
the brain
neuroplasticity & tools of discovery
biological psychology
the science that deals w/ the biological basis of behavior, thoughts & emotions & reciprocal relations btwn biological & psychological processes
addresses topics such as behavior-changing brain lesions, chem responses in the brain, & brain-related genetics
plasticity
capacity of brain to change as a function of experience
brain activity associated w/ a certain function can be transferred to a diff location, particularly if the original area becomes damaged
brain scans & research tools
eeg (electroencephalography)
amplified recording of electrical waves sweeping across brain’s surface
measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
fMRI
measures brain activity by detecting changes associated w/ blood flow
patient interacts w/ info during scan to show activity
lesion
damaged part of the brain
experimentally destroys brain tissue to study behaviors after such destruction
usually lesions are done for scientific or medicinal purposes
brain structures & functions

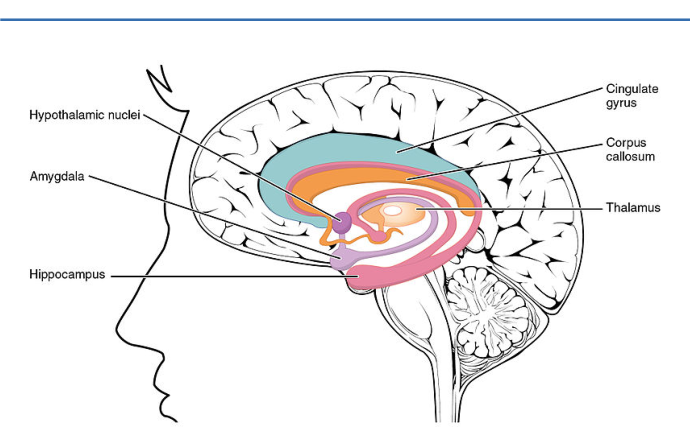
brain structures | functions | helpful ways to remember |
medulla |
| |
reticular formation / reticular activating system (RAS) |
| |
pons |
| |
cerebellum |
| |
thalamus |
| |
hypothalamus |
| |
pituitary gland |
| |
amygdala |
| |
hippocampus |
| seeing a hippo on campus = very memorable |
corpus callosum |
| |
cerebral cortex |
|
lobes
frontal lobe
aka prefrontal cortex
linguistic processing
higher-order thinking
executive functioning
judgement
planning
producing speech sounds
controlling emotions
personality
temperament
motor cortex mvmnt
gage railroad accident example
motor cortex
located at back of frontal lobe (headband spot)
voluntary actions
parietal lobe
touch
pressure
temp
pain
sensory cortex
front of parietal lobe
temporal lobe
hearing (primary auditory cortex)
storing long term mems
speech & language understanding
occipital lobe
vision (primary visual cortex)
association areas
wernicke’s area = comprehension & expression
broca’s area = speech
aphasia if damaged
hemispheres
two hemispheres are roughly mirror images of each other
corpus callosum connects
contralateral hemispheric organization
right hemisphere
spatial ability
nonverbal memory
non-language sounds & music
geometric patterns
left hemisphere
language (Language Lives in the Left except emotional tone of speech)
verbal memory
language sounds
words & letters
brain plasticity
aka neuroplasticity
brain’s ability to continuously change throughout one’s life due to use
if you don’t use it, you lose it
split-brain procedure
two hemispheres split from each other by cutting corpus callosum
subjects behaved normally w/ no major loss of brain function
side effects
the brain
neuroplasticity & tools of discovery
biological psychology
the science that deals w/ the biological basis of behavior, thoughts & emotions & reciprocal relations btwn biological & psychological processes
addresses topics such as behavior-changing brain lesions, chem responses in the brain, & brain-related genetics
plasticity
capacity of brain to change as a function of experience
brain activity associated w/ a certain function can be transferred to a diff location, particularly if the original area becomes damaged
brain scans & research tools
eeg (electroencephalography)
amplified recording of electrical waves sweeping across brain’s surface
measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
fMRI
measures brain activity by detecting changes associated w/ blood flow
patient interacts w/ info during scan to show activity
lesion
damaged part of the brain
experimentally destroys brain tissue to study behaviors after such destruction
usually lesions are done for scientific or medicinal purposes
brain structures & functions


brain structures | functions | helpful ways to remember |
medulla |
| |
reticular formation / reticular activating system (RAS) |
| |
pons |
| |
cerebellum |
| |
thalamus |
| |
hypothalamus |
| |
pituitary gland |
| |
amygdala |
| |
hippocampus |
| seeing a hippo on campus = very memorable |
corpus callosum |
| |
cerebral cortex |
|
lobes
frontal lobe
aka prefrontal cortex
linguistic processing
higher-order thinking
executive functioning
judgement
planning
producing speech sounds
controlling emotions
personality
temperament
motor cortex mvmnt
gage railroad accident example
motor cortex
located at back of frontal lobe (headband spot)
voluntary actions
parietal lobe
touch
pressure
temp
pain
sensory cortex
front of parietal lobe
temporal lobe
hearing (primary auditory cortex)
storing long term mems
speech & language understanding
occipital lobe
vision (primary visual cortex)
association areas
wernicke’s area = comprehension & expression
broca’s area = speech
aphasia if damaged
hemispheres
two hemispheres are roughly mirror images of each other
corpus callosum connects
contralateral hemispheric organization
right hemisphere
spatial ability
nonverbal memory
non-language sounds & music
geometric patterns
left hemisphere
language (Language Lives in the Left except emotional tone of speech)
verbal memory
language sounds
words & letters
brain plasticity
aka neuroplasticity
brain’s ability to continuously change throughout one’s life due to use
if you don’t use it, you lose it
split-brain procedure
two hemispheres split from each other by cutting corpus callosum
subjects behaved normally w/ no major loss of brain function
side effects
 Knowt
Knowt