B1
CELLZ
All living things are made of cells there are:
Eukaryotic cells- A complex cell with a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes- Usually part of a multicellular organism
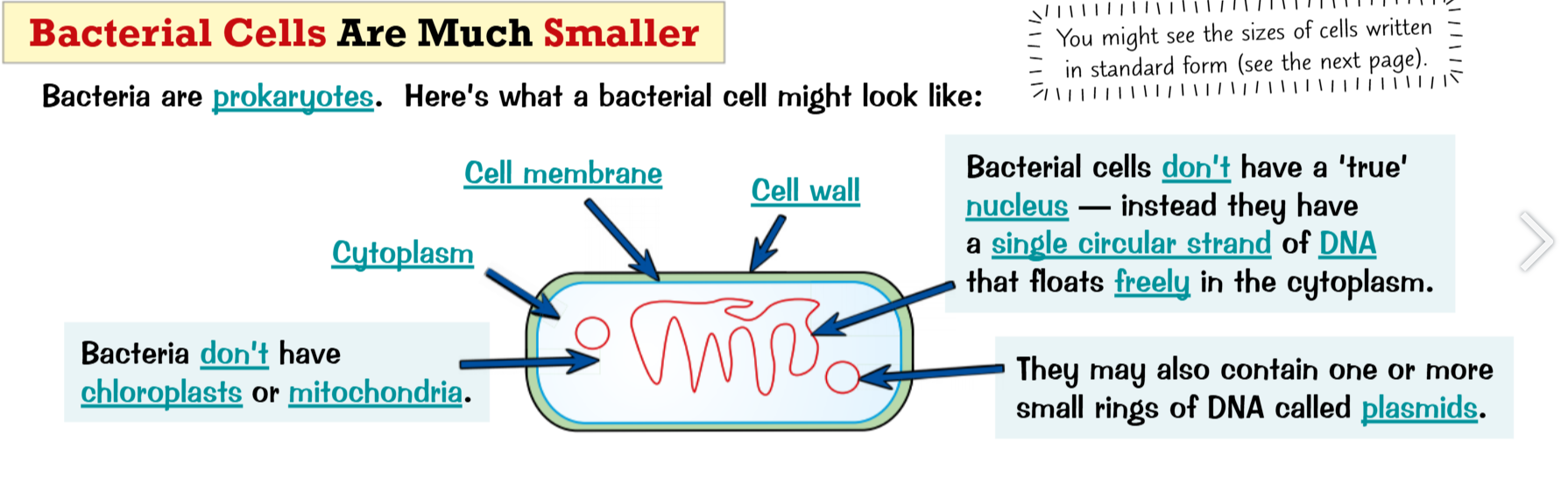
Prokaryotic cells- A simple cell without a nucleus- usually a single celled organism
Plant cells have a:
Nucleus- Contains genetic materials that controls the cell
Cytoplasm- Gel-like substance where most the chemical reactions happen
Mitochondria- The site of aerobic respiration making ATP
Cell membrane- Holds the cell together, controls what goes in and out
Ribosomes- The site of protein synthesis
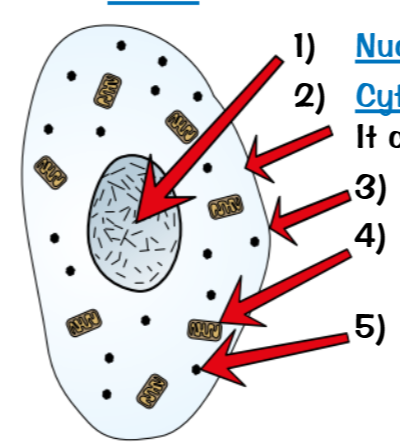
Cell wall - Supports the cell and strengthens it
Permanent vacuole -Contains cell sap, a weak solution of sugars and salts
Chloroplasts- Contains chlorophyll, that absorbs light for photosynthesis
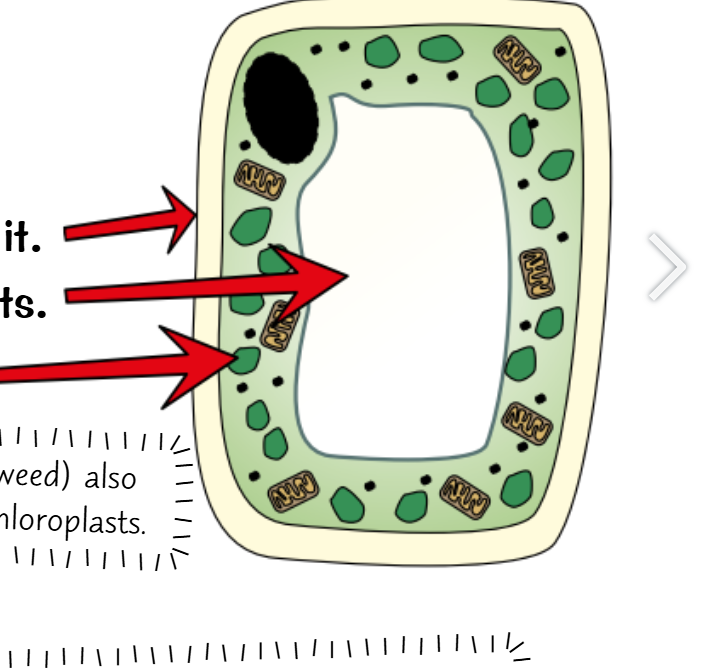
Plasmids- Small rings of DNA
Strand of DNA- Contains genetic information
Microscopy
Resolution- The quality of the image and ability to distinguish 2 points
Microscope- An instrument that magnifies small objects so that they can be seen
Magnification- How zoomed in something is
Specimen- What you are trying to look at with a microscope
This is usually for particles and objects that can’t be seen with the naked eye, there are two types:
