3.3 Population Growth and Resources Availability
No population can grow in definitely due to limiting factors such as…
- light
- water
- space
- competition
- predation
- disease
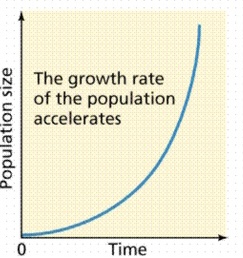
^^INTRINSIC RATE OF INCREASE (r):^^ Rate of population growth with unlimited resources
4 CHARACTERISTICS OF RAPIDLY GROWING POPULATIONS
- timing of reproduction
- amount of time between generations
- length of reproductive lives
- \
# of offspring (fecundity)
- many offsprings= high fecundity
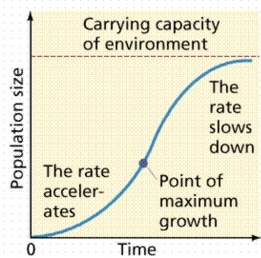
CARRYING CAPACITY (K)
- Determined by ^^biotic potential^^ = maximum reproductive rate of a population in ideal conditions (capacity for growth) and ^^environmental resistance^^ (factors that limit growth)
- As population reaches carrying capacity, growth rate decreases because resources become more scarce, among other factors
Types of Curves
 |  |
|---|
Exponential Growth Equation

Density Dependent Factors
- will change their intensity depending on the density of the population
- ex: competition, diseases, predation, parasitism
Density Independent Factors
- will have the same intensity depending on the density of the population
- Natural: Floods, hurricanes, fire
- Anthropogenic: Pollution, habitat destruction
4 TYPES OF POPULATION FLUCTUATIONS
Stable
fluctuates slightly above and below carrying capacity
Tropical Rainforest
- temps/rainfall stay steady
Irrupt
Usually stable, but sometimes explodes and then crashes
Algae, insects
- due to seasonal changes, nutrient availability
Cyclic
- Rise and fall in predictable pattern
- predator/prey
Irregular
- no reoccurring pattern