IB Biology 8: Photosynthesis
The purpose of photosynthesis is to transform light CO2, water and light energy into simple sugars that the plant uses as food. Plants are autotrophs (meaning they produce their own food in this way)
Overall photosynthesis word equation: carbon dioxide + water + (light energy) → glucose + oxygen
Overall photosynthesis symbol equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
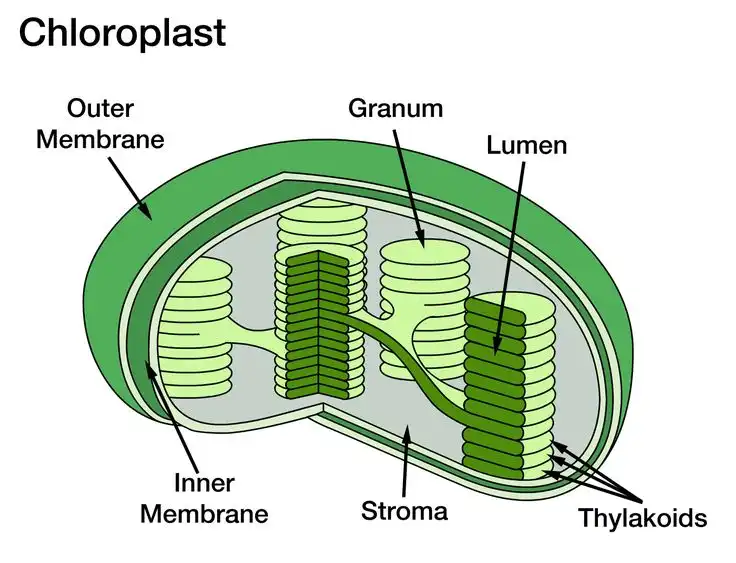
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast
Light dependant and independent reactions:
Light dependant reactions- photolysis, photoactivation, electron transport, chemiosmosis, ATP synthesis, reduction of NADP. Light energy is converted into chemical energy (ATP and reduced NADP)
Light independent reactions- carbon fixation, carboxylation of RuBP, production of triose phosphate, ATP and NADPH as energy sources, ATP used to generate RuBP, ATP used to produce carbohydrates
Light dependant reactions take place in the intermembrane space of the thylakoids
Light independent reactions take place in the stroma
Parts of the chloroplast:
Thylakoids – flattened discs have a small internal volume to maximise hydrogen gradient upon proton accumulation
Grana – thylakoids are arranged into stacks to increase SA:Vol ratio of the thylakoid membrane
Photosystems – pigments organised into photosystems in thylakoid membrane to maximise light absorption
Stroma – a thick, protein-rich central cavity that contains appropriate enzymes and a suitable pH for the Calvin cycle to occur
Lamellae – connects and separates thylakoid stacks (grana), maximising photosynthetic efficiency
Stages of light-dependant reactions
Photolysis-
Photoactivation- protons excite electrons in chlorophyll molecules in the photosystems, causing them to move to a higher energy level
Electron transport-
Chemiosmosis-
ATP synthesis-
Reduction of NADP-
Stages of light independent reactions/ Calvin cycle
Carbon fixation- CO2 in the stroma reacts with the 5C sugar ribulose biphosphate to create a 6C compound. Catalysed by enzyme rubisco*. Immediately forms 2 molecules of glycerate-3 phosphate.
Carboxylation of RuBP*-
Production of triose phosphate-
Six turns of the Calvin cycle produce 1 hexose sugar. This is because three turns of the cycle produce 6 molecules of triose phosphate (2 molecules of triose phosphate per molecule of carbon dioxide) but five out of the six are needed to regenerate RuBP.
TP and GP* are used are used to make carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Hexose sugars: 2x TP
Starch: many hexose sugars
Lipids: fatty acids from GP and glycerol from TP
Proteins- some amino acids from GP
*RuBP= Ribulose biphosphate
Rubisco= RuBP carboxylase
GP=glycerate-3 phosphate (3C)
TP= triose phosphate (also 3C)
Sources: bioninja, Oxford IB Diploma course companion textbook (2014), image from toppr
 Knowt
Knowt