocated, especially with taxes
- Rise in unemployment as well because money was being taken
- Americans had no representatives in Parliament where these laws were being passed
- This upset them because they had believed that they had natural rights and and a social contract with the government, thanks to the Enlightenment and our goat John Locke
- Colonists started to protest taxation without representation
- British argued it was virtual representation
- Parliament represented interests of all British classes, even though they weren’t from colonies
- Colonists disagreed and said that they wanted someone from the colonies
- Colonists saw representation through location, and British saw it by class
- Sons and Daughters of Liberty, Vox Populi
- Organized groups that had groups of people from all types and classes fighting for representation
- Sprung up mainly due to the Stamp Act
- Gathering of Stamp Act Congress
- 27 delegates from 9 Colonies
- Goal was to get British to repeal stamp act, because they believed that taxation without representation was tyranny
- The congress still acknowledged they were loyal subjects
- Simply wanted what they were owed as members of Britain
- Stamp and Sugar Act did end up getting repealed in 1766
- British did however pass the Declaratory Act, saying parliament had the right to pass whatever they wanted in the colonies
- Townshend Acts 1767
- Tax of paper, glass, tea, which were imported into the colonies
- Colonists boycotted these goods, and united the colonists across all classes, including women!
- Women would make their own tea and cloth instead of buying from the British
- Yay girlpower
- Tension grew between American and England
Boston Massacre 1770:
- Men and boys became harassing british soldiers
- Threw snowballs and stones at the British
- Gun was fired, and British shot at colonists
- Event enraged the colonists
- Soldiers were put on trial, and were defended by John Adams…? (welcome in bud)
- Adams defended the colonists and they were acquitted (okay minor john adams slay)
- Increased British opposition
Boston Tea Party in 1773:
- Tea Act was passed on Tea, giving rights to sell tea only to the British East India Company
- Colonists were used to smuggling tea
- Sons of Liberty disguised themselves as Indians and dumped tea into the harbor
- Parliament passed the Coercive Acts in 1774, which closed down the Boston Harbor until they were repaid for all the tea
- Passed another Quartering Act
- Quartering II + Coercive = Intolerable Acts
- Colonists began to call themselves Patriots, and armed themselves and gathered into militias, to protect from British tyranny.
Unit 3, Topic 4: Philosophical Foundations of the American Revolution
- Revolution was not yet a choice for colonists, as seen from Stamp Act Congress
- Continental Congress 1774
- Delegates from every colony met (except georgia pull up cuh the func is lit)
- Deliberated about wat the colonists should do about British tyranny
- All agreed they needed to resist
- Revolution was not the answer tho
- Wanted to reach a mutual agreement
- Parliament and King said no, because they thought the colonists were rebelling against the rightful british authority
Enlightenment Effect
- John Locke DA GOAT
- Two treatises on Government influenced colonist leaders
- Power to govern is in the hands of the people, not the hands of a monarch
- Humans are endowed with natural rights, which are god given
- Government didn’t grant the rights, so government couldn’t take them away
- Life liberty and property
- Self-Rule
- Two treatises on Government influenced colonist leaders
- Rosseau
- Power to govern is in the hands of the people
- Social Contract: Some power from the people was given to the government in exchange for protection
- If that power was abused, colonists could revolt
- Montesquieu
- Checks and balances from Montesquieu,
- three branches
- Yet in 1774, Continental Congress delegates still wanted to be British citizens
- Revolution was not an option
- Common Sense, Thomas Paine
- Used everyday language to argue against British rule
- Used Biblical language
- Main population read Paine, not just enlightenment writing for the elites
- Adams thought that Thomas Paine was stupid, but it didn’t matter
- Colonists felt represented by Paine
- Realized that they couldn’t feel free until they were out from British rule
Second Continental Congress 1776
- Jefferson was given the task to write the declaration of independence, which was imbued with natural rights and enlightenment ideas
- Delegates accepted the declaration on the second and was made public on the fourth of July
Unit 3, Topic 5: The American Revolution
- America should not have won the war
- Britain was the most powerful nation in the world
- Not everyone wanted independence
- Patriots were embodied by the continental congress nad common sense
- Loyalists wanted to stay with the British Crown
- Opposition within America and from the outside
- Washington was appointed as the general of the Continental Army
- They did not win conflict for 6 months
- Poorly armed and untrained
- Army didn’t want to fight battles in places they didn’t live, and would just desert the army if they didn’t want to fight
- William Howe
- British general
- Came with 10,000 trained troops plus American Loyalists
- Washington realized that the only way to win the war was to keep the war going until the British tired out
- Black people fought in the war too, in exchange for their freedom, like the British were doing
- Most important victory was the Battle of Saratoga 1777
- Franklin had been trying to convince the French to join the Patriots
- French didn’t want to join because it was clear that the British were going to win
- However, the Battle of Saratoga changed the French’s minds, and they joined the Patriot cause
- French King saw it as a way to weaken Britain
- Spain and Holland also joined the Patriot side
- The introduction of new countries spread out the British resources and made the war even more expensive for them
- The final battle was The Battle of Yorktown 1781
- Forced British surrender
- Paris Peace Treaty was signed in 1783
- British recognized America as a separate country
Unit 3, Topic 6: The Influence of Revolutionary Ideals
Affect on American Society:
- Slavery
- Jefferson wrote “all men are created equal”
- Northern states abolished slavery
- Continental Congress abolished import of enslaved laborers
- Once southerners realized that enslaved were making them money, and support died down
- Democracy
- Legislatures worked to establish suffrage, granting people the right to vote
- Abolished titles of nobility or aristocracy
- Women
- Contributed during the war greatly
- Took on farming roles as well as domestic
- Joined organization like the Ladies Association of Philadelphia
- Made food and clothes for the soldiers
- Some even dressed as men and went to fight in battles
- Women had seen the autonomy and freedom, and wanted more permanent expansion of that freedom
- Republican Motherhood
- Women were vital to a healthy democracy because they could raise sons that had democratic ideals
Effect on Global Society:
- Americans beat out the monarchy to build a government based on Enlightenment ideals
- Inspired the French Revolution of 1789
- Caused the third estate in france to create their own national assembly
- Storm on the Bastille to protest
- Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen, which was based on the American ideals of democracy and independence
- Haitian Revolution 1791
- French colony
- They wanted freedom from France
- Enslaved rose in revolution and killed masters
- Toussaint L’ouverture led the rebellion
- Haitians won against the french and established Haitian government
- Latin American revolutions against Spain and Portugal
Unit 3, Topic 7: The Articles of Confederation
- First constitution was the Articles of Confederation ratified in 1781
- New constitution was needed after the declaration of Independence
- Influenced by existing state constitutions
- These constitutions focused power largely into the Legislative Branch
- Branch responsible for making laws
- Wanted the power of the government to be answerable to the people
- People who made the state constitutions made the articles, putting the power in the people
- Did not provide for a president
- No supreme court, with each state having an equal vote
- Needed a super majority, 9/13, for anything to change in the articles
Problems With Westward Migration:
- Kept running into native americans
- Kept squatting in random places of the land
- Passed the Northwest Ordinance of 1787
- Promoted public education
- Protection of private property
- Abolished slavery in the northwest territory
- Provided orderly means by which the western territories could get a population and apply to be a state
Shay’s Rebellion
- Proved that the Articles were flawed
- The American economy was a mess
- Farmers fell into debt while fighting
- Couldn’t pay debt back because of inflation and new taxes
- Asked the government for help, but were unanswered
- Daniel Shays
- Angry farmer
- Gathered militia of 1000
- Massachusetts crushed the uprising
- Called the president to send federal troops
- No one answered, because there was no president or federal army
- This rebellion showed that the Articles were weak,
- Local and federal leaders began to think about replacing the articles
Unit 3, Topic 8: The Constitutional Convention and Debates Over Ratification:
- 55 delegates from the states met in Pennsylvania for the Constitutional Convention, where they were to discuss the weaknesses in the Articles
- Question arose to fix the Articles, or write a new one
- Decided to make a new one, giving the federal government more power
- Debates over representation
- Virginia Plan
- Strong centralized state
- Bicameral Legislature
- Two houses, with representation based on population
- This means big states have more representation than small states
- New Jersey Plan
- Favored by small states
- Unicameral legislatures
- Equal votes per state
- Favored by small states
- Virginia Plan
- New representation plan was proposed, called the Great Compromise
- The first house would be the House of Representatives, which was based on population
- The second house would be the Senate, where each state got two votes
Slavery:
- Slave and Free states, and whether the enslaved in the south especially would be counted as people for representation in the House
- North argued that slavery was based on the fact that slaves weren’t actually counted as people, so they wouldn’t get votes
- South wanted them to be people because then they would get more votes
- Southern states threatened to leave the convention if they didn’t get some sort of representation using slaves
- 3/5ths Compromise was created
- Every slave counted as 3/5ths of a person, so every five people was 3 votes
- Slavery was simultaneously being outlawed, so southern states wanted to make sure that they would still have salve votes, so slavery outlaw was postponed till 1808
Voting In:
- House of Representatives
- Elected by the people for two year terms
- Senate
- Elected by the state for six year terms
- Executive Branch
- Electoral College
- Elected by the states not the people
- Delegates wanted the election of the president taken out of the hands of the people, and given to a small group that had the skills to choose a president
- In order for the Constitution to become the governing body, it had to be ratified, where 9/13 states agreed to it
- Two opposing sides sprung from the ratification issue
- Federalists
- Tried to persuade the people to ratify
- Hamilton, Adams, John Jay wrote the Federalist papers, supporting the Constitution
- Anti-Federalists
- Convinced people to not ratify the Constitution because it invested too much power in the hands of the central government
- Federalists
- No protection against the intrusion of the federal government on the rights of the states
- No Bill of Rights
- Federalists ended up getting the Constitution ratified
- Conceded to add a Bill of Rights
- Protected individual rights
- Protected state rights from the federal government
Unit 3, Unit 9: The Constitution
Federalism:
- The sharing of power between the national government and the state government
- Doesn’t mean one has more power over another, just that they share power
- Article VI - Supremacy Clause
- National law trumps state law
- Article I Section 8 - Enumerated Power
- Only certain powers fall under the supremacy clause, like the power to declare war
- Tenth Amendment
- Powers not listed in Article I Section 8 are given to the states
Separation of Powers:
- Legislative Branch
- Makes the laws and carries
- Executive
- Carries out and enforces laws
- Can veto laws
- Judicial
- Interprets the laws and ensures that they align with the Constitution
- Constitution framers made the branches to be able to check and balance each other
- No one branch had all the power
- Framers took measures to spread the right to govern over entities so no one thing or body could take total power
Unit 3, Topic 10: Shaping a New Republic
George Washington
- Unanimously voted as the President
- Established the Treasury, State, and War department
- Each department was headed by a secretary, and those secretaries made up Washington’s Cabinet
- Hamilton - Secretary of the Treasury
- Established a national bank
- Unified the states and improved the credit
- Wanted to absorb the state’s debts from the Revolution, and would turn them into a national debt
- This would allow the US to borrow money from other nations, and would make the states more dependent on the federal government
- Policy was contested, especially by states that had no debt
- Necessary and Proper Clause aka Elastic Clause
- Gave Congress some wiggle room for the laws that it could make, even if they weren’t specified in Article I section 8
French Revolution
- Should the states help the French or not
