NOTE: Unit 1 Biology of Behavior (copy)
Nervous System
Central Nervous System - Brain and spinal cord
2 types of cells in the brain: neurons & glial cells
Peripheral Nervous System - sensory and motor neurons connecting the CNS to the rest of the body
Somatic - voluntary control of skeletal muscles
Autonomic - involuntary control of glands and internal organs
Sympathetic Nervous System - responds to stressful or dangerous situations
Parasympathetic Nervous System - responsible for the body's rest and digestion response when the body is relaxed, resting, or feeding
Nerves, Neurons, Neural firing
Nerves - electrical cables formed from bundles of axons, linking the CNS with the body's sensory receptors, muscles, and glands
Sensory Neurons - neurons that carry incoming information from the body's tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
Motor neurons - neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons - neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Reflex - simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus
The Neuron
Dendrites - receive messages from other cells
Soma (cell body) - cell's life support center
Axon - passes messages away from cell body to terminal branches
Myelin Sheath - covers the axon, helps speed up neural impulses
Axon Terminal Branches - form junctions with dendrites of other neurons
Axon Terminal Buttons - convert electrical impulses into chemical messages (neurotransmitters)
Synapse - the meeting point between neurons
The Synapse
Sending neuron (terminal branch)
Synaptic vesicles - store and release neurotransmitters
Receptor sites - places where receiving neuron accept neurotransmitters
Receiving neuron (dendrite)

Neurotransmitters & Hormones
Hunger Regulation
Grelin - Hunger-arousing hormone, produced by empty stomach
Lack of sleep and restricting calorie intake →oversupply causes overeating and weight gain
Sleeping and eating high protein foods →undersupply causes decreased appetite, unintended weight loss
Leptin - Hunger-repressing hormone, secreted by fat cells
Oversupply causes leptin resistance, leading to overeating and potential obesity
Undersupply causes difficulty in regulating weight → excessive hunger and weight gain
Arousal and Stress Reactions
Norepinephrine - Produces fight or fight response by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar for more energy
Oversupply causes high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, excessive sweating, anxiety
Undersupply causes lack of energy and concentration, ADHD symptoms, feeling unmotivated
Adrenaline (Epinephrine)- Produced by adrenal glands, response to stress or excitement, prepares body for fight or flight by increasing heart rate and energy
Oversupply causes muscle cramps, increased heart rate, excessive salivation, nausea, sweating, difficulty sleeping, stress-related disorders
Undersupply causes memory issues, decreased attention span, fatigue, decreased heart rate
Learning and Curiosity
Acetylcholine (ACh) - Involved in muscle activation, learning, memory, facilitating communication between nerve cells, and muscles
Oversupply causes muscle cramps, muscle weakness, severe cases can cause paralysis
Undersupply linked to memory issues learning difficulties, may contribute to conditions like Alzheimer's disease and muscle weakness
Glutamate - Brain's most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in memory and learning
Oversupply can lead to excitotoxicity, damages nerve cells, and associated with conditions like Alzheimer's and ALS
Undersupply impairs cognitive functions like memory and learning
Happy Feelings
Endorphine - Natural opiate-like transmitter, distraction from pain (and pleasure)
Oversupply causes reduces pain
Undersupply causes mood issues and difficulty managing stress
Oxytocin - 'Love hormone’ invovled in social bonding, sexual reproduction, childbirth, increased feelings of trust and empathy
Oversupply causes to social cues, anxiety, and overattachment
Undersupply causes difficulties in making social bonds, lower trust, loneliness or depression and low motivation
Dopamine - Involved in reward, motivation, pleasure, and plays a role in motor control and cognitive function
Oversupply is linked to schizophrenia, hallucinations and delusions, and addictive behaviors due to overactivation of dopamine receptors
Undersupply is linked to Parkinson's disease, PD tremors, difficulty motor control, and depression
Serotonin - Regulates mood, appetite, and sleep, contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness
Oversupply causes mania and serotonin syndrome, leading to confusion, agitation high blood pressure
Undersupply is linked to mood disorders like depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances
Miscellaneous
Melatonin - Produced by pineal gland, regulates sleep-wake cycle by promoting sleepiness in response to darkness
