U2 M46 Elasticity
Price Elasticity of Demand
Measurement of consumers responsiveness to a change in price.
What will happen if the price increases? How much will it affect Quantity Demanded?
Usages
Used by firms to help determine prices and sales
Used by the government to decide how to tax
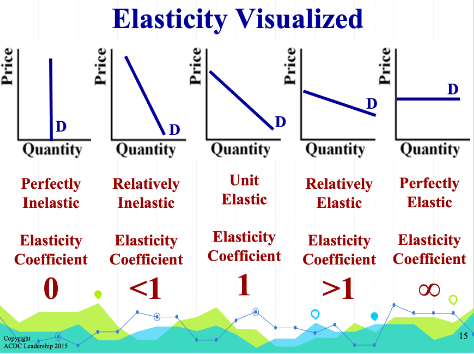
Inelastic Demand - Quantity is insensitive to a change in price
If price increases, quantity demanded will fall a little
If price decreases, quantity demanded increase a little
Ex. medicine, Gas, toilet paper
Characteristics
few substitutes
necessities
small portion of income
required now, rather than later
elasticity coefficient less than 1(steep curve)
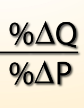
Elastic Demand: Quantity is sensitive to a change in price
If price increases, quantity demanded will decrease a lot
If price decreases, quantity demanded will increase a lot
Ex. Real Estate
Characteristics
many substitutes
luxuries
large portion of income
plenty of time to decide
elasticity coefficient greater than 1 (Elastic Demand curve is Flat)
Elasticity and Effect on Total Revenue
Total Revenue = Price * Quantity
Inelastic Demand-
Price increase causes TR to increase
Price decrease causes TR to decrease
Elastic Demand-
Price increase causes TR to decrease
Price decrease causes TR to increase
Unit Elastic-
Price changes and TR remains unchanged