- Washington went against Jefferson, and decided to not help out since the US was still so fragile and new
- Proclamation of Neutrality
- Edmond Genet tried to go to the Americans to join the French, but became a citizen…? Idk either man
- British continued to seize american ships and sailors who were going to France, even though they weren’t helping in the revolution
- John Jay, supreme court chief justice, was sent to tell the British to stop
- Jay’s Treaty made the British give up their posts on the Western Frontier
- The Spanish got annoyed because America seemed to be getting too close to Britain
- Continued to expand missions down California
- Pinckney Treaty
- Allowed spanish to use port at New Orleans for trade
- Southern Border of US would fall along the 31st Parallel
- Difficult to stop Americans from moving west
- Caused conflict with the natives
- Rumors that British were supporting the Indians and telling them to attack
- Battle of Fallen Timbers
- Americans fought indians and won
- Led to the natives surrendering all land in the Ohio Valley, opening it to American settlement
- Whiskey Rebellion 1794
- Hamilton got Congress to tax whiskey
- Pennsylvanians started to beat up tax collectors instead of paying
- Unlike Shay’s Rebellion, Washington was able to use the federal army to shut down the rebellion
- This proved that the new Constitution to do its job
- Jefferson was not a fan, but it didn’t matter
Two Party System:
- All these issues caused tension, and two parties emerged
- Federalists:
- Led by Hamilton
- Strong central government
- Favored urban and elite
- Southern Motherfucking Democratic Republicans (OHHH)
- Jefferson and Madison (duh)
- State rights
- Rural and Agricultural interests
- Federalists:
- Washington stepped down after two terms, and gave his Farewell Address
- John Adams succeeded him as president
- Federalist
- Pro British
- War broke out between France and Britain, Adams had originally planned to be neutral, but French kept attacking US ships
- Adams went to compromise with the French, but they seeked a bribe before even sitting to discuss
- XYZ Affair:
- The diplomats were only identified as X, Y, and Z
- Outrage about this was shared between both parties
- Adams encouraged congress to pass the Alien and Sedition Acts
- These acts allowed Congress to deport any non-citizens they wanted
- Aimed at Irish and Scottish immigrants, who didn’t like the British
- This stopped people from being able to openly share their political beliefs, and was seen as an overreach of federal power
- Fundamental violation of Constitutional Rights
- Virginia and Kentucky Resolution
- States had a right to nullify any law passed by the federal government that went beyond the rights explicitly granted to it
- Adams was not re elected in the election of 1800
- Jefferson was the 3rd president
Unit 3, Topic 11: Developing an American Identity:
Women:
- Diminished role in early american society
- Leaders were convinced that wives and mothers were important because of Republican Motherhood
- Came from the Benjamin Franklin’s Essay on Female Education
- Said that women should be educated too because they were responsible for raising boys to become educated advocates of liberty
- This expanded schooling for girls and academies for girls
- Only applied to white women, black women were enslaved or household servants
- Women in native tribes also had no role, even though women traditionally had the maternal rights
- Because of all the fighting that had been happening, the roles of men became far more important and therefore, they took primarily roles in the household
Art, Literature, Architecture:
- During colonial days, paintings were based off of British and European ideals and styles
- This change could be seen in American painters painting George Washington, rationality and education
- John Trumble painted important historical events in a romanticized way
- Used light to add drama and made the images look idealistic
- Added a sense of nationalism
- Architecture was similar to Europe, with columns and domes
- Literature was also adopted by Americans, showing off the identity of being industrious and hardworking
- Virginia Statue for Religious Freedom
- Defined separation between church and state, which was very american
- Showed that people could not be forced to go to church
UNIT FOUR 1801-1848
Unit 4, Topic 2: The Rise of Political Parties and the Age of Jefferson
- Hamilton was in charge of the Federalists, and strongly opposed Jefferson and the Democratic Republicans
- Jefferson favored agrarianism, a nation of self sustaining farmers
- When Jefferson won the election, he called it the Revolution of 1800, where the power was transferred peacefully between two parties
Policy Debates Over the Power of the Federal Government
- Democratic Republicans abolished the Whiskey Tax
- Limited the power of the government by minimizing the military and reducing the number of government jobs
Louisiana Purchase
- French owned the middle swath of land, including the Mississippi River
- After losing the Haitian Revolution, it was difficult for Americans to access the land
- Jefferson sent James Monroe to get rights to the land
- Napoleon offered the entire territory to Monroe for 1,500, when he was originally planning on paying 2 million
- Strict Constructionism: The government can only do what was explicitly written in the Constitution
- Jefferson was a firm believer in this and the Louisiana Purchase went against these ideals
- Justified the purchase on the ground that he could move natives farther west
- Corps of Discovery was founded, headed by Lewis and Clark
- Accurate mapping, diplomatic relations with indians
- John Marshall
- Fourth chief justice
- Expanded power of the court
- Marbury vs. Madison 1803
- Judiciary Act
- Created 16 openings for new Judges
- Adams filled these openings with Federalist judges, called the Midnight Judges
- Madison was made secretary of state, and since these judges were appointed so late into Adams’ term, Madison just decided he wasn’t going to appoint them
- Marbury was one of the Judge elects, and argued that he had to be appointed as stipulated by the Judiciary Act
- Marbury had a right to his commission
- Marshall then declared that the Supreme Court was in charge of deciding whether laws were constitutional, and decided that the Judiciary Act itself was unconstitutional
- This power became Judicial Review
- Mcculloch vs. Maryland
- Whether a state could tax a federal bank
- National law trumps state laws whenever they contradict
- Expansion of federal power
- Jefferson opposed paying money to Barbary states of North Africa in exchange for protection
- He decided he wasn’t going to pay, especially not after the rates increased, so Barbary pirates started attacking the merchant ships
- In order to avoid war, reduced tribute payment was agreed
The War of 1812
- Causes
- Impressment of Americans into fighting for British, and was worse now because they weren’t even British citizens anymore
- Issues on the Frontier, kept running into natives
- Found out that the British were sending aid to natives that were attacking migrating Americans
- House of Reps was Democratic Republicans, and wanted to war
- They were known as the War Hogs
- Federalists were extremely against war
- Held a meeting called the Hartford Convention, where they threatened to secede from the union
- Americans ended up winning the war, which made the Federalists look outdated, and misaligned with the American ideals
- This war led to the decline of the Federalist Party
Unit 4, Topic 3: Politics and Regional Interests
- War of 1812, but put competing regional interests on display
- America winning the war led to a rising feeling of nationalism
- Showed that without a National Bank, there was no reliable source of credit
- Also showed the weakness of US infrastructure and transportation
- Difficult to move people and resources
- Henry Clay came up with the American System to try and solve these problems
- Federally funded internal improvements like roads and canals for farmers and merchants
- Federal tariffs for US manufacturers
- Forced people to buy domestic goods, because imported were more expensive
- Second National Bank of the US
- Madison and Monroe opposed the roads and canals because they thought federal spending was an overreach of federal power, and would harm the south
- Regional tensions were worse because of expansion west
- Improved roads and cheap land sold by the federal government, more americans moved to the frontier
Slavery:
- Missouri applied for statehood
- Settlers had already brought 1000’s of slaves into the territory
- Assumed Missouri would enter as a slave state
- This caused issues because:
- Country was already balanced between slave states and non slave
- More northern representatives in the House of Reps because they had majority, ut southerners could block any disadvantageous decisions because of the equal balance
- Adding Missouri as a slave state would tip this balance
- Tallmadge Amendment was proposed by Tallmadge
- Proposed an amendment to Missouri’s statehood that would ban slavery after 25 years in the state
- Southerners saw this as a threat because they thought it would lead to the abolishment of slavery in every state
- Southerners threatened to secede from the union because of these issues
- Clay came back with the Missouri Compromise/Compromise of 1820
- Missouri would be admitted as a slave state, but they would also create Maine, which would enter as a free state, maintaining the balance
- 36”30’ line for free and slave states
- Any states entered above it were free, any states below it were slave
- Missouri would be admitted as a slave state, but they would also create Maine, which would enter as a free state, maintaining the balance
Unit 4, Topic 3: America on the World Stage
- 1814 Treaty of Ghent
- Ended the war of 1812 between US and Britain
- James Monroe became president in 1817
- John Quincy Adams was sent to London to fix territory issues
- Established US Canada border along the 49th parallel
- Joint occupation of Oregon County between British and American for 10 years
- Florida belonged to Spain, but Spain was having trouble controlling it because they were focused in South America
- Natives and runaway slaves were running from Florida to US territories
- Andrew Jackson was sent to Florida to stop this
- Monroe knew this could start war, so he told Jackson to not directly interact with Spanish
- Jackson was a dumbass and killed Spanish AND British
- They both got mad but neither wanted war so they didn’t do anything
- Spain sold Florida to the US
- Adams-Onis treaty made the purchase official
- By 1822, South American countries had thrown off Europeans
- Mornoe established diplomatic relations with them
- He didn’t want Europe anymore, so he made the Monroe Doctrine
- Established that the land and territory in the Western Hemisphere was for the US, and Europeans couldn’t come over
- Officially challenged Europeans for authority in the Americas
- Trade was another motivating factor for this
- Americans had established a good trade relationship with Mexico, especially New England
- Also expanded trade to Chinese porcelain and silk
- Increased demand for US good led to a Market Revolution
Unit 4, Topic 5: The Market Revolution in America and Industrialization
- Market Revolution: Linking of northern industries with western and southern farms, which was created in advances through industry, agriculture, and transportation
- Coordinated industry in the US, region wide
- Marked the transition from agrarian to capitalist
Innovations in Transportation:
- National Road aka Cumberland road
- Connected Maryland to Illinois
- Big deal because states typically rejected the idea of a road passing through their state
- Canals
- Human constructed rivers
- Erie Canal in New York, linking farms to manufacturing
- Steamboats
- Second hand product of canals
- Allowed goods to be delivered both ways, instead of just with the current
- Efficiency
- Railroads
- Largely replaced canals
- Local and state governments loaned money, land, and tax breaks to railroad companies
Industrial Technology
- New patent laws protecting people's inventions
- Eli Whitney:
- Interchangeable parts
- Factory system in the 1820’s
- Mass production of specific item parts
- Workers could assemble them to be shipped
- Manufactured goods could be produced by unskilled laborers
- Americans had tons of new things to buy
Agricultural:
- Cotton gin:
- Sped up the process of separating cotton seeds from cotton fibers
- Spinning Machine
- Turned cotton into yarn
- Subsistence Farming had been the main goal of agriculture, which was to feed themselves and have a little extra to sell locally
- Commercial farming replaced this, and focused on growing cash crops, grown exclusively to be sold at local and distance markets
- Cotton was the most important cash crop for southerners
- Linked American farms to American industry and American farms to international markets
- Because of increasing advancements in these three regions, market relations within America were interwoven, and international trade relations were also improved
Unit 4, Topic 6: The Market Revolution’s Effect on Society
Migration:
- Industrial cities exploded in size and diversity
- European immigrants like Irish and German
- Irish came because of Irish potato famine
- German came because they had crop failures, and wanted democracy
- Immigrant counts were booming
- Many settled on the eastern seaboard and worked in industry
- Immigrants were cheap and easy labor
- Also changed the landscape where they settled
- Brought their culture with them, including their religion and customs
- Others moved west and established communities along rivers
- Nativists flourished in the 1830’s and 1840’s
- Thought Jews were moneylenders
- Catholics were agents of the pope
Middle Class:
- Emerged due to growing prosperity and immigrant labor
