ap bio : unit 8 cram sheet
Author’s Note
hello there friend! welcome to the LAST cram sheet of AP bio on unit 8: ecology !! I wish you the best on your studying adventures and the EXAMMMM
like this cram sheet? I made more ! check it out at my profile ;))
external links to other resources will also be linked to help you better understand this topic !!!!
╭ Other Resources :
:: cararra ﹒﹒ 42 min ap bio review video based from the campbell biology 11th edition textbook!
:: khan academy ﹒﹒the entire unit 7 course from khan academy!!
:: fiveable ﹒﹒ reviews unit 7 with articles and quizzes for you to practice your knowledge on!
﹙✦﹚﹒﹒please note that abbreviations will be used throughout this guide (kept at a minimum!)
﹙8.1 - Responses to the Environment﹚
✦﹒an organism’s behavior and physiological response is related to environmental changes
stimulus is a combination of signals, or internal/external signal that causes response
behavioral response affects the overall fitness
communication between organisms can change behavior (signaling behavior)
signaling behavior can result in differential reproductive success
communication mechanisms can be visual, audible, tactile, electrical, and chemical signals
helps indicate dominance, find food, establish territory, and ensure reproductive sucess
✦﹒behaviors can be . . .
innate, where they are genetically controlled and can occur w/o prior experience/training
learned, developed as a result of experiences
natural selection favors these, increasing reproductive success and survival
cooperative, involving teamwork between same species, increasing individual fitness survival
﹙8.2 - Energy Flow Through Ecosystems﹚
✦﹒there are different strategies that help regulate temperature and metabolism
endotherms use thermal energy from metabolism to maintain body temperature
can be from heart rate changes, shivering, fat storage
exotherms lack these, relying on behaviors
ex: moving to sun/shade
✦﹒energy is used to grow + reproduce
metabolic rate is the amount of energy used by animal over a specific time
gain → energy storage/growth
loss → loss of mass/death
smaller organism → higher rate
many offspring → less energy efficient, common in unstable environments
few offspring → more energy efficient, common in stable environments
changes in energy causes . . .
changes in population site
ecosystem disruption by changes in resources and trophic levels
✦﹒organisms have different roles in their ecosystem
trophic levels are the position the organism has on the food chain
transfer of energy is inefficient (organisms get 10% of energy from their prey)
limits food length and population size
autotrophs capture energy from physical or chemical sources from the environment
are photosynthetic/chemosynthetic
heterotrophs capture energy present in carbon compounds frm organisms
﹙✦﹚﹒trophic levels, autotrophs and hetrotrophs, and endotherms and exotherms are perhaps the most important thing to note in this section
﹙8.3-8.4 - Population Models﹚
✦﹒population growth depends on many factors—
reproductive maturity age
# of offspring produced
reproduction frequency
survivorship of offspring → reproductive maturity
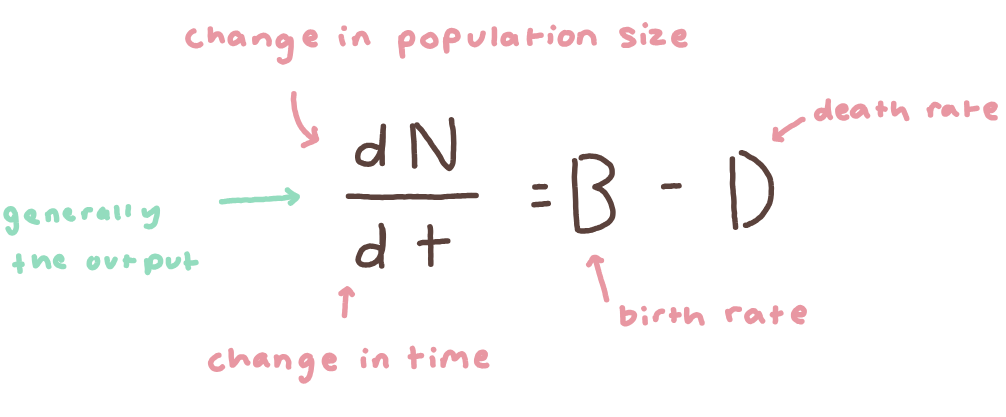
✦﹒reproduction w/o constraints causes exponential growth
exponential growth is a sharp increase of growth
happens in ideal conditions
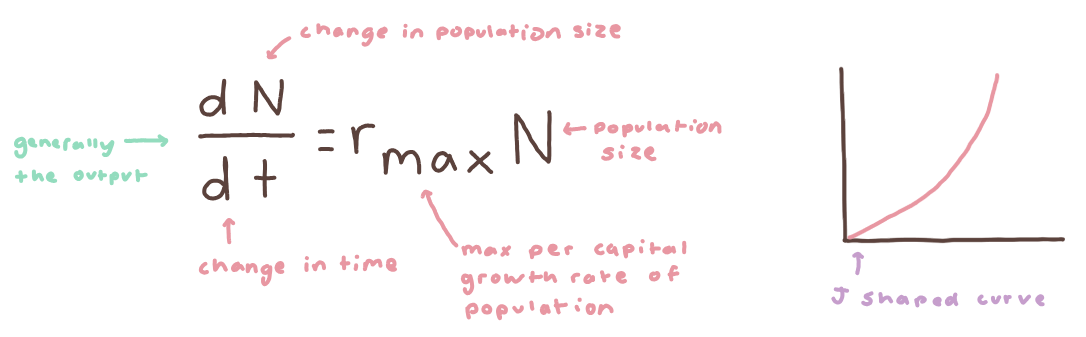 formula for exponential growth. exponential growth is represented graphically on the right.