Light microscopes:
These use light and actual lenses to magnify the specimen
These let us see individual cells and large subcellular structures like nuclei
Electron microscopes:
These use electrons to form an image
These have a much higher magnification and resolution than electron microscopes
This gives us images of:
The internal structure of chloroplasts and mitochondria
Plasmids
Ribosomes
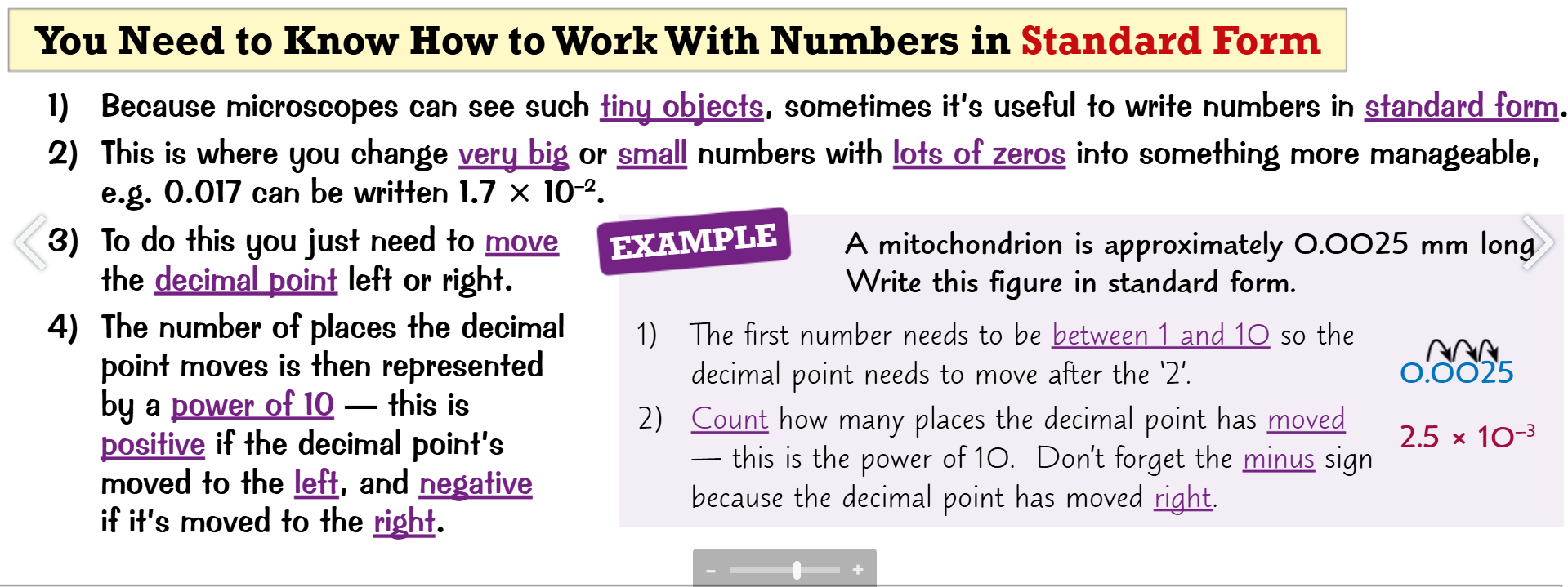
How to prepare a microscope:
Add a drop of water to the middle of a clean slide
Prepare your specimen e.g. the epidermal tissue of onions
Add a drop of iodine solution to stain the specimen
Carefully place a cover slip, in such a way that air bubbles don’t form
As they obstruct your view of the specimen
Clip the slide prepared onto the stage
Select the lowest power objective lens
Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the stage just
look down the eye piece and adjust the stage until it’s roughly in focus
adjust the fine adjustment knob until you get a clear image
If needed, adjust to a higher power objective lens
When drawing your findings draw them clearly, plainly with labels like So’s Dad:
Stem Cells
These are undifferentiated cells that can divide and differentiate and turn into a selection of many different types of cells.