- Business owners, shopkeepers, journalists, etc
- Had their own society and norms
- Education was important
- Temperance was important
- Moderation in alcohol consumption
- Religious affiliation was also important, especially Protestant
- Distinguishing factor from middle and lower was middle had money for leisure activities
Women:
- Cult of domesticity
- Presented to women through books and magazines
- Job of women was to have children, raise children, and provide for her husband
- Husband’s job was to do the actual work
- Women in the laboring class were working because they didn’t have the extra money to stay home
- Women in factories usually worked 6 days a week for barely any wages
- Lowell Factory
- Staffed by New England farm girls who were controlled by their bosses
Unit 4, Topic 7: Expanding Democracy
Causes of Participatory Democracy
- People began to demand franchise, aka the right to vote
Panic of 1819
- Second National bank tightened money lending to combat inflation
- By restricting the money to borrow, state banks started to close
- Decrease in export American goods like cotton
- Unemployment went up and bankruptcy was everywhere
- People who couldn’t pay debt went to prison
- Laboring men wanted to hold politicians accountable
- They couldn’t vote because property was connected with voting
- Eastern and Western states lowered property qualifications for voting
- More people meant the growth of political parties
Realignment of Parties
- Federalists were basically gone at this point after 1812
- Democratic Republicans were basically the only party
- This party began to split up into Democrats and National Republicans
- Two rival factions within Democratic Republicans
- National Republicans
- Expansive view of federal power (similar to federalists)
- More loose with interpretation of the Constitution
- Democrats
- More like Jefferson
- Word for word constitution
- Limited Federal power
- Election of 1824
- Democratic Republicans ended up with four presidents
- John Quincy Adams, Henry Clay, Andrew Jackson, and William Crawford
- Of these, Adams and Jackson were the strongest
- Jackson won the popular votes, but none won the electoral votes
- President then had to be chosen by the representatives
- Clay supported Adams and got him elected
- Jackson got butthurt
- Adams named Clay as secretary of state
- Jackson and supporters called this the Corrupt Bargain
- Democratic Republicans ended up with four presidents
- By 1828, these two factions became more strongly outlined political parties
Unit 4, Topic 8: Jackson and Federal Power
- Democratic Republicans were the only major political party with the democrats and national republicans being within them
- By the 20’s and 30’s they hardened into their own parties
Democrats:
- Followed the more traditional democratic ideals of Thomas Jefferson, which was a rigid constitution and limiting federal power
- Did not like corporate monopolies, national bank, and high tariffs
Whigs:
- More like Hamilton
- Involved central government, national bank, protective tariffs, internal improvements
- Did not like immigrant crimes
Tariffs:
- High tariffs = more domestic purchase
- Protective Tariffs raise prices on foreign goods
- Tariff of 1828
- Passed during the final months of John Quincy Adams
- Raised prices like 40% on imports helped the north and west, but hurt the southerners
- Jackson was president in 1828
- He didn’t care about the Tariff, but his VP John C. Calhoun hated the tariff
- He called it the Tariff of Abomination
- Calhoun developed the Doctrine of Nullification
- If a state didn’t like a tariff and thought it was unconstitutional, they could just ignore it
- Jackson did not like this
- Jackson got Congress to pass a Force Bill, which allowed him to use military power against North Carolina
- This made Calhoun back off
- But he got the tariff reduced
- Force Bill was also nullified
- Second Bank of the United States 1816
- Stabilized the economy
- In the 1830’s state banks couldn’t pay the national bank, so banks had to close
- This left citizens with worthless money
- Because of this Jackson believed that the National Bank was unconstitutional, and Clay wrote a bill for Congress to recharter the bank
- Andrew Jacksn vetoed that bill, calling it a hydra of corruption
- He was re elected by a landslide
- Internal Improvements
- Since Clay’s system was made with federal money, it divided the parties
- Whigs were in favor of them
- Jacksonians saw it as federal overreach and unconstitutional
- Indian Removal
- Indian land taking had always been a problem
- Passed the Indian Removal Act of 1830
- Cherokee nation in Georgia declared itself as a sovereign nation within the state
- Georgia saw them as houseguests
- Gold was then found on that land, and the Indian Removal Act was passed
- Stated that all indians were to move west of the Mississippi
- Cherokee’s challenged this in Worcester vs. Georgia
- Supreme Court agreed, and said Georgia couldn’t apply laws to Cherokees
- In 1835, Cherokee’s met without Georgians, and created the Treaty of New Echota, which exchanged Cherokee lands in the east for reservation territory in the west of the river
- 1838, the forced removal began, and traveled along the Trail of Tears
- Indians were sick and died because they were unprepared to travel that far
- Some resisted removal, and settled on the western portion of North Carolina, becoming citizens of the US
Unit 4, Topic 9: The Development of American Culture
- Deeply shaped by european influence
- Almost all founding documents were laced with Enlightenment
- Enlightenment thinking and rationality gave was to Romanticism
- This would give way to the Second great Awakening
Romanticism: Warmth of emotion and desire, and believes in human perfectibility
Architecture:
- Mostly was restrained and symmetrical
- Transitioned to Greek and Roman revival era
- Domes and pillars
Literature:
- Novels of Walter Scott (British)
- Heroic characters and classical historical setting
- American authors romanticized opportunity and dangers of the west, and cast america into fantasy
- Webster published the dictionary of the american language
- Used in schools, and standardized spelling and pronunciation
Art:
- Hudson River School
- Dramatic renditions of american landscapes
- Pristine and untouched land in the american continent
- Occasionally included civilization which they thought was here to ruin the pristine
- Emotion over fact
Transcendentalism:
- Rooted in Romantic view of the beauty and power of nature
- Belief in human perfection
- Individualism and self reliance
- Thoreau
- Aimed to live simply and understand the truth of life and universe through nature
- Wrote Walden
- Movement away from society and create utopian communities
- Shakers in Kentucky
- Christian, died out because they didn’t repopulation
- Oneida
- Dedicated to perfect equality, with marriage, parenting, property, and wealth
- Shakers in Kentucky
Unit 4, Topic 10: The Second Great Awakening
- The second great awakening was a series of religious revivals among Protestant Christians
- Spread rapidly through america
- Camp Meetings
- Preachers taught day in and day out
Causes:
- Market Revolution
- Individuals learned that economic success and failure was in their own hands
- Hard work = success
- The same ideal was preached to people in the Second Great Awakening
- Do justice
- Reform life
- Control impulses
- Unlike the first Great Awakening with Calvinists, and personal salvation in the hands of God alone
- Rising tide of democratic and individual beliefs
- More participation in democracy, especially lower class
- Caught up lower classes, enslaved, freed, men, women in Camp Meetings, all equal under the movement
- Romanticism
- Emotional Reality over Rational
- Preaching in the first was structured and philosophical, more focused on thinking
- Preaching in the second (Charles Gradison Finney) had less God centered preaching, with great emotion, and audience centered
- Used metaphors and plain language
- Moral message, with reformation of society
- People were being converted to Christian programs of societal reform
Unit 4, Topic 11: An Age of Reform
- Market Revolution caused this reform
- Embedded the idea that economic improvement was in control of the people through hard work and industry
- People felt like they had a role in the democratic affairs
Religious Reform:
- 1840’s Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints aka Mormons
- Founded by Joseph Smith
- Had received visions from God
- The church had strayed from the true teachings, and Joseph Smith was god’s prophet to bring the church back to it’s true form
- Wrote these prophecies in the Book of Mormon
- Commanded polygamy
- Smith was arrested and lynched because polygamy was too far
- Next prophet was Brigham Young, and moved the Mormons to Utah, where they could avoid anti-mormonism
Temperance
- Avoiding overconsumption of alcohol
- Induced by the Second Great Awakening, nad went through the church
- American Temperance Society was created by clergy and businessman
- Directed efforts at working class men
- Over 5,000 chapters of this society were established
- Measures to fight drinking were placed
- Irish and German refused this
Abolitionism:
- Second Awakening convinced people that slavery was sinful
- William Lloyd Garrison
- Published the Liberator
- White people needed to use moral persuasion to end slavery
- Established the American Anti-Slavery Society in 1833
- Still radical, and thought it had to end immediately, burning the constitution publicly
- Frederick Douglass
- Escaped, self-taught slave
- Broke off from Garrison and published a book called The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
- Talked about the dehumanization in the slaves and the slave holders
Women’s Rights
- Anti slavery women realized that they were unable to fight for abolitionism because they had few rights themselves
- Women decided that they needed more rights to advocate
- Seneca Falls Convention 1848
- Women’s Rights in American society
- Drafted the declaration of sentiments and resolution
- Was written like the declaration of independence, holding women and men equal
- Women refused to give up what was rightfully theirs
Unit 4, Topic 12: African Americans in the Early Republic
- Enslaved people carved out a social identity despite the harsh conditions
Culture:
- Claimed their names, and their traditional ways of naming
- Sustained their heritage
- West African and Caribbean language when they were among themselves
- Maintained their folktales and dance
- Spread through the south as people from different plantations met
- Kept their own versions of religion
- Some others joined the Christian ideas because of black preachers who married together their two religions
Resistance:
- Outright rebelled against slavery
- Slaveholders were scared
- Haitian Revolution was a reason why slaveholders were scared
- White plantation owners tried to suppress slaves
- 1831 Nat Turner’s Rebellion
- Virginia
- Believed God had chosen him to free slaves
- Killed his master and 57 white people
- Virginian military squashed the rebellion and he was hung
- Virginian planters beat all their workers out of fear
- Amistad:
- Ship was packed with slaves from africa
- Cook joked about cooking the slaves
- Slaves killed white people on the ship, and the enslaved were tried when they reached the states
- They were represented by Quincy Adams, and the court favored the rebel and set them free
- White owners tried to control them more
- Southern legislatures made it illegal to free a slave, teach them to read and write, and marrying
- Slave holders told themselves that enslaved weren’t actually people, but the rebellions went against this ideology
UNIT FIVE 1844-1877
Unit 5, Topic 2: Manifest Destiny
- Westward expansion had always been the American MO
- John O’Sulliuvan gave a name to this expansion, calling it Manifest Destiny
- Says that Manifest Destiny is the desire to possess the entire continent from sea to sea
- God gave them this destiny
- Manifest Destiny: Notion that Americans have the God given right to have a nation that expands across the country
Practical reasons:
- More access to mineral and natural resources
- Gold found in California
- California Gold Rush
- People rushed to California from the east to try and strike it rich
- New economic and homestead opportunity
- Congress passed the Preemption Acts for anyone to be able to buy land for cheap
- Costed money to be able to travel west, so primarily the middle class moved
- Mormons would continue to migrate West due to religious persecution
Election of Polk 1844:
- Polk was a big believer of Manifest Destiny
- Wanted to add Texas and Oregon to the union
- Americans had been settling Texas, even though it belonged to Mexico
- They were all either slave owners, or sympathetic to slavery
- There were almost triple the amount of Americans as there were Mexicans in Texas
- Mexican government made laws about immigrants
- Mudst convert to Roman catholicism
- Outlawed slavery
- Americans ignored the laws because they didn’t like them
- Mexico shut down the border to immigration
- Americans didn’t gaf yet again
- Change in government, and a new Dictator came
- Texans revolted under Sam Houston, and declared it an independent republic
- Sent forces north to put down the rebellion, and Mexicans won at the Alamo
- Houston and Army engaged in the Battle of San Jacinto
- Captured the mexican general
- Forced the general to sign a treaty
- Texas claimed independence, but it wasn't recognized by Mexico
- Jackson and Van Buren both said no to annexing Texas because they knew it could start a war with Mexico
- Tyler tried to admit, but it was denied by the senate
Oregon Territory
- British and Americans have competing claims over Oregon
- British said they had it because they had been there longer and had their fur trade
- American numbers outweighed British in Oregon
- Polk wanted Texas and Oregon, and California