formula for exponential growth. exponential growth is represented graphically on the right.rmax = (B-D)/N
✦﹒population density refers to how close individuals within a population live near one another
lots of food → higher density
high reproductive rate, limited space
limited food → density may decrease
low reproductive rate, individuals can spread out in limited space
✦﹒limitations occur because of these factors—
density dependent are abiotic/biotic factors whose affect depends on a population’s density
ex: competition, territoriality, disease, predation
density independent affects population regardless of a population’s density
ex: natural disasters, and pollution
✦﹒logistic growth model describes growth that starts as exponential, but then stabilizes at a certain point
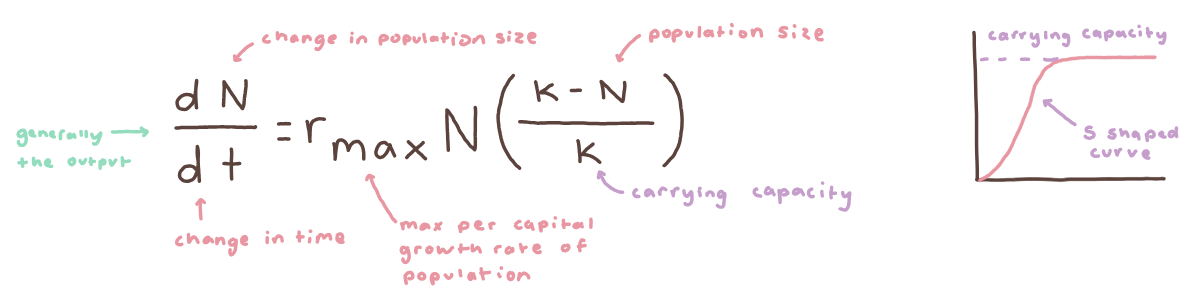 formula for logistic growth. to the right is what logistic growth looks like graphically.
formula for logistic growth. to the right is what logistic growth looks like graphically.
carrying capacity is the maximum amount the environment can substain
caused from density factors
upon exceeding the capacity, limiting factors bring it down, and fluctuations may occur
!! tips for calculating things using logistic growth model
when asked to find the expected population size
plug all values into the equation. it should give you dN/dt, which is the value of how much more individuals would be added
add that value with N (population size)
when asked to find the rmax
subtract population after one year by starting population to find dN/dt
combine already given terms
divide that value to the other side

when asked to find the carrying capacity
subtract population after one year by starting population to find dN/dt
multiply K on both sides
find the value of rmax*N and distribute that value into (K - N)
move the distributed K to the other side
divide the coefficient of K on both sides

╭ Other Resources :
:: bozeman science ﹒﹒ 11 minute video explaining in depth about logistic growth and its meaning!!
:: lasseter’s lab ﹒﹒ introduces populations growth equations and problems practice math problems! its 6 minutes long.
﹙✦﹚﹒math = important. this is perhaps the HARDEST math in AP bio so it is HIGH ENCOURAGED to practice!