Therapeutic cloning is a type of cloning that gives embryonic stem cells the exact same DNA as the patient, reducing the changes of an immune reaction
There are 3 main types:
In adults they mainly just exist in the bone marrow, and can only turn into certain types of cells e.g. blood cell
Embryonic stem cells have the ability to truly turn into any type of cell of choice
And meristems are plant stem cells which are found at roots and shoots and can turn into any type of plant cell
Embryonic stem cells can be used to replace faulty cells in diseases such as:
Nerve cells with paralysis
Insulin producing cells with diabetes
Meristems in plant cloning: can be used to clone and protect endangered or rare species of plants
Risks and issues:
There are issues of ethnicity of using an embryo which is the potential for life
However others think the lives it could save come first
If the embryonic stem cells get infected with a virus then they could make patients sicker
Mitosis
But firstly chromosomes:
Chromosomes Are the 23 pairs of Coiled up lengths of DNA in the nucleus of the cell From an organisms Mother and farther, That controls the organisms Characteristics e.g. Hair colour, height etc, through their many genes
Body cells divide in a process called the cell cycle as part of processes of growth and replacement:
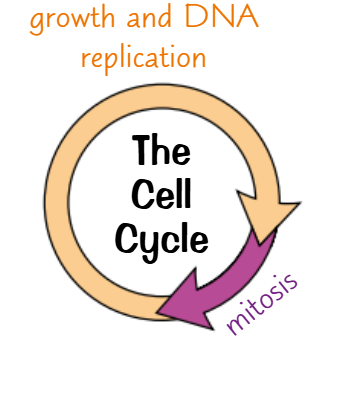
DNA replication and growth:
This is when the cell increases the amount of all subcellular structures
An the DNA duplicates and Chromosome forms the following X’s:

Mitosis:
The chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell
And cell fibres pull the to opposite sides of the cell
These become the
Cell adaptation
Differentiation- The process of a cell changing into a specialised cell that preforms a specific task
Specialised cell- A cell adapted to preform a specific function in the body
Stem Cell- An undifferentiated cell
In an animals the ability to differentiate into any type of cell is lost as they reach maturity, and differentiation is mainly used to repair damages skin or blood cells.