- Big fan of Manifest Destiny
- Saw his election as the people saying he should annex
- Tyler brought the last months of his presidency to annex Texas
- Also made a treaty with the British to divide Oregon at the 49th Parallel
Unit 5, Topic 3: The Mexican-American War
Causes:
- Texas had declared its independence from Mexico in 1866
- Tension between Texans and Mexicans cooled after the conflict
- Things would have been fine if Texas stayed independent
- Texas didn’t want to be independent it wanted to be annexed into the US
- Van Buren, Harrison, and Tyler decided against annexation because they didn’t want this war
- Polk, however, wanted Texas, so he annexed Texas
- John Tyler was the one who actually annexed Texas, but he did it at the end of his campaign
- Mexico was not happy about it being annexed, so Polk sent John Slidell to Mexico
- Asked the Mexicans to to the US, namely california
- Mexicans said no
- Settle the location of the southern Mexican Border
- Mexicans said it ran along one river, Americans said it ran along another river
- Mexicans no
- Asked the Mexicans to to the US, namely california
- Since Mexico was unmoving, Americans sent Zachary Taylor to station troops in the land along the Rio Grande, where Americans said their land was
- Mexicans met them at the divide, and Mexicans killed 11 americans
- Polk wanted a war with Mexico
- In 1836, Polk got his war against Mexico
Mexican-American War:
- Under Winfield Scott, America won and forced Mexico to give up California
- Also took Mexico City
Effects of the War:
- Huge swaths of land went to the Americans
- Signing of Treaty of Gudalupe Hidalgo
- Established Rio Grande as the southern border of Texas
- Outlined the Mexican Cession
- Mexico ceded California and Mexico City to the US for 15 million
- All of this land was in the Gadsden Purchase
- Mexico lost like half its land
- Congress already knew that the war was going to be won
- David Wilmot made the Wilmot Proviso
- Any land gained from victory in the Spanish American war was off limits for slavery
- While this got shot down, it did show the growing tension over slavery
- Contentious
- First round in the fight that led to Civil War
- Any land gained from victory in the Spanish American war was off limits for slavery
- Politicians who voted dit down believed in free soil
- Wanted to acquire land for homesteaders to settle on, without competition from slavery
- More economic than moral
- Wanted to acquire land for homesteaders to settle on, without competition from slavery
- People on the contested land were mostly Mexican and Indian, and stayed put through the conflict
- Guadalupe Hidalgo specified that all Mexicans could be granted US citizenship
- Indians who had become Mexican citizens were not offered US citizenship
- Both groups were discriminated against
Unit 5, Topic 4: The Compromise of 1850
- All land won in Mexican-American caused tension with the expansion of slavery
- Wilmot Proviso barely lost in Congress
- Southern Position
- Slavery was a constitutional right
- Question about where slavery could and couldn’t be was already decided in Missouri Compromise
- To the southerners, Missouri Compromise was a promise that slavery would continue to live on
- Any attempt to curtail slavery was a nod to its destruction
- Free Soil Movement
- Northern democrats and Whigs
- Wanted new territories acquired to be the dominion of free laborers, and not the enslaved
- There was conflict within the free soil movement as well
- They didn’t think slavery was a moral evil, they just wanted the economic benefits
- They wanted white opportunity
- Abolitionists wanted slavery to be banned completely, and everywhere
- Free Soil Party was created
- Popular Sovereignty
- People living in each territory should decide whether slavery was legal or not
- The idea that slavery was so up in the air did not work for the other two parties, in the chance that the territory didn’t choose the value they aligned with
- This caused even more tension over slavery, rather than fixing it
- All of these ideas were incompatible, and compromise was not possible
- The fight got worse when the new land was included from the Mexican-American
- Worsened because California and New Mexico were entered as free states
- Southerners threatened secession from the Union
- The inclusion of these two new non slave states meant the balance was disrupted
- Tipped the balance in the senate towards the free states
- Henry Clay proposed the compromise of 1850
- Said that the mexican cession will be divided into Utah and New Mexico, and would practice popular sovereignty
- California would be a free state
- Washington DC would have slavery banned
- Stricter Fugitive Slave Law
- Fugitive Slave Law
- This would cause issues because it asked the north to return slaves to the plantations from which they had escaped
Unit 5, Topic 5: Sectional Conflict: Regional Differences
- Expansion of slavery was one thing that caused tension
Immigration:
- Huge number of immigrants from Ireland and Germany settled in cultural enclaves when they arrived in america
- Settled in communities together and kept their culture
- Lived in slums with disease and infant mortality
- Germans moved west to find land to farm
- Nativist Movement
- Nativism was the policy of protecting the interests of native born people against immigrants
- Irish were also Catholic, not Protestant
- Limiting immigrant cultural and political influence
- Know-Nothing Party
- Nativist Party opposing immigrants
Slavery:
- North
- Economy stimulated from free-wage laborers working in manufacturing
- Population was growing far more rapidly
- South
- Enslaved labor working on agricultural plantations
- Northerners didn’t object to slavery on moral grounds, but more economic grounds
- Impossible for free wage laborers to get job if slavery was allowed
- Free Soil Party
- In favor of the Wilmot Proviso, which stopped new states from becoming slave states
- Weren’t interested in abolishing slavery, just didn’t want it to expand to the new territories
- Abolitionists:
- Wanted to ban slavery everywhere
- Free black and white members of the party
- Highly influential and effective
Words
- The liberator
- Influenced the abolitionist
- Beecher Stowe’s: Uncle Tom’s Cabin
- Northerner readers saw the wickedness of slavery
- Southerners tried to banish this book
- Speeches from Frederick Douglass
- Wove together abolitionist speeches
Escape
- Underground railroad
- Could escape from the South to the North
- Some even traveled to canada to escape the stricter fugitive laws
Violence
- John Brown
- Believed the only way for America to be freed of slavery was through a slave uprising
- Raid at Harpers Ferry to steal weapons and give them to the enslaved
- Plan fell to pieces and was unsuccessful, and was hung
- Had connections to the northern abolitionists like Douglass
- Southerners saw this as a symbol of what abolitionists were really about, not just to abolish slavery but also to incite a race war
Unit 5, Topic 6: The Failure of Compromise Pre-Civil War
- Kansas Nebraska Act 1854
- Northern section of Louisiana Purchase was above the Missouri Compromise line, meaning slavery could not exist
- Stephen Douglas proposed that it should be divided into Kansas and Nerbraska, and should be decided by popular sovereignty
- This enraged Northerners because it essentially overturned the Missouri Compromise
- Violence erupted in Kansas over pro-slavery and anti-slavery
- This violence became known as Bleeding Kansas
- There were 1500 men were eligible to vote, yet somehow there were 6000 votes
- The extra votes came from Missouri, a bordering slave state
- Thousands flooded over the border and voted illegally
- The solution was that two rival legislatures were proposed
- Franklin Pierce recognized the pro slavery one as legitimate, and the anti as fraudulent
- Dred Scott Decision:
- Enslaved man in Missouri
- Was taken in illinois and wisconsin by master, where slavery was illegal
- He sued his master for freedom, but lost
- He wasn’t a citizen so he couldn’t sue
- Congress needed due process to deprive a citizen of property
- This decision meant that any slavers could take their slaves to a free state and set up shop there
- Increasing division over slavery weakened the two party system
- The Whig Party divided into proslavery, Cotton Whigs, and anti slavery, Conscience Whigs.
- The Democratic Party was gaining strength as a pro slavery party
- The Republican party was also formed
- Members of the Know Nothing, abolitionists, free soil, and conscience whigs
- Didn’t advocate the abolition, just argued against the spread of it into new territories
- Democrats saw this as a threat to slavery
- Republicans did well in elections, scaring southerners for the election in 1816
- A republican getting elected would mean the demise of slavery and the south
Unit 5, Topic 7: The Election of 1860 and Secession:
- Republicans were freaking out
- Democrats Nominated Stephen Douglas because of Kansas Nebraska
- Republicans nominated Abraham Lincoln
- Free soil controlled the spread of slavery not the abolition
- Democrats were divided between the North and the South
- Northern - Douglas
- Popular sovereignty for slavery
- Southern - Breckenridge
- Slavery protected by federal slave code that would then turn into federal sovereignty
- Northern - Douglas
- Lincoln won 41% popular and through electoral votes, none of which came from Southern states
- Lincoln was clear about not changing slavery that already existed
- This still scared the south because they still didn’t have power to win
- Even before Lincoln was inaugurated, many of the Southern states began to secede from the union
- The new Confederacy created their own Constitution
- Similar to the US constitution., but had limited federal power
- Made slavery to never be abolished
Why did they Secede?
- To protect slavery
- On the grounds of states rights
- Each state drafted articles of secession as to why they left
- Slavery must be protected
Unit 5, Topic 8: Military Conflict in the Civil War
South:
- Defensive war, fought off the aggressor
- More experience military general
- Robert Lee and Stonewall Jackson
North:
- Population 4x of South
- Had robust Navy
- Economic advantage with banks, railroads, and manufacturing
- Well established central government
- Neither side could look at the other and assume that they would win
- North modernized their manufacturing and industry
- South relied on tariffs and taxes on exports to raise money for the war
- South was a mess financially
- South imposed a war tax, but since the power was given to the states, the states just refused
- North dealt with more opposition
- New York City Draft Riots 1863
- Men could pay 300 dollars to duck out of the draft responsibility
- Working class men saw this as unjust
- Violent protest against this 120 died
Course of the War:
- Lincoln was clear that he wouldn’t stand for secession, but didn’t want to start a war wither
- Fort Sumter was a federal possession in Confederate SC
- SC cut off supplies to the Fort from the North
- Lincoln sent provisions to the troops
- The south blew up the Union supply ships
- First official squabble of the war
- First Battle of Bull Run
- 30,000 Union confronted Confederate at Bull Run Creek
- Virginia
- Civilians came with picnics to watch the battle
- Began with Union winning, but Confederate reinforcements under Stonewall Jackson got Confederacy the victory
- Union
- Anaconda Plan
- North would lean on naval advantage and blockade Southern Ports
- Would split the confederacy in half
- Anaconda Plan
- Southern
- Relied on foreign help from Britain and France
- They helped because both of those countries wanted cotton
- King Cotton would convince both countries to come to their aid
- Except both countries realized they could get cotton from Africa and Asia
- King Cotton was not as strong as they thought it would be
- Union ended up defeating the south
Leadership:
- Lincoln didn’t have any good generals but Ulysses S. Grant slayed
Strategy:
- Emancipation Proclamation 1862
- Only freed enslaved people in the states that were rebelling against the Union
- The Border states that were slaves states within the Union did not have slaves freed
- He only freed the confederate states
- Changed the scope of the war from beating the confederacy to abolishing slavery
- Enslaved workers in the Confederacy escaped plantations and ran to Union
- Some even fought for the union
- British involvement with the South was abolished
- Enslaved workers in the Confederacy escaped plantations and ran to Union
Battles:
- Battle of Vicksburg
- Grant won
- Grant sent another general, Sherman, to capture Atlanta
- March to the Sea
- Destroyed railroads and crops, making it impossible for the South to regain its strength
- General Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, April 9
Unit 5, Topic 9: Government Policies During the Civil War
- Emancipation proclamation was more a military tactic than a moral one
- Ended slavery only in the Confederacy
- It cut off military aid to the south because Britain had abolished slavery
- It created the occasion for enslaved people to escape to the Union
- Gettysburg Address November 19
- Sought to unify the nation
- Portray the struggle against slavery as the fruition of democratic ideals
- Reframed the meaning of the war
Unit 5, Topic 10: Reconstruction
- Reconstruction was the process of bringing the Union and Confederation back together again
Abraham Lincoln:
- Lenient
- South never left technically
- Treating the south harshly would make tension
- Ten-percent Plan
- If a southern state was going to return they could reestablish their state governments if 10% of the electorate pledged loyalty to the Union
- Had to abolish slavery and ratify the 13th Amendment
- Lincoln was unable to bring this plan to fruition because he was assassinated
Andrew Johnson:
- Abe VP
- Was not a fan of equality
- Major douchebag