﹙8.5-8.6 - Community & Diversity﹚
✦﹒communities are described based on species composition + diversity
species diversity is the variety of species and quantity of individuals included in each species
ex: a shark and turtle species w/15 sharks and 62 turtles
species compositions is the identity of each species
ex: ocean community has 2 species of angel fish— namacanthus paru and pomacanthus xanthmetopan
✦﹒the Simpson’s Diversity Index measures biodiversity using random samples from the environment
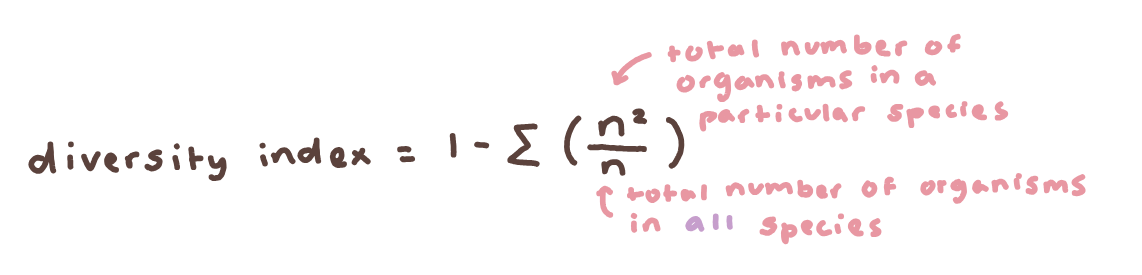
higher index value → more diverse
✦﹒interactions among populations determine how they access energy and matter
positive interactions —
mutualism is where both species benefit (+/+)
commensalism is where one benefits, but the other is not harmed or helped (+/0)
negative interactions —
predator-prey is where one uses the other as a food source
parasitism - one benefits, other is harmed (+/-)
there is also neutral interactions → none is benefited or harmed (0/0)
interactions can be modeled
ex: predator-prey
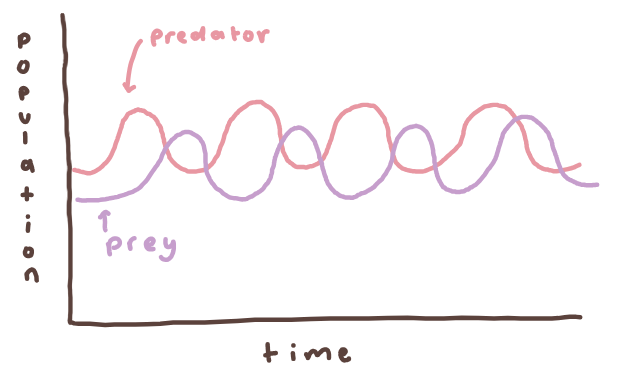
inc in prey → inc in predator
inc in predator → dec in prey
trophic cascade is the negative effect the removal/decrease of a key species has on tropic levels
causes exponential growth/death
interrupts flow of energy
key/keystone species are species that community structure depends on
smaller population, removal of this = ecosystem downfall
overpopulation → depletion of resources
niche partitioning is the decrease in competition over limited resources because of each species accessing resources differently
✦﹒abiotic and biotic factors help maintain biodiversity
abiotic factors are the non-living things that help maintain diversity in the environment
ex: includes climate, water + nutrient availability, light availability
biotic factors are the living things that help maintain diversity in the environment
includes producers, as many depend on them for food + habitats
reduces erosion; areas that have NO life
includes dominant predators, which help stabilize prey population
╭ Other Resources :
:: amoeba sisters ﹒﹒ a 6 minute video covering symbiotic relationships! (mutualism, parasitism, etc.)
:: bozeman science ﹒﹒ 7 minute video covering biodiversity and well as the importance of a keystone species
﹙✦﹚﹒know each of the individual interactions (ex: mutualism), the difference between abiotic and biotic factors, trophic cascades, keystone species, and niche partitioning!!!!
﹙8.7 - Disruptions to Ecosystems﹚
✦﹒invasive species are non native to the environment, and harms the community it is introduced to
exploits new niches
outcompetes other organisms for resources
✦﹒human activity can disrupt/change the ecosystem
this includes deforestation, urbanization, erosion, pollution, extinction, and climate change
overpopulation of humans can easily spread diseases which devastates native species
✦﹒geographical and meteorological events can cause. . .
large habitat disruption
chemical disruptions
extinction
biogeographical studies illustrate these changes
analyzes species distribution
can characterize biome
﹙✦﹚﹒don’t really worry about this part, its pretty logical and straightforward
 Knowt
Knowt