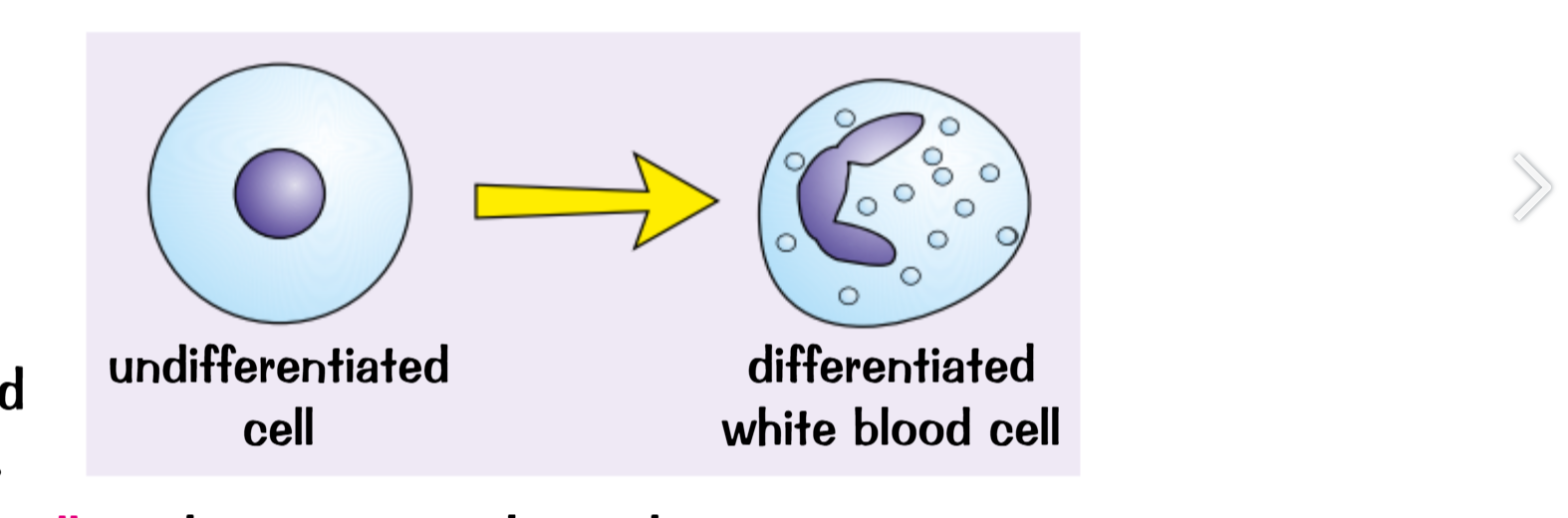
Specialised cells include
Sperm cells-
Their function is to get the male DNA to the female DNA
So they have a streamlined head and long tail to help it swim
They have lots of mitochondria to provide it with energy
They have enzymes to digest through the egg cell membrane
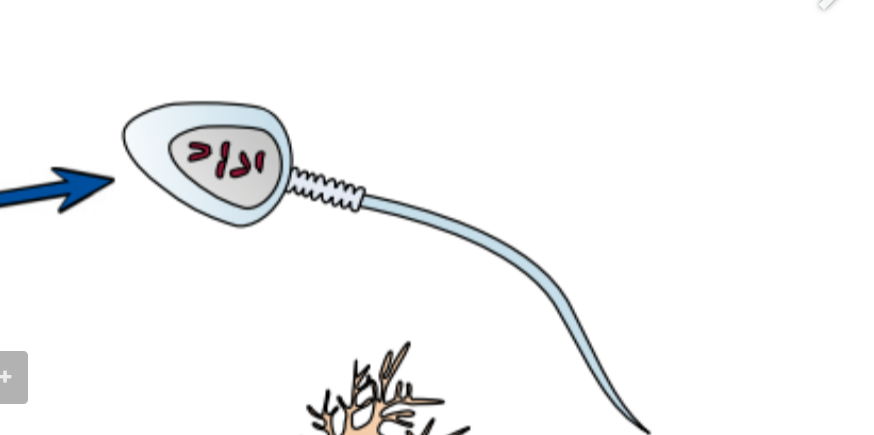
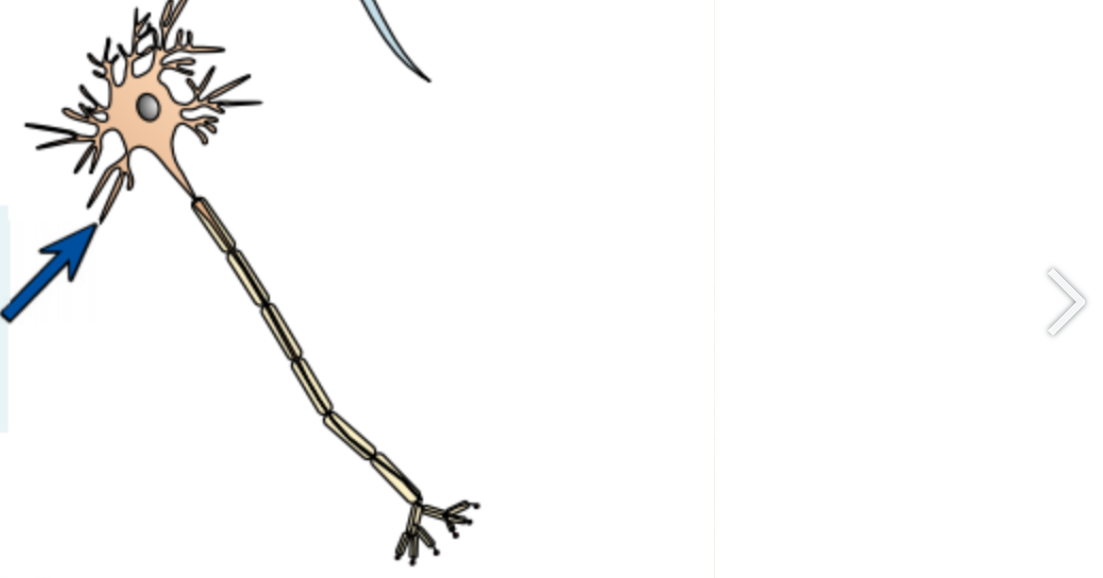
Nerve cells-
Their function is to carry electrical signals
So they are long to cover more distance
And have branched connections at their end to form more networks

Muscle cells-
Their function is to contract quickly
They are long so they have space to contract
They have lots of energy to provide energy for contraction
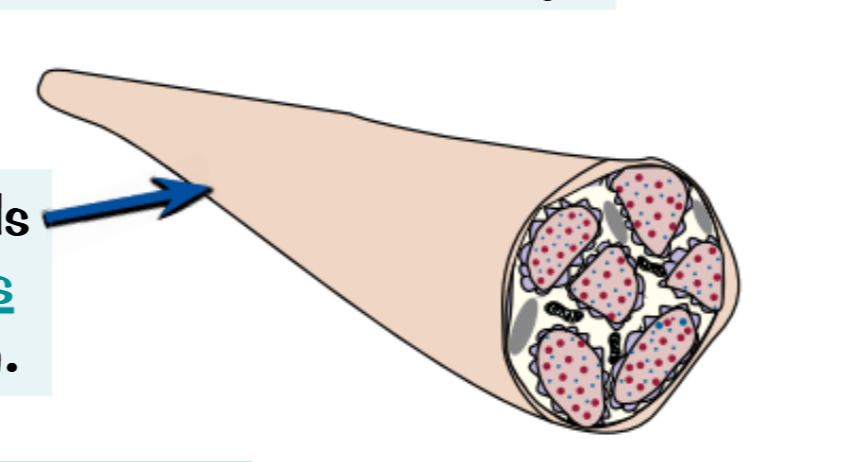
Root hair cells-
These have absorb water and mineral ions form plants
So have a large SA: V ratio for absorbing water and mineral ions
