Marketing
Buyer Decision Process
Need Recognition → Information Search → Evaluation of Alternatives → Purchase Decision → Post purchase behavior
Buyer’s black box
-Buyer’s characteristics
-Buyer’s decision process
- Buyer’s environment: This includes cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors that influence the buyer's decisions.
- Buyer Responses (we can measure and understand the response of consumers): Buying attitudes and preferences, Purchase behavior: what the buyer buys, when, where, and how much, Brand engagements and Relationships
Perception
Selective Attention- the tendency for people to screen out most of the information to which they are exposed
Selective Distortion – describes the tendency of people to interpret information in a way that supports what they already believe
Selective Retention – means consumers are likely to remember good points made about a brand they favor and forget good points made about competing brands



3 Other Psychological Factors
Learning – When we learn it impacts our responses. For example, a positive experience will lead to stronger attachment while a bad experience is very difficult to overcome.
Beliefs – This is a descriptive thought that a person holds about something.
Attitude – Describes a persons relatively consistent evaluation, feelings and tendencies towards an object or idea.
Beyond Meat Example
Create Value for targeted customers
Select Customers to Serve:
-Market segmentation - Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes.
-Market targeting - Evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to serve
Decide on a value proposition:
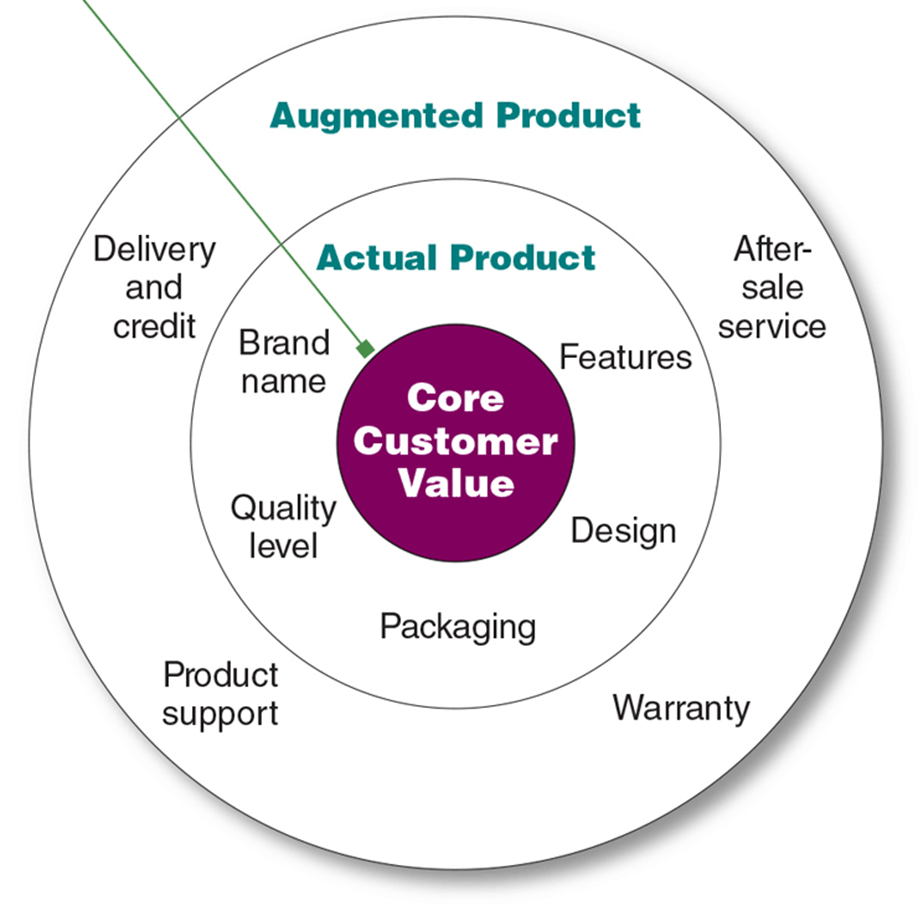
-Differentiation - Actually differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value.
-Positioning -Arranging for a market offering to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target consumers.

