Chapter 12: National Income and Price Determination
12.1 Aggregate Demand
- Aggregate demand: total demand for goods and services
- Inverse relationship between price and GDP
- Caused by:
- The Real Wealth Effect
- The Foreign Trade Effect
- The Interest Rate Effect
12.2 Short-run and Long-run Aggregate Supply
- Aggregate supply (AS): curve shows total value of output produces are willing + able to supply at different price levels during a certain time
- Aggregate demand (AD): total demand of goods/services
- Price level: average level for all prices
- Long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS): stands at level of output that corresponds with full employment
12.3 Equilibrium and Changes in the Aggregate Demand-Aggregate Supply Model
Cost-push (supply inflation): when inflation is due to increase in resource costs (shifts AS curve to left)
Stagflation: rising prices and falling output
Demand pull inflation: result of AD curve shifting out to the right relative to AS curve
Creeping inflation: inflation at a low rate that remains teady for a long period of time
Galloping inflation: unsteady inflation that exceeds 10% per year and grows monthly
Hyperinflation: rapid price incrase greater than 50% per year
Inflationary gap: amount the equilibrium real GDP would need to increase to reach the LAS
Spending multiplier: number the initial amount of new spending needs to be multiplied by to find total resulting increase in real GDP
Marginal propensity to consume (MPC): amount consumption increases for every dollar of real income
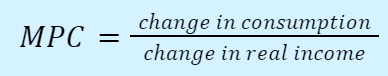
Marginal propensity to save (MPS): fraction of each dollar of income that is saved \n

Spending multiplier (expenditure multiplier)

12.4 Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy: when government tries to counteract fluctuations in aggregate expenditure by changing purchases, transfer payment, taxes