Oversupply causes excessive drowsiness, lethargy, and concentration problems. May disrupt circadian rhythm
Undersupply causes insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, may impair immune function
GABA - Main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, helps calm the NS and promote relaxation
Oversupply causes excessive relaxation, drowsiness, impaired motor coordination, sluggishness
Undersupply causes anxiety, insomnia, restlessness, and epilepsy due to lack of inhibitory signals in brain
Substance P - Involved in transmitting pain signals to the brain, plays a role in body’s response to pain and inflammation
Oversupply linked to increased perception of pain and chronic pain conditions
Undersupply causes reduced pain perception, which can be dangerous if injuries go unnoticed
Psychoactive Drugs & Substance use
DSM 5 criteria of Substance Use Disorder -
Continued drug use despite significant life disruption. Brain changes can persist after quitting use, which causes strong cravings. Indicators:
Diminished Control
Uses more substance, or for longer, than intended
Cannot regulate use of substance
Lots of time getting, using, or recovering from substance
Craving of substance
Diminished Social Functioning
Disrupts commitments at work, school, or home
Continues use despite social problems
Reduced social, recreational, and work activities
Hazardous Use
Continues use despite hazards
Continues use despite worsening physical or psychological problems
Drug Action
Experiences tolerance
Experiences withdrawal when attempting to end use
Psychoactive Drugs - Chemicals that change perceptions and moods
Impact on central nervous system and/or brain | Positive effects and Negative after effects | Specific examples & types | |
Depressants | Calm neural activity and slow body functions; disinhibitor - slow brain activity that controls judgment and inhibitions | Positive: - Reduced self-awareness can be reason why people drink to cope with failures or shortcomings - Induce sleep - Reduce anxiety - Pain-relief Negative: - Impairs memory and judgement - Slowed neural processing: slurred speech, slow reaction time, lower performance - Reduced self-awareness | Alcohol - Increases helpful tendencies and harmful tendencies Can shrink brain Barbiturates (tranquilizers) - Ex: Nembutal, Sconal, Amytal Opiates - Heroin and medically-prescribed narcotics (codeine, morphine, methadone) |
Stimulants | Excites neural activity and speeds up body functions. Pupils dilate, heart and breathing rates increase, blood sugar levels increase, appetite drops NTs: serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine | Positive: - Energy and self-confidence increase - Feel alert - Lose weight - Boost mood or athletic performance - Boost academic performance Negative: - Fatigue - Headache - Irritability - Depression - Sleep impairment - Chronic disabilities - Divorce - Seizures | Caffeine Nicotine - Delivered by cigarettes, e-cigs, and other tobacco products Cocaine - From coca plant Amphetamines - More addictive: Methamphetamine Ecstasy - Also MDMA or molly Both stimulant and mild hallucinogen |
Hallucinogens | Distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input Psychedelics | Positive: - Experience dreamlike scenes - Enhance spirituality - Promote feelings of personal growth - Euphoria - Alleviate chronic pain Negative: - Panic - Impaired motor coordination, perceptual skills, reaction time - Risk of traffic accidents, psychosis, bronchitis - Social anxiety disorder - Impaired attention, learning, and memory | LSD - Also acid MDMA - Also ecstasy Marijuana - Produce THC |
States of Consciousness (Sleep)
Sleep patterns
Circadian rhythm - (Latin circa “about” and diem “day”) 24 hour cycle of bodily rhythms, biological clock based on the sun and moon / when light and dark hits our eyes
Suprachiasmatic nucleus - pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that control circadian rhythm
Stages of sleep - 90 minute cycles
Stage 1-3/4 to 2 to REM every 90 mins
Deep sleep occurs during stages 3-4: Immune system restores, muscles restore, process memories
REM sleep is when you dream
Sleep cycle
Stage 1 NREM
light sleep
5% of sleep
hallucinations and hypnagogic sensations (feeling like falling)
theta waves
Stage 2 NREM
light sleep
45-50% of sleep
easy to wake, more relaxed
sleep spindles and K-complexes
Stage 3-4 NREM
deep sleep
5-10% of sleep
difficult to wake, muscle restoration, consolidation of learning (latent learning - consolidation of learning during sleep; subconscious retention of information without reinforcement or motivation), release of growth hormone
delta waves
REM
deep sleep
20-25% of sleep
paradoxical, muscle atonia, dreaming
similar to wakefulness (alpha waves)
Sleep theories - why do we sleep?