Differentiation & Positioning
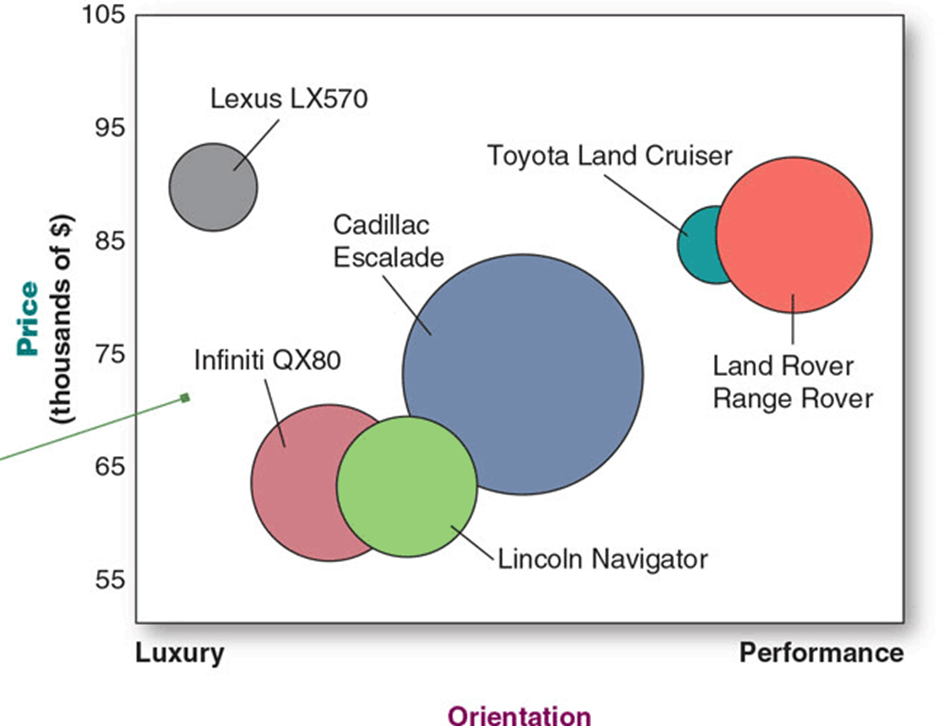
-Requires a very well-defined target market
-Understanding of the needs and preferences of that market
Positioning Strategy
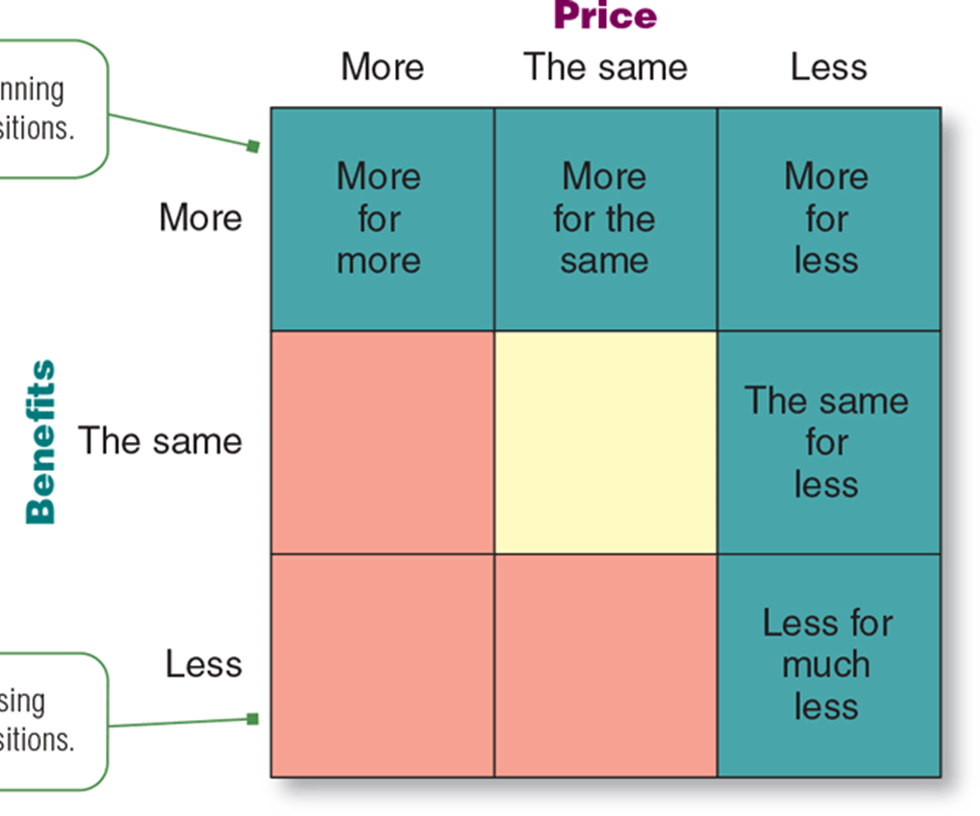
What is a positioning statement and why is it important?