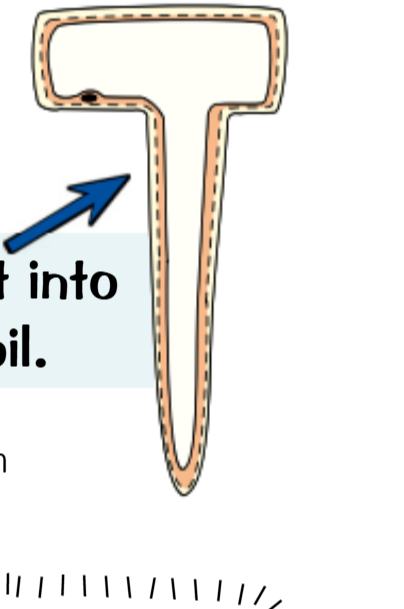
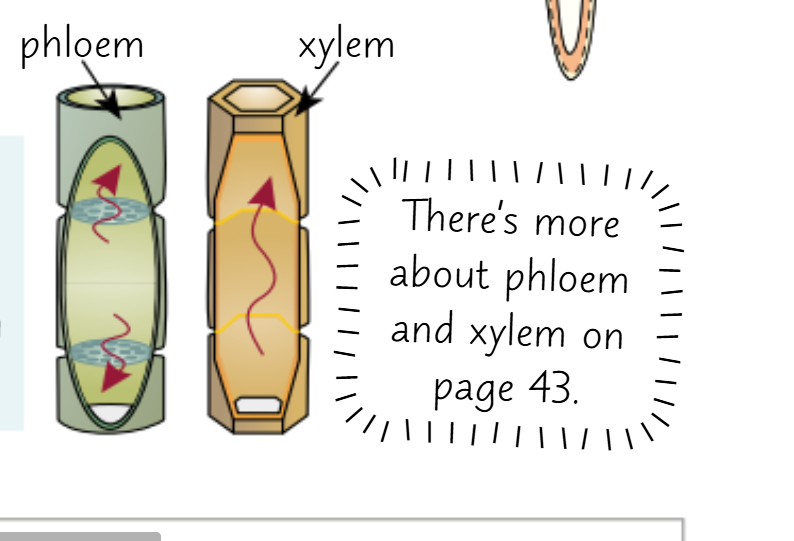
Phloem and xylem cells
These are Mostly hollowed out to allow the transport of substances
And have very few subcellular structures to avoid obstruction of transport
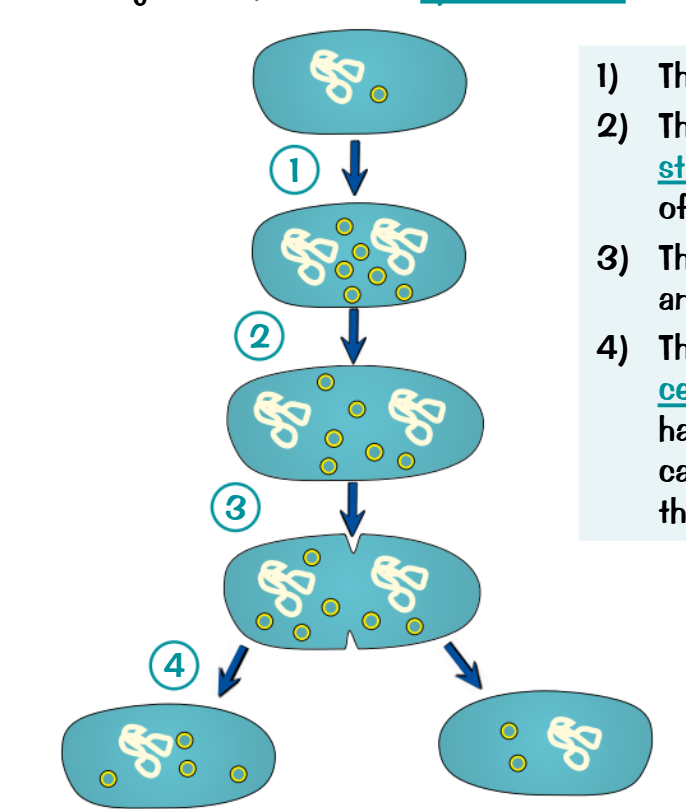
Binary fission
This is how prokaryotic cells reproduce
The circular DNA and plasmids replicate
The cells get bigger and the DNA strands move to opposite poles
The cytoplasm divides
And two daughter cells are produced with circular strands of DNA and a variable amount of plasmids
In a warm environment with lots of nutrients some bacteria e.g. E-coli can take 20 mins to replicate. In bad conditions however they stop dividing and die out

Bacteria need food (carbohydrates, proteins, minerals etc), water, oxygen, suitable temperature and a suitable Ph (preferably neutral) to grow
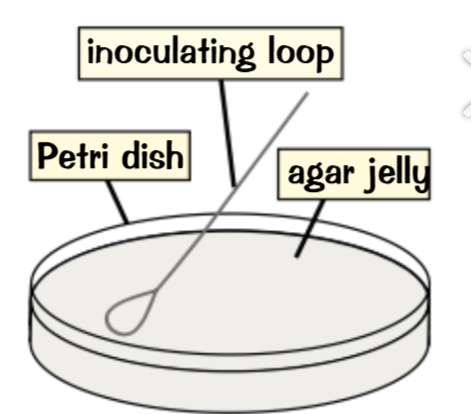
Culturing Microorganisms
Bacteria (and other things) can be cultured using a culturing medium - which can be a nutrient broth solution or agar jelly which allows bacteria to grow in a petri dish:
At school labs the temp has to be under 25oc to stop harmful pathogens from growing
But this rule is bypassed on an industrial scale to make the process faster.
You can prepare the thing above by:
Pouring hot agar jelly into a petri dish
Use a sterile inoculating loop to get an even spread of bacteria
Then let it multiply
After this you can place different disks that were soaked in a certain disinfectant into the bacteria culture. And leave them to kill non-resistant strains of bacteria to see which disinfectant is strongest by which one has the largest area of inhibition
You can find the area of inhibition zones to compare effectiveness and you can find the area of bacteria covered.