Protection - darkness & hunting/gathering (evolutionary)
Recuperation - immune system & brain repair
Restoration & rebuilding - consolidating memories, reactivates recent experiences for cortex
Inspiration for creativity - problem-solving, innovation, boosting insight
Supporting growth - pituitary gland releases HGH for muscle development
Sleep deprivation
“The brain keeps an accurate count of sleep debt for at least 2 weeks”
More conflict in friendships and relationships
Predictor of anxiety & depression, increases cortisol
Contributes to weight gain, increases ghrelin and decreases leptin
Decreased ability to focus attention, process, and store memories
Decreased production of immune cells, increased risk of viral inflections
Increase inflammation, reduces muscle strength and slower reaction time
Dreams
Wish-fulfillment - Sigmund Freud, psychodynamic theory; dreams express otherwise unacceptable feelings
Latent content: underlying or hidden meaning behind meaning; pertains to unconscious wants, desires, or fears (more prevalent)
Manifest content: actual dream content remembered in day
Information processing - filing memories, sorting the day’s events
Physiological functions - developing & preserving neural pathways (REM sleep promotes brain stimulation)
Activation-synthesis theory - making sense of neural static (triggered by REM), evoking random visual memories and creating stories
Cognitive development - stimulates life, reflect individual cognitive development
Sleep disorders
Insomnia - recurring problems in falling or staying asleep
stressful life event, birth of a child, death of a loved one, hustle culture, naturally being a night owl
evolutionary: we need both night owls and early birds
Narcolepsy - characterized by attacks of overwhelming sleepiness