To (target, segment, needs) our (brand) is (concept) that (point of differentiation)
Everything in the company has to align with the positioning statement
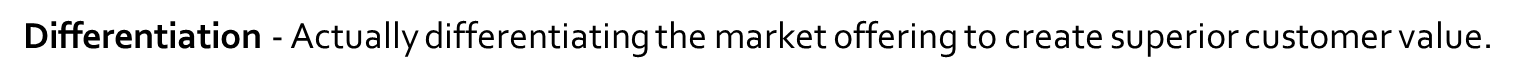
Consumer Products:
•Consumer Product
-Convenience Product
-Shopping Product
-Specialty Product
-Unsought Product
•Industrial Product
-Materials & Parts
-Services & Supplies
-Capital Items
•Something Else
-Organization
-Person
-Place
-Idea

Services Marketing
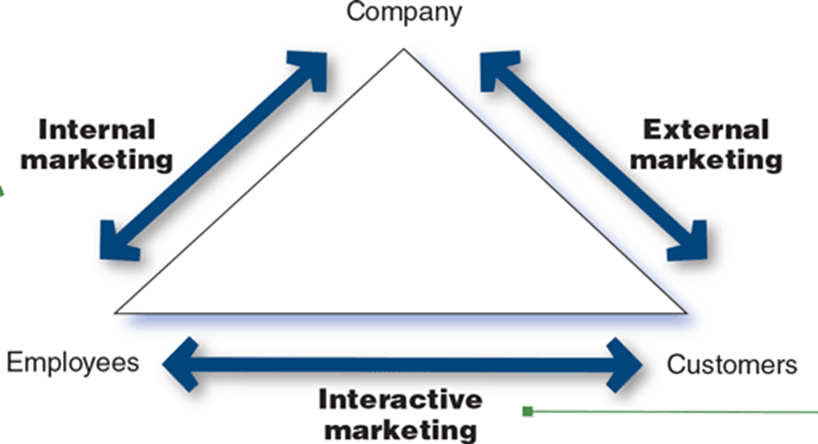
Service Profit Chain
•Internal Service Quality
•Satisfied and Productive Service Employees
•Greater Service Value
•Satisfied and Loyal Customers
Healthy Service Profits and Growth
New Product Development
Research and Development