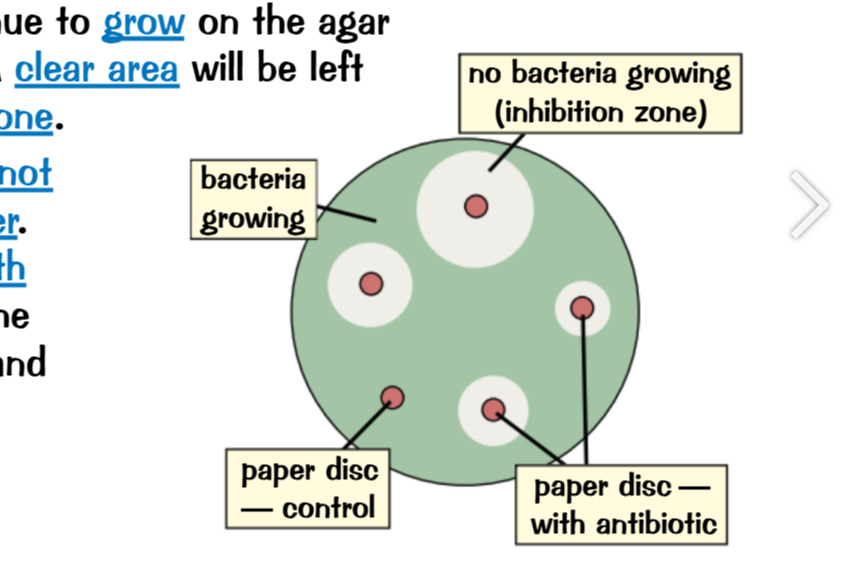
Area = πr2
Aseptic technique:
Heating the petri dish to sterilise it beforehand
Passing inoculating loop through hot fire
Tapping petri dish lightly to let air through
Storing petri dish upside down to prevent condensation falling on agar jelly
Diffusion , Osmosis and active transport
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration
- Takes place in liquids and gasses
Factors that increase rate of diffusion
High Temperatures- Particles have more energy to move faster, generating greater net movement
Steep concentration gradient- The greater the difference in particle concentration between areas
Diffusion distance- Less distance to travel means faster diffusion
Surface area- Higher SA == faster diffusion, allows passage of more molecules at a given time
Cell membranes use diffusion
Via transporting substances quickly to maintain a steep concentration gradient and allowing the substance they want in through the cell membrane, Whilst being designed with a high surface area: e.g.: Villi + Alveoli
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of low concentration
This movement is usually chaotic however has a net movement (overall movement) which shows an overall movement of water.
A strong sugar or salt solution will have the lower water concentration
Practical
Cut potatoes into identical cylinders
Measure their mass
Add them to a 0.2 mol/dm3 solution sugar
Take it out after x mins
Dry off excess water
Measure it’s mass
Repeat steps 2-6 with a different concentrations,
Record percentage change
Active transport
This is the movement of substances against the concentration gradient using energy form respiration
Sped up by a greater surface area and used in root hair cells:
They have a large surface area for absorbing mineral ions
However things need energy from respiration to use active transport
Active transport happens in the gut when there is more glucose in the gut than the blood but usually the concentration gradient favours the gut meaning that glucose naturally enters is via diffusion
Exchange
An exchange surface is a plane on which substances move across.
The larger the surface area to volume ratio is, the quicker exchange of substances happen
Exchange surfaces adaptations are:
Thin membranes-( Lowers exchange distance)
Large surface area- So lots of substance can diffuse at once
Good blood supply- To get things in and out the blood quickly
Ventilation- For space to diffuse in for gasses
Adapted organs are:
Leaves
Small intestines
Large intestines
Lungs
Root hair cells
Gills
Lungs~
Their job is to get oxygen in the blood and CO2 out
They do this with millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli with~
Good blood supply
Very thin lining
Large surface area (Roughly 75m2)
Moist lining- For dissolving gases
Small intestines
These have millions of tiny projections called villi which absorb digested food into the bloodstream
They have:
Very good blood supply
Thin single celled lining
Leaves:
Stomata
At the bottom as to not interfere with palisade mesophyll tissue
Controlled by guard cells
Air spaces in the leaf increase SA:V ratio
flattened shape increases SA:V ratio
Gills:
Water (containing oxygen) enters through gills
Oxygen diffuses from water into blood in the CO2
Gills covered in gill filaments covered un lamellae, Increases SA:V ratio
Lamellae have:
A good blood supply
Are very thing
Maintain a good concentration gradient