- States passed Black Codes
- Forced black people to work for low wages
- Radical Republicans: Did not like Johnson’s leniency
- South secession needed to be punished
- Wanted the Reconstruction to be led by Congress
- Freedmen’s Bureau
- Agency to help newly freed black people get back on their feet
- Civil Rights Act of 1866
- Protected the protection of black people and their citizenship
- Andrew Johnson vetoed both of those
- Congress and Radicals overrode the vetoes through the ⅔ majority
- Proposed constitutional amendment 14 to preserve those two laws
- All people born in the US were citizens
- Reconstruction Acts of 1867
- Assured all laws in the south would be enforced
- Republicans divided the south into five sections under federal supervision
- States also had to ratify the 14th amendment
- Universal male voting rights, white and black
- Women also wanted rights but didn’t get them
- Impeachment of Andrew Johnson
- Congressional Republicans wanted him impeached
- Passed the Tenure of Office Act
- Made it illegal to fire a member of the cabinet without congressional approval
- He did it anyways This caused the trial for impeachment
- Unable to remove him by one vote, but left him powerless
Women’s Rights
- 15th Amendment
- Granted voting rights to the newly free black people from the south
- Women were upset because they didn’t get the right to vote
- Women’s rights were split into two groups
- National Woman Suffrage Association
- Continued to fight for the right to vote
- American Woman Suffrage Association
- Others said that it was important to support the federal reconstruction and leave voting rights up to the states
- National Woman Suffrage Association
Unit 5, Topic 11: The Failure of Reconstruction
Southern Society:
- Black people had to adjust to freedom
- Black schools and colleges
- Elected to representative offices
- Established the Freedmen’s Bureau
- Reconnected families
- Helped for economic and social welfare of freed
- White population in the south were trying to create rules that were like slavery
- Sharecropping
- Black people would agree to work in the fields, but had to sign a contract that bound them to the plantation and allowed the field owners to extract unlimited labor from them
- Sharecropping was less extreme, and landowners gave farm supplies to the worker in exchange for part of the harvest
- Turned into basically slavery
- White Supremacy
- Formation of the KKK
- White people were superior, and spread this message by lynching black people, burning buildings, and threatening politics
- Black Codes
- Prohibited money borrowing to buy or rent land, meaning they were prime candidates for sharecropping
- Illegal for them to testify against a white person in court
- Racial segregation of southern society
- Sharecropping
- All of this happened while there were still federal troops supervising
- End of Reconstruction in 1877
- Election of 1876 between Samuel Tilden and Rutherford Hayes
- Tilden won the popular vote
- Neither won enough electoral votes to win
- Special electoral commission was formed to fix this, and was made of a majority republicans, ended up electing Hayes
- Democrats were made
- Compromise of 1877 was made
- Democrats agreed to concede to Hayes, but the federal troops from the South had to be removed
UNIT 6 1865-1898
Unit 6, Topic 2: Westward Expansion: Economic Development
- Massive change in agriculture
- Mechanization of agriculture
- Mechanical Reaper
- Combine Harvester
- This meant farmers could plant and harvest far quicker
- Decrease in small farmers, who couldn’t compete with the big farmers
- Prices for crops steeply declined
- Farming changed drastically
- Industrial trusts made sure prices were high on manufactured goods
- Farmers had to buy their other goods like clothing from manufacturers
- Since that was so expensive, farmers struggled to pay for everything
- Farmers were also having railroad issues
- Farmers relied on trains and railroads to ship their crops for sale
- Railroads started charging more and farmers were made
- National Grange Movement
- Wanted to bring farmers together
- Granger Laws
- Pushed states to regulate railroad rates
- Wanted to ban abusive railroad practices
- Commerce Act 1886
- Railroad rates had to be reasonable and just, and enforced the Interstate Commerce Commission to regulate these rates
- Federal government could see that mass migration was possible through railroads
- Pacific Railroads Act
- Federal government gave land to railroad companies to build the Transcontinental Railroad
- Transcontinental Railroads stretched from the east to the west
- Homestead Act 1862
- Granted migrants 160 acres of free land out west, as long as they farmed and settled it
- While this sounded great, these small farms eventually got swallowed up by bigger farms, and that land wasn’t large enough to sustain a life
- Extraction of Gold and silver
- Gold was found in Pike’s Peak, and led to migration to this surrounded region
- This happened in multiple western places, and created Boomtowns
- Boomtowns were extremely diverse
- Pacific Railroads Act
Unit 6, Topic 3: Westward Expansion: Social and Cultural Development
- Americans moved west to achieve independence and self sufficiency
- The West was basically closed and settled
- Settlers brought a ton of cattle to the Great Plains
- Cattle trade through the Transcontinental Railroad
- Cowboys drove herds of cattle to market across the plains
- Homesteaders would throw fences up around their property
- They became known as sodbusters, cutting through the soil first with their plow
- Because of the mechanization of agriculture, many of these small farms folded
- The US Census Bureau in 1890 said the Western Frontier was officially settled and closed
- Frederick Jackson Turner
- Wrote an essay saying the closing was not a good thing, because westward expansion was gone to release american discontent
- There was no promise of fresh start anymore, and America would devolve into European conflict
- Oklahoma Territory
- Designated as indian territory
- Many indians had been relocated from the indian removal act
- After the mass migration post transcontinental, the government moved to solve the indian problem
- Reservation System
- Indians were made to live on reservations with strict rules
- Indians didn’t like this
- Buffalo had been killed for sport and food, and that was the main source of indian migration technique
- Several indian groups resisted, and it led to violence
- Sioux Wars 1886
- Natives destroyed the Americans easily
- This caused the federal government to make more treaties with the indians and shrink them to smaller reservation
- Indian Appropriation Act 1871
- Nullified all previous treaties made with indians
- Ended federal recognition of indian nations
- Led to another sioux war and another war
- Indians lost to the army and settlers
- Dawes Act 1887
- Government abandoned the reservations
- Divided them into 160 acre plots to be farmed by the indians
- Allowed the indians to become american citizens as long as they assimilated
- Assimilationist movement
- Attempt to end indian culture
- Education, christianizing
- Ghost Dance Movement
- Developed by indian prophet
- If indians participated in the ritual, the ghosts of the ancestors would drive the white people from their lands
- The last battle of the indian wars was happening in Wounded Knee
- US was trying to disarm a group
- Old man did the ghost dance
- Army killed more than 200
Unit 6, Topic 4, The “New” South
- Henry Grady coined new south
- North was industrially advanced which is why the south suffered
- South needed to become more like the north
- Southerners manufactured more textiles, and had more railroads
- Fields were still growing and plantation owners still needed sharecropping
- New form of slavery since sharecroppers remained indebted to the land
- This was intentional
Racial Segregation
- Compromise of 1877 ended reconstruction
- Removal of federal troops was a part of this compromise, and were meant to enforce new laws
- Segregation became worse when they left
- Plessy v Fergueson
- Homer Plessy was ⅞ white, but was still considered black
- He rode in a white only passenger car and was arrested
- Racial segregation was constitutional as long as they were separate but equal
- Jim crow laws kept everything segregated
- Black people couldn’t run for office or serve on jury
- Lynch mobs dealt out justice
- Black people weren’t guaranteed trials
- Ida B. Wells
- Edited a black southern newspaper
- Fought against lynching and Jim Crow
- Henry Turner
- International Migration Society
- Moved black americans to Liberia, even though they suffered from disease
- Booker T. Washington
- Black people didn’t need to fight for equality politically
- Needed to be economically self sufficient, which would lead to voting power
- He did this for himself and tried to help others
- His vision was deemed impractical
Unit 6, Topic 5: Technological Innovation in the Gilded Age
- Industry changed significantly
- Prior to industrialization, americans made things for themselves or to sell locally
- Americans began to mass produce goods to be sold all over the world
- The biggest technological innovation was the railroad
- Quick and easy means to transport goods
- Opens up mass production and consumption
- Post civil war, the railroads built increased five times
- The federal government was funding the railroads, and could see it was good for the economy
- Land was needed to build the railroad
- The government is the one who provided this
- 170 million acres of land for this
- Four new transcontinental railroads were built
- East and west were now easily accessible to each other
- Steel Production
- Bessemer made stronger steel
- Bessemer Process
- Enabled manufacturers to produce a higher quantity and quality of steel than ever before
- Greater access to coal and oil
- Coal
- First major source of energy for locomotives and energy
- Oil
- Later this surpassed the use of coal
- Communications
- Telegraph wires multiplied significantly
- Could travel long distances very quickly
- Transatlantic cable connecting america to Europe
- Created an international market for basic goods like coal, oil, steel and grain
- Graham Bell made the telephone
- By the end of 1880 there were about 15,000 telephones in america
Unit 6, Topic 6: The Rise of Industrial Capitalism
- Industrialism
- The change in the way things are made for sale
- Especially mass production
- This period of time was called the Gilded Age
- Small, locally owned business became obsolete
- Railroad, steel, and oil eradicated small business
Oil:
- John D. Rockefeller
- Forced his competitors to sell their companies to him, making him the only competitor
- Horizontal integration - bought out his competitors
Steel:
- Andrew Carnegie
- Dominated the steel industry
- Vertical Integration
- Bought out all the complimentary industries
- Bough out all the countries that were in charge of the steps of steel manufacturing
- Began to increasing look outside the US to control foreign resources
- Americans had no interest in America becoming an empire, but this was not the case with industry leaders
- All of these industry leaders grew really wealthy
- Laissez Faire - Government let economy alone
- No government regulation or intervention of the business practices
- Industry leaders would pay off the government leaders so they wouldn’t be stopped
- Relied on poor, immigrant labor
- Underpaid, and no government regulation on wages
- They couldn’t ask for higher wages because there were ten other people ready to replace them for the lower wage
- They realized that because the manufacturing was unskilled labor, they could have women and children also work for them
- Women could be paid even less than men
- Social Darwinism
- Strong companies should eat weak companies
- The world’s wealth would be concentrated into the hands of those deemed the most fit
- These were all standard practice for the industry leaders
- Carnegie mitigated these brutal practice through the Gospel of Wealth
- Gospel of Wealth
- Thought that the wealthy should reinvest their money into the people and the betterment of society
- Positively called Captains of Industry, negatively called Robberbarons
Unit 6, Topic 7: Labor in the Gilded Age
- A dividing line was drawn between the rich and the poor
Wealthy:
- Surpassed the previous generation in wealth
- Conspicuous Consumption
- Rich people wanted to flaunt their wealth to everyone
Poor:
- People were wildly underpaid
- Working class suffered economically
- Panic of 1873 found the working classes having their wages dropping tremendously
- Even though the wages of the working class were small, the price of goods was going down greatly due to mass production, meaning they were more accessible than they had been in the past
- Standards of living rose even though the wealth gap was getting larger
- Working class tried to get better wages and safer working conditions
- The formation of Labor unions was the way to get around being replaced by other immigrants
Union Tactics:
- Political Action
- Slowdowns
- Strikes
- Great Railroad Strike
- Railroads had cut wages to save money during a recession
- Unionized workers went on strike and shut down more than 60% of railroads
- Violence broke out and president hayes sent in troops to restore order
- Railroad employers could see the power of unionized resistance and improved their wages and conditions
- Pullman Strike
- Sleeping cars for train
- Panic of 1893, Pullman cut wages
- Union workers tried to bargain but he fired them
- They all went on strike
- He told them not to work on any trains that had Pullman on the
- Hooked up Pullman cars to trains carrying federal mail
- If the workers messed with the trains they had to mess with the government
- They were arrested
- Great Railroad Strike
Labor Unions:
- Knights of labor
- National union with membership open to anyone, like actually anyone.