Research – finding something new that either has not been done before or is new to your company
Development – enhancing the offerings provided to the market, upgrades, changes
•Research vs Development
Typically, longer time commitment
Higher risk of adoption
Cost is higher
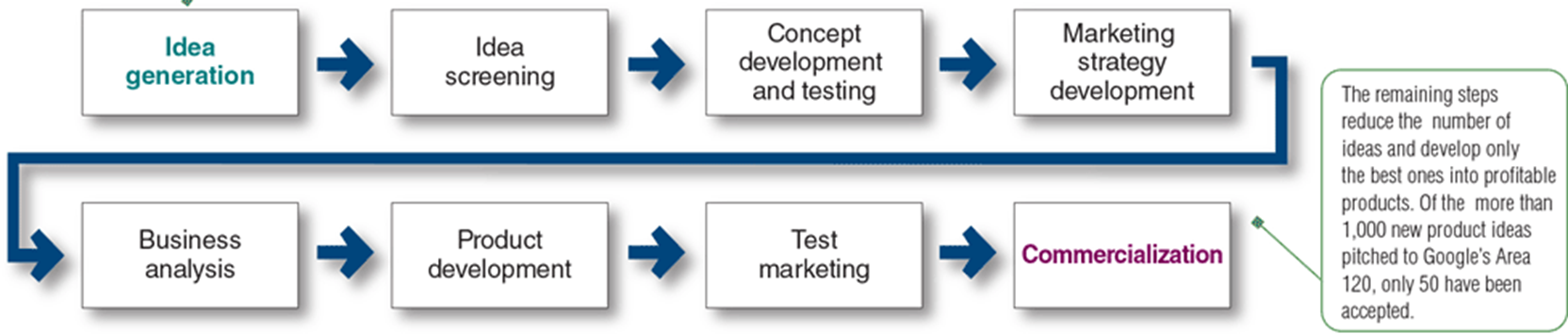
Concept Development – cost to supply and time
Marketing Strategy – target market, first year costs and sales, long term expectations
Product Development:
Complexity and risks impact development time
Features to bring value to target market
Organization setup critical
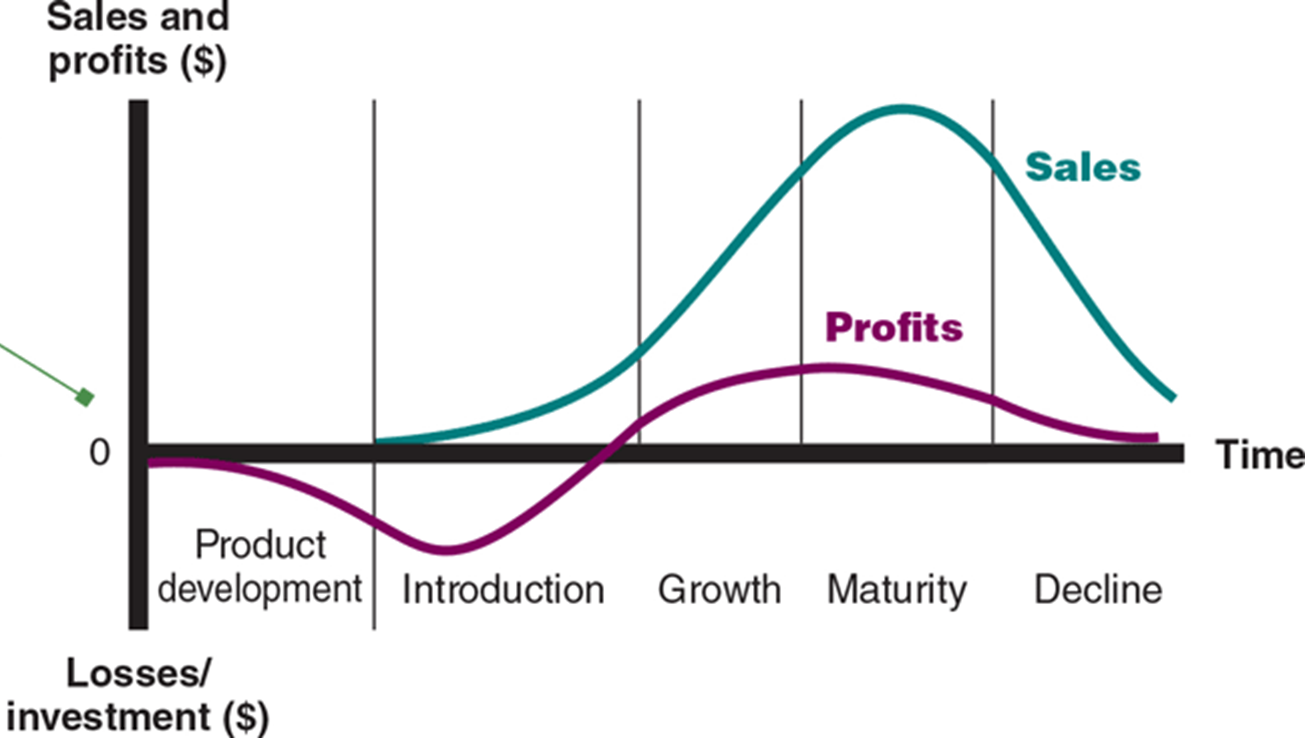
Product Life Cycle
Top 3 Items:
-Auto Fridge Dispenser
-Ice Maker
-Auto Defrost