Exam1StudyGyude BIO
Chapter 1
List the Characteristics of Life
What do all cells have?
Define
-Matter: is any substance that occupies space and has mass
-Atom: they are fundamental building bocks of chemistry, and are the smallest and fundamental unit of matter. It also has a nucleus surrounded by electrons, they form nucleus.
-Element: nique forms of matter with specific chemical and physical properties that cannot break down into smaller substances by ordinary chemical reactions.
-Atomic Number: the number of protons and electrons in its nucleus
-Mass Number: the sum of all protons plus neutrons in the nucleus
- Molecules:a chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms held together by one or more chemical bonds.
-Compounds: a substance composed of molecules consisting of atoms of at least two different elements
-Polar: is a separation of charge, leading to one part of a bond or molecule becoming positively charged and the other negatively charged
-Electronegativity ( what is the periodic trend? What difference in electronegativity creates a polar covalent, nonpolar covalent and ionic bonds?)
Explain the differences between the bonding patterns
Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds |
|---|
Covalent bond is a bond that shares electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. Iconic Bonds is a bond that are held together by the attraction of opposite charges |
List the interactions from strongest to the weakest ( hydrogen, london dispersion, covalent, and Ionic)
List the Key properties of Water and give explanations of each property
Define
● Cohesion
● Adhesion
● Process Diffusion
● Solvent
● Convection
What happens to proteins when placed in water?
-Hydrophilic group ( likes to interact with water)- have a charge, electric negative, it goes on the outside of the protein
-Hydrophobic(doesn't like to interact with water)- so it folds itself to be away from the water, protein folding
These two are important because it determines the folding
Define
● Acids
● Bases
● Strong A/B
● Weak A/B
● Acid- Base Homeostasis
● Buffers
● Buffer Capacity
Explain and Draw out the Human buffer (Bicarbonate / carbonic acid buffer system) What happens to the system when the blood becomes acidic?
What happens to the blood when you hyperventilate?
Why is the Ocean becoming more acidic?
What is causing shell depletion?
Be able to explain a graph of a Titration of a buffer.
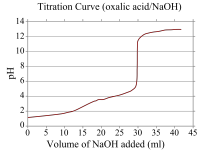
Chapter 2
Define
● Catabolic Pathways -molecules are breaking apart and releasing energy at the same time
● Anabolic Pathways - molecules using energy to create bigger molecule growth
List the 4 macromolecule groups
Define polymers and monomers. What type of bond holds together polymers? Define and draw a dehydration/ condensation reaction
Define and draw a hydrolysis reaction
List the properties of Carbon.
Define Allotropic
What are Functional Groups?
Functional Group | Structure Properties (polar? Non-polar?acidic? basic?) |
|---|
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl | |
|---|---|
Carboxyl | |
Amino | |
Methyl | Non polar |
Sulfhydryl | |
Phosphate |
What is an Isomer?-
Type of Isomer | Key properties Give an Example/ Draw |
|---|---|
Structural | |
Geometric | |
Enantiomer |
Carbohydrates
What are the characteristics of Carbohydrates?
It gives energy to the organisms, they conceit of hydrogen,oxygen and carbon
● Monosaccharide
● Disaccharide
● Polysaccharide
● Aldose (Draw it)
● Ketose (Draw it)
What happens to carbohydrates in water?
Isomers of Glucose- where is the OH located?
● Alpha form
● Beta form
Properties Where is it found? | |
|---|---|
Starch | Define: Amylase and |
Amylopectin | |
|---|---|
Glucose | Glycogenin Glycogen Synthase Glycogen Phosphorylase Insulin |
Cellulose | |
Chitin |
Lipids
What are the Characteristics of Lipids?
What type of bonds are in Lipids?
What is a Triglyceride made of?
Fat | Properties Draw what the Fat looks like |
|---|---|
Saturated Fats | |
Unsaturated Fats | |
Trans-Fats |
What is an Essential Fat?
Omega Fatty Acids
● Omega-6
● Omega-3
What are fats stored in?
What is Lipolysis?
What is a Phospholipid? What are the two components of Phospholipids? Define and give an example of a steroid?
Define Lipoproteins?
Describe the two types of lipoproteins(HDL, LDL)
Proteins
What are the Characteristics of Proteins?
Define Nitrogen Fixation and draw the Nitrogen cycle
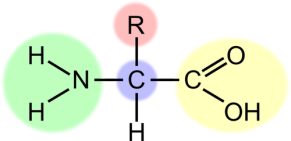
Be able to identify the parts of the Amino Acid
Define
● Amphoteric
● Zwitterion
What are the 4 ways to classify amino acids?
What are symptoms of low protein intake?
-brittle and thin hair
Define
● Polypeptide (how is it made?)
● Peptide Bonds
● Peptidyl Transferase
Protein Structure | Define( what type of bonds Draw can be found?) |
|---|---|
Primary | |
Secondary | Alpha helix: beta -sheet: |
Tertiary | |
Quaternary |
What are Chaperonins?
What causes proteins to Denature?
If a mutation occurs what happens to the protein? Give an example of a disease that is caused by a change in a protein's primary structure?
Nucleic Acids
List the Properties What are the What is the structure functions | |
|---|---|
DNA | |
RNA |
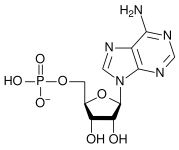 Identify the different parts of the nucleic acid List the Nitrogenous bases and the characteristics. (specifically how many rings each has) - Purines
Identify the different parts of the nucleic acid List the Nitrogenous bases and the characteristics. (specifically how many rings each has) - Purines
- Pyrimidines
What are trinucleotides?
What direction are nucleotides added?
What bonds are between the sugar and the phosphate? What bonds are between the nitrogen bases in DNA?
Be able to identify the primary and secondary structures of DNA
List the characteristics of the Conformations of DNA
● B-DNA
● A-DNA
● Z-DNA
Be able to identify the conformations of RNA
● Single strand
● Double strand RNA
● Stem and loop
● Bulge loop
● Interior loop
● Junctions