- Goals were to destroy trusts and monopolies, and abolish child labor
- Children were also subject to injury
- Had over 7,000 members and became a powerful voice for laborers
- Fell apart in the Haymarket Square Riot
- A bomb exploded and the American pubic thought that the Knights of Labor set off the bomb
- Now everyone thought they were violent and radical
- American Federation of Labor
- Led by Samuel Gompers
- Goals were the same as KOL
Unit 6, Topic 8: Immigration and Migration in the Gilded Age
Immigration: When a group of people moved from one country to another
- Population grew to massive waves of immigrants
- Left Europe because of poverty and joblessness
- Religious persecution
- Settled in industrial cities
- Saw America as the land of opportunity
- Mainly on the east coast
- West Coast
- Chinese have been coming since the Gold Rush
- Asian immigrants continued to arrive
- Industrial cities themselves began to change
- During the Gilded age, the middle class and the wealthy moved into suburban areas, and the larger cities were left with the immigrants
- The working class districts became crowded and gross
- Tenements: Poorly constructed and ventilated homes
- Close proximity to one another
- Frequent disease outbreaks
- Immigrants from the same culture did find each other and establish ethnic enclaves
Migration: When a group of people moves within a country to another region
- Significant migration during this period was the Exoduster Movement
- Southern black people into the west
- Black population was left to defend themselves without protection
- Fleeing Jim Crow and KKK
- Starting in the late 1870’s had black people moving to Kansas, Oklahoma, and Colorado
- Colored Relief Board
- Kansas Freedmen’s Aid Society
Unit 6, Topic 9: Responses to Immigration in the Gilded Age
- European and asian immigrants were arriving by the millions
- Many worked in factories and lived in industrial cities
- Debates sprung up over what to do with the immigrants
- Americans began to grow concerned with the identity of America
- Immigrants were grappling with their own identity within american society
- Immigrants partially assimilated and partially held on
- Nativists
- Not a fan of immigrant “attack”
- Protecting the interest of natives of immigrants
- Henry Cabot Lodge, argued that allowing other races was committing race suicide
- American protective Association
- Against Catholics
- Most of the Irish immigrants were catholic
- Didn't like that Catholics were being voted into the government, and thought it was the Catholic church plotting to take over
- Labor Unions also were not a fan of the influx of immigrants
- Immigrants would agree to be hired for barely anything
- Union leaders worried immigrants would undermine the ability for the unions to try for higher wages
- Social Darwinists also didn’t like immigrants
- Thought that immigrants were racially inferior to american whiteness
- They were going to rule the gene pool
- Especially hated the Irish
- Thought the Irish were a completely different race
- West Coast Immigrants
- Most were Chinese, 50,000
- Responsible for a majority of the work done on the railroads and the unwanted jobs
- Experienced the same kind of hostility
- Panic of 1873, California nativists blamed it on the Chinese since they were willing to work for such little wages
- Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882
- Banned further Chinese Immigration to the United States
- Only law to exclude a specific race from immigration
- Jane Addams
- Could see the immigrants in Chicago were suffering
- Established Settlement House
- Hull House
- Help immigrants better assimilate so they could find better opportunity
- Taught english, democratic ideals, and recreational outing
- Immigrants had it hard during the Gilded Age and many worked against them
Unit 6, Topic 10: Development of the Middle Class:
- All major corporations were structured the same way
- Executives
- Managers
- Managers kept the day to day operations of the company going
- Referred to as White Collared Workers
- Accountants, legal services, healthcare
- Laborers
- Men and women filled these clerical roles
- Many women learned how to type, and earned wages through typewriters
- Women were also being hired to teach school children
- They made enough money to be above the working class, but they weren’t rich enough to be a part of the elite
- Thus the middle class was created
- Wages rose
- Had extra money and time
- They bought new stuff
- Increase in leisure activities
- Coney Island building and amusement parks
- PT Barnum’s Circuses also gained popularity
- Sports like baseball and football also rose
- Philanthropy in the upper class
- Inspired by the Gospel of Wealth, Carnegie
- God given duty to not hold onto the wealth
- Wanted to reduce the societal distance between the rich and the poor
- He believed that hard work created wealth
- Wanted to provide opportunity for the poor to better themselves, public libraries, concert halls, and universities
- Phoebe Apperson Hearst
- Another philanthropist
- Education was important, wanted the poor to be educated at the same level as the rich
Unit 6, Topic 11: Reform in the Gilded Age
- Laissez Faire Capitalism: US government rarely intervened with American businesses, wealth stayed in the hands of the upper class
- Henry George
- Didn’t like how wealthy got to live well and poor were dirt poor
- Single tax, thought that the wealthy with large amounts of land were becoming even more rich because the land increased in value
- Thought the rich should be taxed more so it would be evened out
Utopian:
- Edward Bellamy wrote a novel about capitalism being crushed
Socialism:
- All means of production should be owned by the community and equal
- Got popular but never got as big as it did in Europe
- Eugene Deb (who organized the American Railroad Union) founded the Socialist Party of America
- Didn’t do too well
- Social Gospel
- Christian principles should be applied to oneself and society
- Protestants crusaded for social justice for the poor and the middle class
Women’s Suffrage
- NAWSA, Susan B Anthony
- Women also took up the fight against temperance
- Women’s Christian Temperance Union
- Anti-Saloon League
- There was also a more radical strain of women
- Carrie Nation
- Carried a hatchet and hacked at liquor barrels to protest temperance
Unit 6, Topic 12: Controversies Over the Role of Government in the Gilded Age
- Debate over the role of government in the federal economy
- Hamilton and Jefferson argued over the National Bank
- Henry Clay argued about his American System and federal spending on infrastructure
- Adam Smith had published the Wealth of nations in 1776, and he was the creator of Laissez Faire
- The only way Smith’s ideals would work was if there was competition, this was not the case in the new industry
- Panic of 1893
- Cleveland did nothing to help with the economic situation
- Government created federal agency called the Interstate commerce commission
- ICC was underfunded, so they didn’t actually do anything to help
- Government did get involved when gains for the economy and business could be made
- Business leaders worked with republican politicians to expand markets overseas
- Strongly supported the overthrow of the Hawaiin monarchy allowed for Hawaii to be annexed
- Open Door Policy, advocated for equal trading rights in the ports of China
Unit 6, Topic 13: Politics in the Gilded Age
- Corruption was strong
- Democrats
- Mainly Southern
- Championed states rights
- Racial Segregation
- Big City political machines and immigrants
- Republicans
- Black people
- Middle Class
- Protestants
- Neither party had a strong legislative agenda
- Politicas was just a game of winning elections and giving federal jobs to party supporters
- This was known as patronage
- Civil Service
- Jobs in the federal government
- When a candidate won the candidacy, the President would sit and look through applications for jobs
- James Garfield was assassinated
- One of the people he chose to not put into the job killed him
- To correct this system, the Pendleton Act was passed
- Replaced patronage with a high scoring exam instead
- This fizzled out with the way the candidate funding changed
- Candidates used to be funded by the party that was supporting them, which is why the people felt like they deserved jobs in the government
- Now, the funding changed to coming from wealthy individuals, so patronage wasn’t as binding
- Gold Standard
- Government would only print the amount of paper currency as there was gold in their vaults
- This combated inflation and price raises
- Argued money supply to should be increased past the gold standard
- More currency would allow more money borrowing at a lower interest rate
- To them inflation wasn’t a bad thing
- Tariffs were also argued over
- Tariffs provided over half the federal revenue
- During the war Congress had put tariffs in place to help fund the war
- Now that the war was over, Congress didn’t want to take the tariffs away
- Protective Tariffs remained in force
- Protects america’s businesses
- When taxes are high on foreign goods, people are more likely to buy the American goods
- This was bad for farmers because it meant that american goods sold for less internationally, and consumers couldn’t afford the more expensive american goods they needed
- The rise of a new political party changed this
Populist Party
- Worked for the people
- Wanted to correct the overconcentration of economic power held by elite banks and trusts
- Political
- Direct election of senators
- Allowed the people to propose and vote on legislation
- Economic
- Unlimited coinage of silver
- Graduated income tax (more you make = more tax)
- 8 hour work day
- No populist candidate ever won a presidential election, but they did gain a lot of attention
- 1896, the democrats took up themes of the Populist party, notably the coinage of silver
Politics in Urban Centers
- Political Machines: Groups of people who knew how to get votes for their parties
- Tammany Hall - Boss Tweed
- Organized the needs of businesses, immigrants, and poor so they could all flourish
- They didn’t do it to help the people, they did it so that the communities they helped would be in debt to them, meaning they would have to vote for whoever Tweed wanted
- There was still a mutual benefit
- Tammany Hall - Boss Tweed
UNIT 7 1898-1945
Unit 7, Topic 2:
- Imperialism: The expansion of empires
- In 1867 we purchased Alaska.
- Russia and Britain had claims to Alaska, but Seward wanted to buy it
- Seward’s Folly because the land was claimed to be a cold wasteland
- This was until they found gold there
- Since territorial expansion was basically done because the Western Front was closed, imperialism was more exciting
Imperialists:
- Looked to the gold in Alaska, and saw that if there’s gold there, there are probably valuable materials in other places too
- Took up Social Darwinism
- Strong eat the weak and the fittest survive
- Racial Motivations for expansion
- Josiah Strong,Our country, it’s Future and it’s purchase
- White anglo saxons were the pinnacle of human existence and deserved to conquer
- Christian duty to teach the world
- Alfred Thayer Mahan
- Robust navy is the key to imperialism
- Congress approved the construction of new ships
- To conquer with a navy, you need ports for the navy to land at and refuel
- The race began for ports
Anti-Imperialist
- Self determination of nations
- America taking over less powerful countries means that they’re taking away the power of self determination
- George Washington had warned against foreign entanglement
- Drawn into war and economic disputes
- Racial Arguments
- Did the constitution follow the flag
- Would the conquered people become american citizens with american rights and privileges
- Anti imperialists argued that the Constitution should follow the flag
- This was a ruse to hide the real argument, that taking over a country of brown people shouldn’t mean they get to be citizens
Unit 7, Topic 3: The Spanish-American War
- Really wanted Cuba
- 1895 Cubans wanted their independence under Spain, but they were crushed
- Yellow Journalism:
- Joseph Pulitzer
- Willian Randolph Hertz
- Published stories that exaggerated the atrocities against the Cubans by the Spanish
- This made people think that people must intervene in Cuba because it was the humanitarian thing to do
- American public was riled up, the US established a naval presence on the island
- The USS Maine exploded in Havana Harbor, killed Americans
- Yellow Journalists claimed the explosion was started by the spanish
- Explosion was found to be accidental, but it didn’t matter to the journalists
- McKinley Adams issued an ultimatum
- Back off or go to war
- Spain agreed, and they started a war
- America won the Spanish American war quickly, launching America into the imperial war
Cuba
- Gained independence as a result of the war
- Platt Amendment
- American politicians insisted this amendment be entered in the Cuban Constitution
- This meant that the American government could intervene any time there was an economical advantage in Cuba for them
- America could manage their foreign debts and policies
Annexation of Philippines:
- Got the Philippines
- Roosevelt sent the new navy into the Philippines before the Spanish American even ended
- In the treaty that ended the Spanish-American, the philippines was ceded to the US
- Philippines thought the Americans were trying to help them, but instead were just being passed to the US
- Emilio Aguinaldo had his people rise up against the US, but they couldn’t throw them off
- The Philippines are really far away, so they wanted to have Hawaii in between the two
- 1893 we annexed hawaii
Economics:
- Open Door Policy with China
- China had been divided into European spheres of influence
- John Hays saw the economic opportunity in China going away, so he sent the Open Door note to Europe, telling them to have an open door policy with trade in china
- They didn’t reject it, so America kept their trading rights in the Asian market
Unit 7, Topic 4: The Progressive Era
- Progressive Causes
- Growing power of big business
- Uncertainties in the economy
- Increasingly violent conflict between labor and employers
- Jim Crow segregation
- Alcohol
- Women
- Political machine power
- The people in the Progressive movement were diverse
- Didn’t always agree on which causes were most important
- All agreed that society was deteriorating and government intervention was needed
- If society was going to be corrected, the government had to be heavily involved
Progressive Journalists:
- Roosevelt called them Muckrakers
- They embraced the insult, and raked the muck of American corruption
- Upton Sinclair, The Jungle
- Upturns the meat factory conditions in the US
- Ida Tarbell, exposed Rockefeller
- Jacob Riis
- How the other half lives
- Poor and working class living conditions
Expansion of Democracy:
- Wanted voting power back in the hands of the people
- Against tammany hall