may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times
cataplexy - brief bouts of muscle weakness or paralysis
Sleep apnea - characterized by temporary stopping of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
fatigue and depression, as a result of slow-wave sleep deprivation
associated with obesity, especially among men
Night terrors - characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during NREM-3 sleep
within two or three hours of sleep
usually not remembered
Sleep walking/sleep talking - doing normal activities (sitting up, walking, speaking) while asleep
sleep talking can occur during any sleep stage
sleep walking (also somnambulism) occurs in NREM-3 sleep
Electroencephalogram (EEG) used to study sleep
Brain Structures and Function
Cerebral Cortex - control center
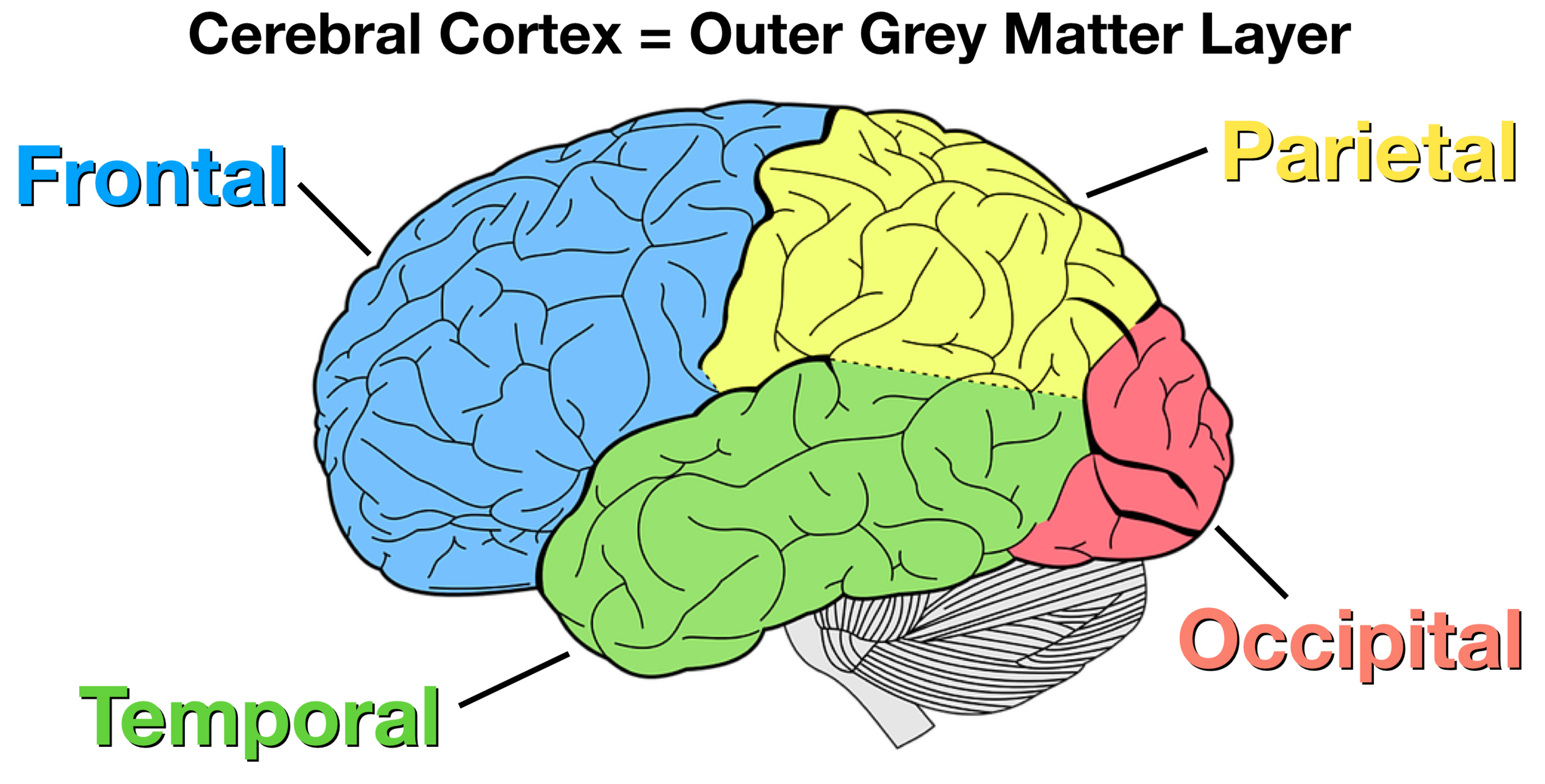
Cerebrum
Frontal lobe - Broca's area
Includes prefrontal cortex
making judgments, executive functions, rational decisions
Speaking, muscle movement
Parietal lobe
Includes somatosensory cortex
Processing information from the body’s senses
Touch, temperature, pain
Association areas
Behind frontal lobe
Occipital lobe
Interpreting incoming visual information
In the back
Temporal lobe - Wernicke's area
Auditory information
Above ears
Cerebellum
Voluntary bodily movement and balance
Under occipital and temporal lobes
Dependent on GABA, sensitive to alcohol - loses balance
Limbic System
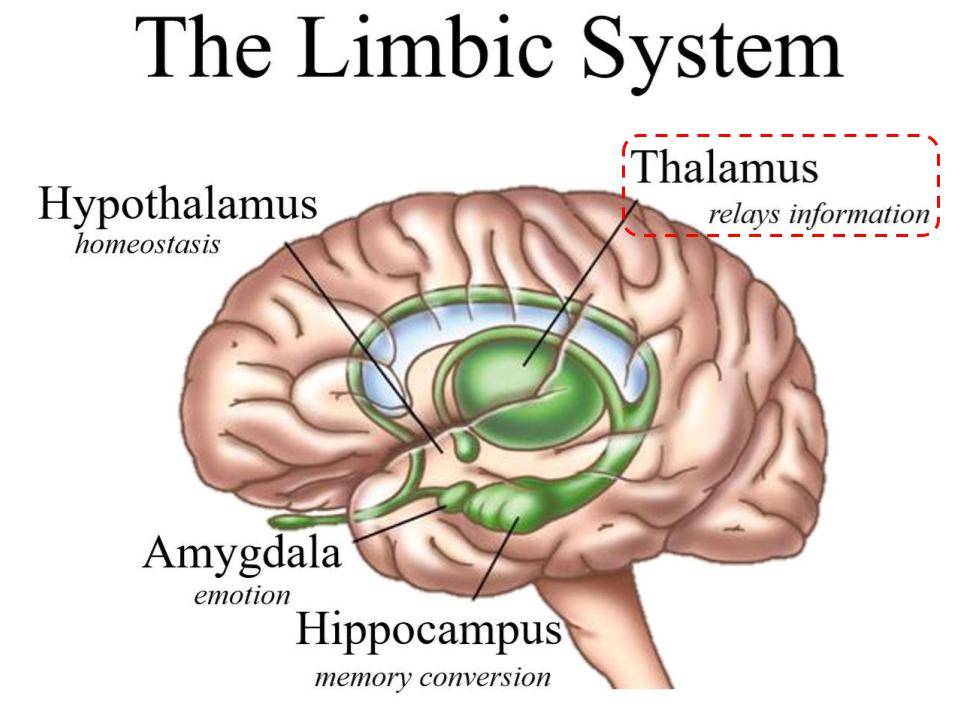
Thalamus
Relays information of senses (except olfactory), before being sent to cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
Maintenance functions like eating and sleeping
Homeostasis
Pituitary gland
Makes, stores, and releases hormones
Puberty
Hippocampus