- Bosses forced their workers to vote for who they wanted
- Secret Ballot
- Used to cut the voting power out of the hands of political machines
- Direct Election of Senators
- Senators are elected by state legislatures
- This was problematic in the Gilded Age because senators in office were being paid off by big business owners
- Got the 17th Amendment passed, which transferred electing senators from the state legislatures to the people
- 18th Amendment
- Women fought for prohibition
- Anti-Saloon and American Temperance Society
- Prevented the manufacturer and make of alcohol
- 19th Amendment 1920
- Officially recognized women’s right to vote
- One a politician was elected, they could choose to ignore the will of the people
- Initiative
- Voters could require legislators to consider a bill they chose to ignore
- Referendum
- Voters themselves could vote on the adoption of proposed laws
- Recall
- Way to remove corrupt politicians before their term was complete
- Initiative
- During the Gilded Age, people had no political power because it was all taken by big corporations
- In the Progressive Era, the people were able to take their political power back
Government Efficiency:
- Frederick Taylor
- Scientific Management
- Timed the workings of the factory, and find ways to save time and productivity
- This worked well and progressives tried to apply this to the government
- Black progressives tried to achieve social justice too
- Segregation was the law of the land as long as it was separate but equal
- Niagara Movement
- W.E.B. Dubois
- Met with other black people to plan protests
- NAACP - National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
- Expand education for black people
- End segregation
- Mostly did this on their own
Progressivism Nationally:
- Elected a string of progressive presidents
- Teddy Roosevelt
- McKinley was assassinated rip
- Square Deal
- Presidents had consistently sided with big business
- Roosevelt did not take either side during the Anthracite Coal Strike, instead working for a square deal for both
- Took up the role of trust buster
- Sherman Antitrust act, breaking up big businesses
- Distinguished between good trusts and bad trusts, separating businesses that became large honestly, and businesses that hadn’t
- Consumer Protection
- Got Congress to pass two laws
- Pure Food and Drug Act
- Meat Inspection Act
- Conservation
- America’s forests were disappearing
- Used the Forest Reserve Act 1891 to reserve acres of unspoiled land
Unit 7, Topic 5: World War I, Military and Diplomacy
- War erupted in Europe in July of 1914
- Triple Entente - Allies
- Britain
- Russia
- France
- Triple Alliance - Central Powers
- Germany
- Austria-Hungary
- Italy
- US held to neutrality
Threats to Neutrality
- Lusitania sinking
- Germans kept sinking ships that entered the war zone
- Passenger ship named Lusitania entered the war zone and the Germans sunk it, killed most of the civilians
- Woodrow Wilson was mad about this
- The Germans kept sinking ships, and US threatened to break neutrality
- Germany knew they were screwed if the US interfered so they backed off
- German Unrestricted German Submarine Warfare
- Started sinking the ships in the warzone again
- Woodrow still stayed neutral
- Interception of the Zimmerman Telegram
- Germany sent a note to Mexico, asking them to start a war with the US, and promised Mexico to help it regain the land it lost in the Mexican American War
- The US intercept this telegram
- Wilson asks for war
- April 2 , 1917, the war is official
- American Expeditionary Forces
- Plugged weakness in french and british
- Took command over a portion of the front
- US entry tipped the balance of the war in favor of the allies
- Ended in 1918 with the signing of the Treaty of Versailles
- Wilson was invested in the signing of this treaty because he wanted to make the world safe for democracy
- Britain and France wanted Germany to suffer
- Wilson laid out the Fourteen Points
- Freedom of the seas
- Self determination of nations
- League of Nations
- Wilson got the Spanish flu and was forced to be absent
- His plan got pushed away
- Britain and France punished Germany in the treaty
- League of Nations was created however
- Congress did not want to ratify the Treaty
- They thought that the US would be dragged into war without Congressional Approval
Unit 7, Topic 6: World War I, On the Homefront
- WWI was a total war
- All economic and social resources were used to win
- Wilson established war time agencies that worked with Progressivism, following Taylorism and Scientific Management
- War industries Board
- Kept factories pumping out uniforms and war related material
- Food Administration
- Kept food for troops and at home
- People migrated to find work from rural to industrial cities
- Not everyone liked the war and the US using its assets
- Federal government tried to restrict civil liberties that were in opposition to the war effort
- Espionage Act/Sedition Act
- Made it a crime to oppose the war, resist the draft, and talk bad about the war
- Schenck wrote pamphlets telling people to resist the draft
- Court upheld the idea the freedom of speech is not absolute
- His speech was a clear and present danger so he had to be silenced
- Espionage Act/Sedition Act
- Spanish Flu
- Government forbid publications about how bad the spanish flu actually was, as well as the death count, in fear of it damaging morale effort
- Red Scare
- Post war, there was an anti-commusit sentiment in 1919
- Russian Revolution was successful
- More xenophobia
- Further immigration restriction
- Palmer Raids
- Mitchell Palmer made J. Edgar Hoover gather information on suspected radicals
- Mass arrest of tons of people, 6,000
Immigration:
- Immigration reached its peak just before WWI
- Rise in Nativism
- Mad that the people weren’t Protestant
- Led to Emergency Quota Act 1921
- National Origins Act 1924
- Both of these set the quota for more immigrants very low
Migration:
- Great Migration
- Southern Black population moved to the industrial centers of the north
- The main reason they moved was to escape the oppressive atmosphere of southern society
- Jim Crow laws were bad
- Often disenfranchised because of poll tax and literacy tests
- Moved for the sake of finding jobs
- Industrial cities experienced a boom
- There was a shortage of workers because of the immigration quotas
- Just because black people moved doesn't mean that they didn’t experience discrimination, it just wasn’t as rooted in the legal
- Race riots in 1919
- 1921, Tulsa Race Riots/Tulsa Massacre
- White woman claimed a black person assaulted her
- They went to lynch the man
- Mass destruction of property and black neighborhoods leaving people homeless and dead
Unit 7, Topic 7: Innovations in Communication and Technology
- Henry Ford
- Made automobiles
- Ford contributed to manufacturing technology
- Assembly line
- Large conveyor belt that transported partially built car from worker to workers
- So efficient that the price of the cars went down super low
- Replaced skilled workers
- Aligned with Scientific Management
- Knew that there was a huge demand for automobiles, and this shift was intense
Society:
- More people began to settle outside urban centers in suburbs
- Cities like LA and Houston were made with roads now as a dominant urban feature
Economy:
- Mass produced consumer goods
- Toasters, radios, health and beauty
- Willing customers across the country
- Advertising became more popular as well
- Freud’s teaching taught people how to advertise well
- Put the item into the real life situations and questioned the identities of the people without their product
- Popular Culture
- Radios were found in almost every household
- Broadcasters had news programs and entertainment shows
- Cinema
- Spreading mass culture
- ¾ of the Americans were attending movies
- The Jazz Singer ended the silent film era
- New media spread meant homogenized culture
- Emphasized regional and cultural differences in race and ethnicity
- Few depicted the black experience
- Rural people saw only urban life, showing that their way of life was distinct
- Radios were found in almost every household
Unit 7, Topic 8: Cultural and Political Controversies
- More than half of Americans lived in cities
Women:
- Most middle class women were expected to work in the home and have babies
- However, women found more jobs in teaching and nursing
- Could also work in factories, but were paid very little
- Women tried to throw off convention by cutting their hair short, smoking, and drinking
- They were called Flappers, and were seen as a symbol of women’s liberation
International Immigrants:
- Post world war one, there was another huge influx of immigrants
- Nativists got mad yet again
- Workers feared they would lose their jobs to immigrants
- Worried about the mudding of the white race
- Emergency Quota Act
- Immigration was reduced to 3% of the population
- National Origins Act
- Restricted Immigration even further
Internal Migration:
- Great Migration
- A second part of the exodusters movement essentially
- Black southerners moved from the south to the North to get away from harsh segregation and Jim Crow laws
- Harlem Renaissance
- Revival of the arts and culture of the black people
- Birth of Jazz
- Louis Armstrong
- Writers put words to the black experience
- The Lost Generation
- Hemmingway and Fitzgerald
Division Between Protestants
- Urban Protestants considered themselves Modernists:
- Faith embraced the changing culture in gender roles and Darwin's evolutionary theory
- Ruralists -Fundamentalists
- Couldn’t abide the changes of society and that the Bible should be taken literally and seriously
- Scopes Monkey Trial 1925
- In Tennessee, it was illegal to teach Darwin’s theory of evolution (Butler Act)
- John Scopes thought the rule was stupid and began to teach Darwin’s theory
- He was arrested
- Clarence Darrow defended Scopes
- Modernism had triumphed over fundamentalism
Unit 7, Topic 9-10: The Great Depression and the New Deal
- Era of American Prosperity in the 1920’s
- The stock market crashed on Black Tuesday, August 29, 1929
- Crash had been a process, but it was the worst this day
Causes:
- Farmers had been overproducing crops, and were in severe debt
- High tariffs + overproduction = debt
- Tariffs were really high
- Herbert Hoover signed the Hawley-Smoot Tariff into law
- This forced Americans to sell their excess product on the global market
- Stock market was also artificially inflated due to risky investment behavior
- Buying on Margin
- It was assumed that the stock market prices were going to continue to rise, so people took out loans to buy stocks
- If the stocks don’t increase, your stocks lose value and you go into debt
- This is understood as the beginning of the Great Depression
Great Depression
- Property and homelessness was insane
- People who lost their homes took refuge in Shantytowns, which they called Hoovervilles
- They called it this because they criticized Hoover’s Laissez-Faire economic policies
- 1932 Presidential election
- Franklin D. Roosevelt won
- He was the opposite of Hoover
- He campaigned heavy government intervention
- Expanded the size and scope of the government
- Transformed the US into a limited welfare state
- The government would take responsibility of the social and economic welfare of the citizen
- New Deal
- Legislation was passed under this deal to help fix the economy
- Relief for the unemployed
- Public works administration which employed americans to do federal infrastructure work
- Tennessee valley authority which did work in power plants
- Civilian Conservation Corps hired young men to work on soil conservation
- Recovery for businesses
- National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933
- Sought to resolve the business competition that was lowering the wages
- Made codes that created minimum wages and shorter working hours
- National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933
- Reform of economic institutions
- Glass-Steagall Act of 1933
- Increased regulation in banks, and regulated the way that banks could spend people’s money
- Gave way to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
- Guaranteed bank deposits with federal money
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- Regulated the stock market and avoid buying on margin and insider trading
- Glass-Steagall Act of 1933
- Social Security Act 1935
- Safety net of income for workers over the age of 65
- Government withheld part of wages that gave back to retired
- Transformed the US into a limited welfare state and expanded the aims of modern american liberalism
- Dissent with the New Deal
- Criticized by liberals and conservatives
- Liberals thought it did too much for big businesses and wasn’t liberal enough
- Conservatives thought it was an extreme federal overreach
- Some took the New Deal to the Supreme Court and narrowed down the constitutional and unconstitutional
- Roosevelt didn’t like this so he proposed the Court Packing Scheme
- This would allow the president to appoint new Supreme Court justices for every justice that was above the age of 70 and a half
- He appointed 6 additional judges into the supreme court
- Both congress parties opposed this change and thought he was being dictatorial
- The bill did not pass
- New Deal left a legacy of reform and regulatory agency, which also realigning all groups of people into the democratic party
- Those groups believed that Roosevelt and New Deal sought to help them
Unit 7, Topic 11: Interwar Foreign Policy (Between WWI and WWII)
- After WWI, american policy went into Isolationism
- We didn’t want to be involved with Europe
- Elected Warren G. Harding, who said that America doesn’t need to be out and fighting but just relax and be normal
- Increase of Tariffs
- Fordney McCumber Act
- Smoot Hawley Tariff
- Both of these raised tariffs and made foreign goods more expensive
- This does mean that foreign trade decreases
- Kellogg-Briand Pact
- Tried to make war illegal
- Was signed outside the league of nations and couldn't be enforced
- Isolationism became harder to maintain
- Mussolini was the face of the fascist party
- Hitler took control of the Nazi party
- Hirohito became aggressive in Japan too
- Watched as Germany began to take over basically all of Europe
- All these aggressive actions came to a head when Hitler invaded Poland and WWII began
- Isolationists argued that many people lost their lives during WWI, and the world was still not safe for democracy like Wilson had said
- Nye Committee
- Unflattering evidence that certain corporations in America had made bank on the WWI, suggesting that the need for profit was what got us into war
- Interventionists thought it was foolish to stay out of the European development
- Argue the Atlantic wasn’t arguable anymore to stay away when submarines and planes could help you cross
- Were scared Hitler would bring the war to America
Franklin D. Roosevelt
- Sympathetic to Britain’s cause, and knew that America should help
- Didn’t have support from the people
- Began to give aid to the Allies, mainly Britain
- Cash and Carry Program
- Congress passed a looser neutrality act that allowed people to buy resources from America
- Destroyers for Bases
- Roosevelt and PM Churchill
- American destroyers for land rights on British possessions
- Lend-Lease Act
- Arms from the US on credit
- Cash and Carry Program
Pearl Harbor
- Isolationism was destroyed on December 7th 1991
- Roosevelt asked for a war declaration that evening
- Hitler declared war on America
Unit 7, Topic 12: WWII Mobilization
- WWII was a total war too
- Federal spending increased 1000%
- America was not in a great place financially because of the Great Depression
- However, this increased global spending increased our GDP and pulled us out of the Great Depression
- Private industries were used for war resources
- Office of War Mobilization
- War Production Board
- Planes, tanks, and war munitions
- Went from unemployment to labor shortage
- Women began to work in the industries
- Rosie the Riveter
- Strong and necessary
- Women were generally discourage from industrial work, but these ads really contributed to their wants to help
- Black americans joined the war effort as well, and this allowed them to put race issues on the national agenda
- Double V Campaign
- Working for the victory in the war and the victory at home
- While the black and white soldiers were still segregated, some like the Tuskegee Airmen had huge success
- Since many people were leaving to fight in the war, mainly farmers, Mexicans were allowed to come into the US and tend to the land, without having to do normal immigration
- Selective Service and Training Act 1940
- One year before the US entered the war
- First peacetime military draft in US history
- Japanese Relocation
- Lots of Japanese on the west coast, who were American citizens
- They were associated with the Japanese and Pearl Harbor
- How did the government know the Japanese weren’t spies
- Roosevelt issued Executive Order 9066
- This ordered the relocation of thousands of Japanese to internment camps
- This applied to Japanese immigrants and their children
- Confiscated their personal property
- Korematsu V The US 1944
- Forced removal was unconstitutional violation of the fifth
- Court ruled that it was constitutional since it was a marshall necessity
Unit 7, Topic 13: WWII Military Strategy
- Allies won WWII
- US entering the war was a decisive tip towards the allies
- Nod to the expansion of democracy
- Allied soldiers found concentration camps
- Holocaust
- Served to justify that the involvement in the war was just and right
- Pacific Theater was where most the effort of the US was put
- Japan was winning this
- Battle of the Coral Sea
- Battle of Midway
- Both of these battles allowed the US to push back the Japanese from key strategic territories
- Island-Hopping
- Passed the fortified Japanese islands and conquered the less strategic instead, allowing them to cut off Japanese supply lines
- This was successful, and the fortified holdings fell apart
- Atomic Bombs
- Roosevelt died
- Truman took his place
- Truman learned that the US had already tested bombs under the Manhattan Project (yippee Oppenheimer)
- Truman used this against Japan to force surrender
- August 6, 1945 first bomb, August 9 Nagasaki
- V-J Day Japan surrendered
- European Theater
- Russians urged US and Britain to open a second western front in germany
- Tehran Conference in 1943
- D-Day Invasion
- June 6, 1944
- Largest amphibious invasion in the history
- After heavy casualties, France was liberated
- Battle of the Bulge
- 1944-1945
- Strategy to drive a wedge between the allies failed
- Allies got closer to Berlin and on July 7th, Germany surrendered
- This was known as V-E Day
Unit 7, Topic 14: Post War Diplomacy
Consequences
- Americans had everything intact minus Pearl Harbor
- Our whole nation was intact
- Critical Role in winning
- We tipped the scale to the allies when we joined
- We had been aiding the British through Roosevelt’s aid programs
- Nuclear Bombs
- Yalta Conference
- Decided on how Germany would be split into four parts
- Eastern Europeans could choose their leaders through elections
- Instead, post war, Stalin claimed those nations for the Soviet Union
- Buffer zone between Russia and Germany
- This made Britain and US mad
- Marshall Plan
- Ton of money to European nations to help them rebuild
- Worked really well
- Stopped the spread of Communism
- Creation of the UN
- League of nations couldn’t enforce it’s treaty and America wasn’t even in it
- UN was made and had the power to keep the peace
- Has a group of peacekeeping soldiers that stabilize conflict
UNIT 8 1945-1980
Unit 8, Topic 2: The Cold War
- Tension between the US and soviets
- Cold War - Battle of ideologies more than actual warfare
Causes:
- Tension since the russian revolution 1917
- Americans did not like communism
- Americans wanted democracy
- Issue was both ideologies are expansionist, meaning they both need support from people and absolute rule
- Mistrust started before WWII ended
- Allies agreed central and western countries would hold open elections
- Stalin decided to leave troops on the border of Russia and Germany to create a buffer zone, which violated the agreement
- Americans believed this was a violation of the agreement towards the right of democratic government
Berlin:
- Germany would be divided into four parts for each of the four allies
- Berlin would also be divided
- Eastern section became another communist state
- Communists wanted Germany weak so they could extract reparations
- Westerns wanted to strengthen German economy so they would be open to democracy
- Iron Curtain
- Western powers kept west berlin alive, and soviets started Berlin Blockade
- Berlin blockade stopped westerns from accessing Soviet Berlin through blocking canals and trade routes
- Goal was to absorb West Berlin into the soviet union
- Berlin Blockade resulted in the Berlin Airlift
- US and allies flew 200,000 flights to carry supplies into West Berlin stopping the takeover
US Responses:
- Containment
- Truman Doctrine - Contained communism by lending support to any country facing communist threats
- Result of soviet pressure of turkey and greece
- 400 million in aid and support
- Marshall Plan (george marshall)
- 13 billion in aid for Europeans to rebuild
- Healthy economy means democracy over communism
- Stalin did not like that these plans were working
- NATO was also made, offering alliance to any countries being threatened by communists
- Warsaw Pact was made by soviets to counteract this, basically same thing for the bad guys
Nuclear Proliferation
- Arms race between US and soviets
- Truman ordered development of hydrogen bomb
- Both sides stockpiled increased amounts of nuclear bombs, but knew they would never be able to use them because of mutually assured destruction
Proxy Wars:
- Korean War
- Korea was a Japanese colony, but after the war it was divided along the 38th parallel
- US was in control of the South and Soviets were in control of the North
- 1950 North Koreans invaded the south and the UN sent lots of troops and resources to support the south
- The south was able to push back the north up to china’s border
- China sent them back to the 38th parallel
- Korea ended at the exact same spot they started in
- Illustrates the proxy war between the US and soviet
- Direct result of the containment policy.
Unit 8, Topic 3: The Red Scare
- Second red scare after WWII
- Red refers to soviet communism
- US tried to contain, but there was a big push to take it out from US as well
Labor Unions
- Taft Hartley Act 1947
- Response to waves of strikes in labor unions making it more difficult to strike
- Labor union leaders were forced to pledge that they weren’t communist
Federal Government
- Federal Employee and Security Program passed by Truman
- Federal employees had to swear federal employees weren’t communist, and allowed for provisions for federal investigations into federal workers
- UnAmerican Activities Committee
- Searched for communist influence in society, especially hollywood
- 1947, Hollywood Ten were singled out alleged for communism
- Joseph McCarthy
- Claimed to have the names of 205 communists in the state department
- People freaked the fuck out
- Later admitted it was only 57 but he made shit sm worse
- Phenomenon was named McCarthyism
- Senate held meetings to give McCarthy a chance to prove his claims
Rosenberg Case
- Soviets tested their first atomic bomb, and US people thought the ideas were given to Soviets from US through spies
- People though soviet spies were all throughout the country
- Rosenberg couple was thought to be spies for the soviets
- They were both killed rip the dude was actually a Soviet spy tho
Unit 8, Topic 4: Economy Post 1945
- In the years after WWII, the economy was booming
Causes:
- Increased productivity, and spending on infrastructure, notably the interstate highway system
- Servicemen's Readjustment Act 1944
- Gave WWII veterans the chance to go back to college and get an education
- Was funded by the government
- Allowed to take out low interest loans for house
Baby Boom
- People were freaky yay new babies
Constructions
- Suburbs, contributed to by the growing popularity of automobiles
- People wanted to create more roadways, and were more interested in using their vehicles to drive and live outside of the city.
- White middle class thing
- Minorities and impoverished were left in the cities because all the white people left in their whips
Levittown
- Suburban mass produced homes
- Provided a cheap solution to the lack of housing
- Some people said suburbs were monotonous
- Interstate HIghways 1956
- Gave people the ability to travel quickly from cities to suburbs
- Mass migration to the sunbelt states, where weather was much nicer
- Veterans and families moved there
- This movement caused the shift in economic priority from the defense spending to the sunbelt states
- This also caused a shift in political sway, moving it to the south instead
Unit 8, Topic 5: Culture
- Mass culture, how it was maintained, and how it was challenged
Mass Culture:
- Widespread homogenous ideas and behaviors
Maintained:
- Pressure to conform culturally
- People wanted to be “predictable”, so that they wouldn’t be suspected of communism or anything out of the ordinary
- This was a direct result of McCarthyism
- Technology:
- 90% of people had a TV by the end of the 50’s, and allowed for a platform to consume mass culture
- Suburban sitcoms were the most popular, and showed off the ideal american nuclear family
- Advertising
- Prosperity of the time allowed people to have a little extra income to spend
- This meant that ads became more aggressive, and catered to the emotional needs of people, not just survival
- People ended up wanting more things than they could afford, which introduced the credit card
- People could buy more than they could afford and pay it off over time
- Rock and Roll
- Another widespread form of spreading mass culture, mainly to the youth of US
- Took on a white face, despite black roots
- Older people did not like rock
Challenging Mass Cultures:
- Beatniks - Group of poets who used their poetry to rebel against the conformity of the age
- Jack Kerouac
- JD Salinger - Catcher in the Rye
- Main character had a distaste for conformity
- Called for spontaneity and truthful living.
Unit 8, Topic 6: The Civil Rights Movement
- Promises were made to black people after the reconstruction era, with laws allowing them protection and voting rights
- Jim crow laws created suppression tactics
- Poll taxes
- Money needed to vote
- Literacy Tests
- Target black americans who weren’t able to secure a proper education and stop them from voting
- Racial segregation as the law of the land
- Jim Crow laws protected this
- Poll taxes
- Truman supported civil rights and issued an order which banned segregation in armed forces
- Enforced his new law two years after end of Korean war 1950
- Was afraid he would lose support of south by supporting civil rights too strongly
- Committee of Civil Rights 1946
- Explained the real civil rights situation in america
- Recommend Truman on how to address these issues
- Wanted to abolish poll taxes and protect from lynching
- Truman urged congress to make these suggestions into law
- 24th Amendment was passed in 1962 abolishing poll tax
- Brown V. Board of Education
- Racial segregation of school
- Overturned plessy unanimously
- Argued that it violated the 14th amendment
- Southerners opposed this measure, and stalled the desegregation because of the vague language in the decision
- Southern Manifesto
- Argued that the government abused their power in the brown decision
- Southern states shut schools down instead of integrating
- Little Rock Nine
- Sent troops to protect nine black students entered a white school
- School integration and other efforts only really made a small gain
Unit 8, Topic 7: America As A World Power
- After WWII there was a massive decolonization movement
- Most of the major empires in africa, asia, and latin america crumbled
- This meant the US and Soviet union had lots of opportunity to expand
- The beginnings of these new nations were shaky, and therefore needed aid, becoming perfect for the US or soviet
US Intervention in Latin America
- Guatemala
- Leader turned out to be too socialist for americans
- Nationalized land under cultivation
- CIA trained a group of people to overthrow the leader and become a military dictatorship
- Fidel Castro overthrew the Cuban government, and frustrated America because Castro was a communist
- Communist threat in our own territory
- Eisenhower allowed US troops to train Cuban exiles to overthrow Castro
- This overthrow was called the Bay of Pigs Invasion, but it was a massive failure
- Under Kennedy’s presidency
- Led to further alienation of US and Cuba, and stronger communist ties in Cuba
- This led to the Cuban Missile Crisis
- US found soviet style nuclear weapons being stockpiled in Cuba
- Cuba was much closer to US, so delivering a nuclear bomb would be very feasible
- US was also stockpiling nuclear weapons in Turkey
Middle East:
- Iran
- 1953 CIA implemented a plot to overthrow the prime minister, in favor of the Shah Pahlavi
- Wanted to this because the prime minister had intended to nationalize the oil industry
- US was dependent on the oil because of automobiles
- Shah was more easily swayed
Asia:
- Vietnam - Indo-Chine
- Finally decolonized from French and Chinese
- Divided along the 17th parallel
- North was communist under Ho Chi Minh
- Similar to Korean conflict
- Under Eisenhower, about 1 billion dollars was extended in economic aid to stabilize south vietnam
- The reason he did this was because of the domino theory, saying that if one country fell, it would start the domino effect on communism
- Military-Industrial Complex
- Eisenhower was warning americans about the relationship between the military production and the industrial capacity
 Knowt
Knowt