Where memories are stored
If needed important/long-term, moves from hippocampus to cortex
Amygdala
Emotion center
Misc.
Medulla
Controls autonomic (nervous system) functions
Carries signals from the brain to the rest of the body for essential life functions
breathing, circulation, swallowing, and digestion
Includes Reticular Activating system (reticular formation)
Filters out unnecessary information
Regulates behavioral arousal and consciousness in brain stem
At base of brain, where it meets the spinal cord
Left vs Right Brain
Left Brain
Logical, analytical, verbal, factual information
Right Brain
Creative, intuitive, artistic, emotional, imaginative information
Corpus Callosum
Connect left and right spheres of brain so they can communicate
Sensation
5 senses
Sight
Smell (olfactory)
Touch (tactile)
Hearing (auditory)
Taste (gustatory)
Sensation: sensory receptors detect info and nervous system transits that information
Gustav Fechner + Ernst Weber
Absolute Threshold - minimum stimulus energy needed to detect a particular stimulus, detectable at least half of the time
Examples: when someone is about to touch you, turning up music very slowly
The minimum intensity of light we can see
The lowest volume of a sound we can hear
The smallest concentration of particles we can smell.
Just-noticeable difference - the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable, detectable at least half the time
Examples: changing font size, voice volume level
Transduction: Sensory systems convert outside energy into a form the brain can use
Vision - light energy
Hearing - sound waves
Taste and smell - chemical stimulus
All senses…
Receive sensory stimulation
Transform that stimulation into neural impulses
Deliver the neural information to the brain